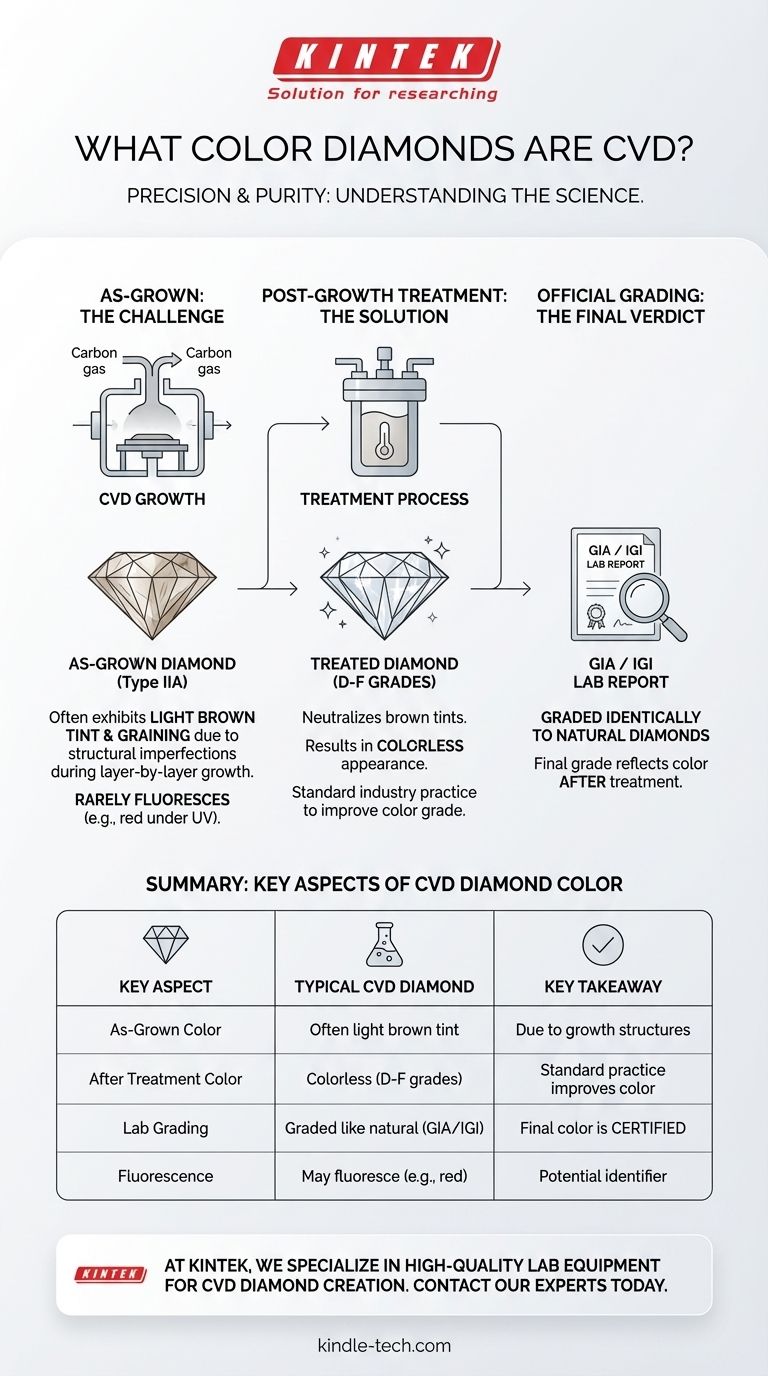
To be precise, diamonds created using the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method are typically grown to be colorless. However, the intricacies of the growth process can sometimes result in undesirable brown tints or internal graining, which may require post-growth treatments to improve their final appearance.
The core goal of the CVD process is to create chemically pure (Type IIA) diamonds that are inherently colorless. The final color you see is a direct result of how perfectly that process was controlled and whether any subsequent treatments were used to correct growth-related imperfections.

The Science Behind CVD Diamond Color
The Goal: A Chemically Pure Diamond
CVD diamonds are classified as Type IIA, a category that is extremely rare in nature.
This classification means they are almost entirely free of nitrogen or boron impurities, which are the primary causes of color (like yellow or blue tints) in most natural diamonds. In its ideal state, a pure carbon lattice is perfectly colorless.
How the Growth Process Can Introduce Color
The CVD method involves depositing carbon-containing gas onto a diamond seed crystal at moderate temperatures and low pressures.
While this technique is highly controlled, it can sometimes create structural imperfections or non-diamond carbon deposits within the crystal lattice. These subtle flaws are what can lead to a brownish hue.
Brown Tints and Graining as Common Traits
The references note that CVD diamonds can exhibit brown tints and internal graining.
This is a known challenge of the CVD method. These characteristics are not caused by chemical impurities like nitrogen but by the physical structure of the diamond as it grows layer by layer in a single direction.
Fluorescence as a Potential Indicator
Some CVD diamonds will fluoresce under UV light, sometimes in distinct colors like red.
While this isn't a universal feature and often isn't visible to the naked eye, it's another characteristic that can distinguish them from many natural diamonds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Need for Post-Growth Treatment
Because of the potential for brown tints, many CVD rough diamonds undergo a post-growth treatment process to enhance their color.
This treatment effectively neutralizes the brownish appearance, resulting in a higher, more desirable color grade. This is a standard and accepted practice in the industry.
The Importance of Official Grading
Like any diamond, CVD diamonds are professionally graded for their Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight (the 4Cs).
The final color grade on a lab report from an institution like GIA or IGI reflects the diamond's appearance after any and all treatments have been completed. A "D" color grade on a CVD diamond is visually identical to a "D" on a natural one.
Identifying Marks of the Process
While rare and typically only visible under high magnification, the single-direction cubic growth of a CVD diamond can sometimes cause strain lines.
These subtle internal features, along with graining, are tell-tale signs of the CVD origin for a trained gemologist, but they generally do not impact the stone's beauty or durability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When considering a CVD diamond, its color is a function of the precision of its creation.
- If your primary focus is a top-tier colorless diamond: CVD is an excellent method for producing high-purity stones, but always rely on the official color grade from a reputable lab report.
- If your primary focus is transparency about treatments: Be aware that a colorless CVD diamond has likely undergone post-growth treatment to achieve its final appearance, which is a standard part of its journey to market.
- If your primary focus is overall value: CVD diamonds provide exceptional value for high color and clarity grades, allowing you to acquire a visually stunning stone at a significant discount compared to a natural equivalent.
By understanding the unique properties of the CVD process, you can confidently evaluate a diamond based on its certified quality, not just its origin.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Typical CVD Diamond Color | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| As-Grown | Often a light brown tint | Due to structural imperfections during growth |
| After Treatment | Colorless (D-F grades) | Standard post-growth treatment improves color |
| Lab Report | Graded identically to natural diamonds | Final color is certified by GIA/IGI |
| Fluorescence | May fluoresce (e.g., red under UV) | A potential identifying characteristic |
Ready to find the perfect high-color lab-grown diamond for your needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support the precise creation of CVD diamonds. Whether you are a researcher, jeweler, or manufacturer, our products help ensure the controlled environments necessary for growing superior gemstones.
Let us help you achieve exceptional results. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific requirements with reliable, precision equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















