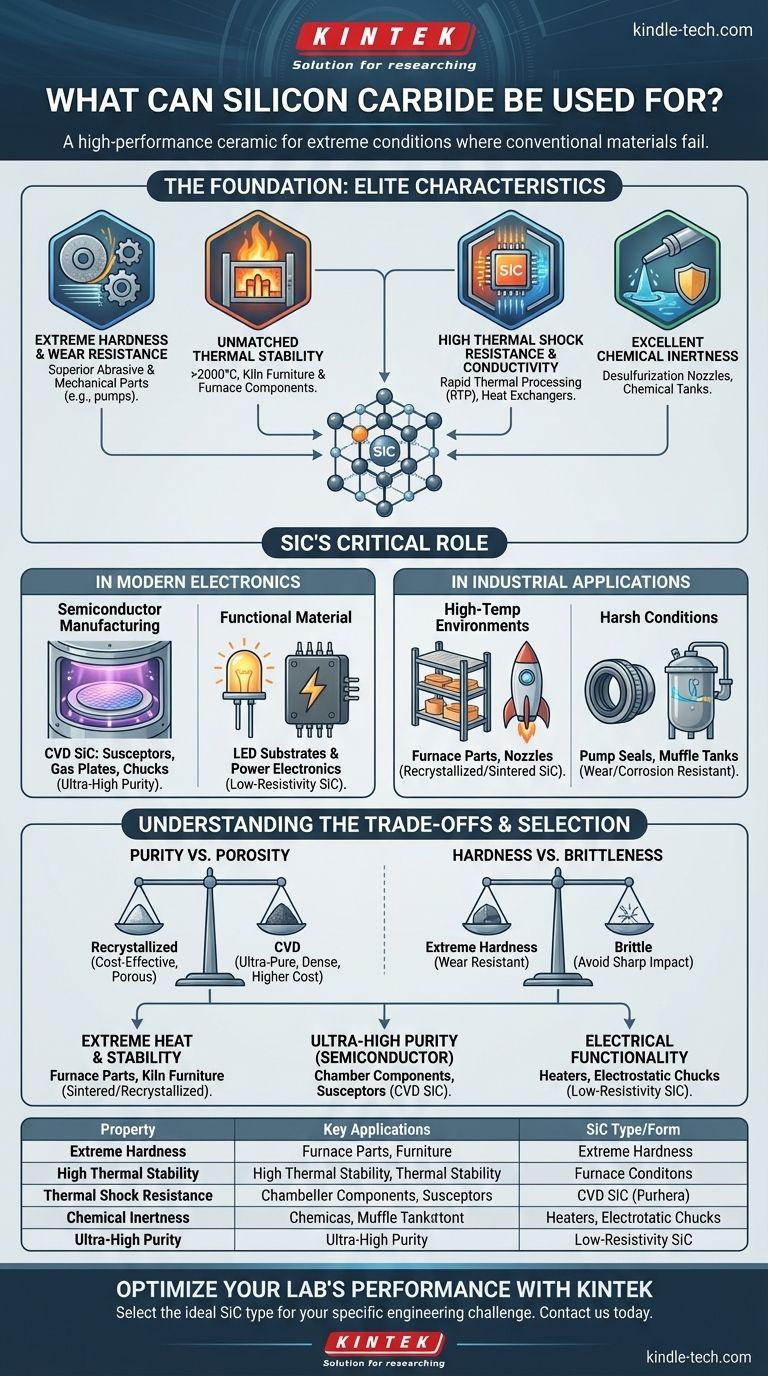
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is a high-performance ceramic used in applications where conventional materials fail under extreme conditions. Its uses span from high-temperature industrial furnaces and wear-resistant components to critical parts in semiconductor manufacturing equipment and substrates for advanced electronics like LEDs.
Silicon carbide's value lies not in a single property, but in its rare combination of extreme hardness, exceptional thermal stability, and versatile electrical characteristics. Understanding which form of SiC to use is the key to solving a specific engineering challenge.

The Foundation: Why SiC Excels in Harsh Environments
Silicon carbide is not a single entity. Its properties are tuned based on its manufacturing process, but all forms share a common set of elite characteristics that make them ideal for demanding industrial and electronic roles.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Historically, SiC was first known for its incredible hardness, second only to diamond. This property makes it a superior abrasive material.
This same hardness translates directly into exceptional wear resistance. It is used for mechanical parts like pump components that must withstand constant friction and abrasive fluids without degrading.
Unmatched Thermal Stability and Refractoriness
Silicon carbide maintains its strength and structural integrity at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 2000°C.
This makes it an essential material for kiln furniture—the shelves and supports used inside high-temperature furnaces for firing ceramics and glass. It is also used to build furnace floors, guide rails, and even rocket engine nozzles.
High Thermal Conductivity and Shock Resistance
Unlike many ceramics that crack under rapid temperature changes, SiC possesses both high thermal conductivity and excellent thermal shock resistance. It can heat up and cool down quickly without failing.
This is critical in semiconductor processing, where CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) silicon carbide is used for components in rapid thermal processing (RTP) and plasma etch chambers, which experience intense, rapid thermal cycling. This property also makes it ideal for high-efficiency heat exchangers.
Excellent Chemical Inertness
SiC is highly resistant to corrosion from acids, alkalis, and high-temperature gases. It is a chemically stable and nearly inert material.
This makes it the perfect choice for desulfurization nozzles in power plants, where it is exposed to highly corrosive gases and liquids, or for muffle tanks that protect heating elements from chemical attack.
SiC's Critical Role in Modern Electronics
While its industrial uses are extensive, silicon carbide has become indispensable in the world of high-performance electronics, both as a component in the manufacturing process and as a semiconductor material itself.
In Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment
The fabrication of microchips involves intensely energetic and corrosive processes. CVD silicon carbide, due to its ultra-high purity and resistance to plasma erosion, is the material of choice for critical chamber components.
Applications include susceptors (which hold wafers), gas distribution plates, edge rings, and electrostatic chucks. Here, SiC ensures a stable, non-contaminating environment for producing flawless silicon wafers.
As a Functional Electronic Material
Specific grades of SiC are engineered for their electrical properties. Low-resistivity silicon carbide, for example, is conductive and used to create robust heating elements and chucks that require electrical conductivity.
Conversely, its ability to act as a semiconductor is leveraged to create substrates for high-brightness light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and next-generation power electronics that are more efficient and can operate at higher temperatures than those based on silicon.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right SiC
The term "silicon carbide" describes a family of materials. Selecting the wrong type can lead to suboptimal performance or unnecessary cost. The primary trade-off is often between purity, density, and manufacturing cost.
Material Purity vs. Porosity
Recrystallized silicon carbide offers high purity and excellent thermal properties but contains some porosity. This makes it ideal for cost-effective kiln furniture and furnace components where absolute density is not the primary concern.
CVD silicon carbide, in contrast, is exceptionally pure and fully dense. This is non-negotiable for semiconductor applications where even microscopic particles or impurities could ruin a batch of microchips, justifying its higher cost.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
Like most advanced ceramics, SiC is extremely hard but also brittle. It can withstand immense compressive forces and surface wear but can fracture under sharp impact or high tensile stress.
This means that while it is perfect for a nozzle or a bearing, it is not a suitable replacement for steel in an application that requires flex or toughness to absorb impacts.
How to Select SiC for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat and structural stability: Seek out recrystallized or sintered SiC for applications like furnace parts, kiln furniture, nozzles, and heat exchangers.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity for semiconductor processing: You must specify high-purity, dense grades like CVD silicon carbide for chamber components, chucks, and susceptors.
- If your primary focus is electrical functionality in a harsh environment: Look for low-resistivity SiC for applications like resistive heaters or electrostatic chucks that require both conductivity and wear resistance.
Silicon carbide is a premier engineering material designed to provide stability and reliability where nearly everything else fails.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Applications | SiC Type/Form |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Abrasives, pump seals, mechanical parts | Recrystallized, Sintered |
| High Thermal Stability (>2000°C) | Kiln furniture, furnace components, rocket nozzles | Recrystallized, Sintered |
| Thermal Shock Resistance & Conductivity | Heat exchangers, RTP chambers, plasma etch parts | CVD, Sintered |
| Chemical Inertness | Desulfurization nozzles, muffle tanks | Recrystallized, Sintered |
| Ultra-High Purity & Plasma Resistance | Semiconductor susceptors, chucks, gas plates | CVD Silicon Carbide |
| Electrical Functionality | LED substrates, power electronics, heaters | Low-Resistivity SiC, Semiconductor-grade |
Optimize your lab's performance with the right silicon carbide solution. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including silicon carbide components for furnaces, semiconductor tools, and harsh environments. Our experts help you select the ideal SiC type—whether for extreme heat, wear resistance, or ultra-purity—ensuring reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your laboratory's capabilities with precision-engineered SiC products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes



















