In short, heat treating specific aluminum alloys makes them significantly stronger and harder. This process, known as precipitation hardening or aging, manipulates the material's internal structure to achieve mechanical properties far superior to the aluminum's natural state, enabling its use in high-performance applications like aerospace and automotive components.
The core principle of heat treating aluminum is not about hardening the aluminum itself, but about dissolving alloying elements into the aluminum at high temperature and then allowing them to precipitate out as microscopic, strength-enhancing particles throughout the metal's structure.
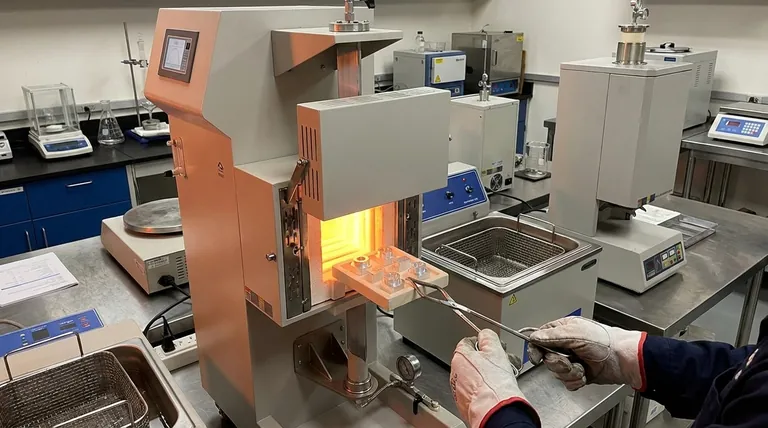

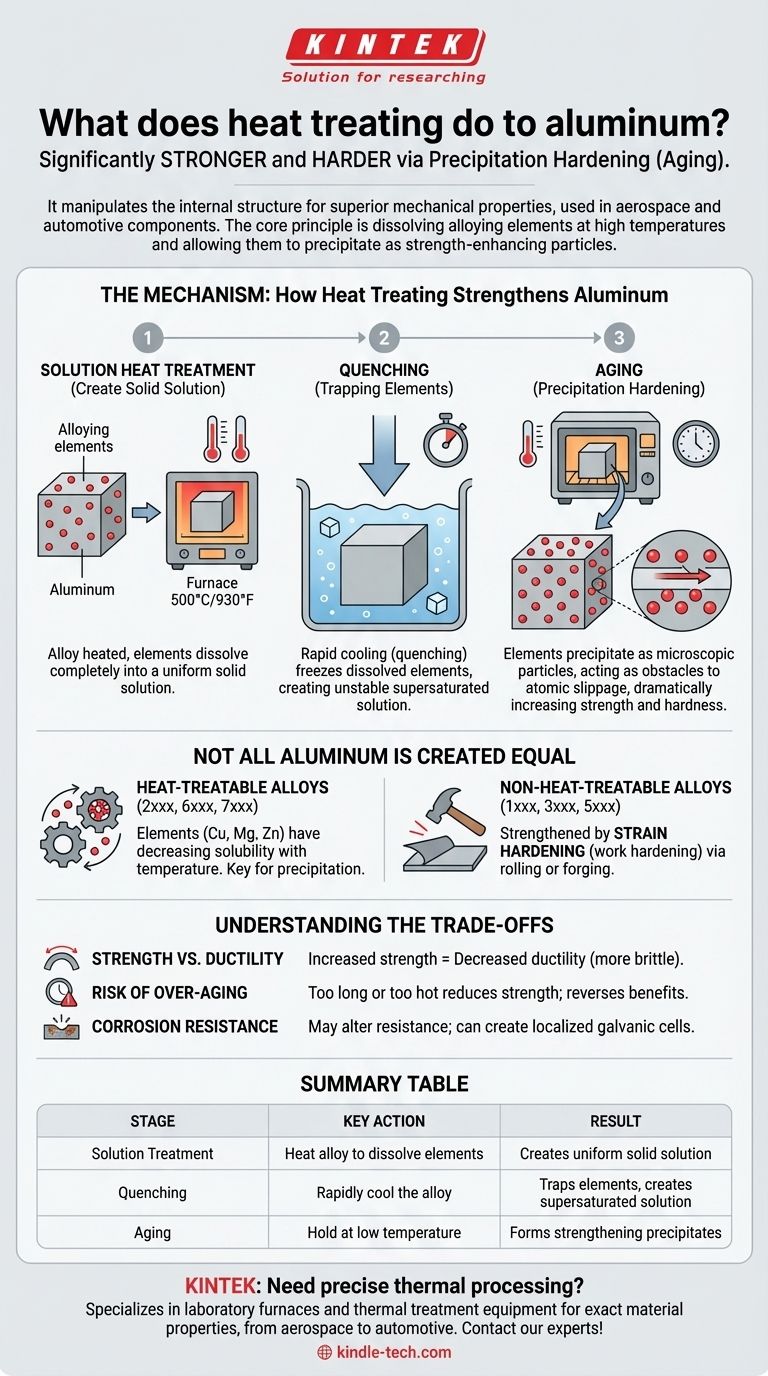
The Mechanism: How Heat Treating Strengthens Aluminum
To understand the effect of heat treatment, we first have to understand the underlying metallurgy. The process is a carefully controlled, three-step sequence designed to create internal reinforcement within the alloy.
### The Starting Point: A Solid Solution
Pure aluminum is relatively soft. To strengthen it, elements like copper, magnesium, or zinc are added. The first step of heat treatment is to create a homogenous mixture.
### Step 1: Solution Heat Treatment
The aluminum alloy is heated to a high temperature (around 500°C or 930°F, depending on the alloy) and held there. At this temperature, the alloying elements dissolve completely into the aluminum, creating a uniform solid solution, much like sugar dissolving in hot water.
### Step 2: Quenching
The alloy is then rapidly cooled, or quenched, typically in water. This sudden drop in temperature freezes the dissolved alloying elements in place, creating an unstable, supersaturated solution. The atoms don't have time to escape.
### Step 3: Aging (Precipitation Hardening)
This is the final and most critical step. The quenched material is "aged" either at room temperature (natural aging) or in a low-temperature oven (artificial aging). During this time, the trapped alloying elements begin to precipitate out of the solution, forming extremely small, hard, and uniformly dispersed particles within the aluminum's crystal structure.
These particles act as microscopic obstacles, making it much more difficult for the atomic layers of the metal to slip past one another. This resistance to internal movement is what we perceive as a dramatic increase in strength and hardness.
Not All Aluminum is Created Equal
It is critical to understand that not all aluminum alloys can be strengthened by heat treatment. The ability to be hardened depends entirely on the alloy's chemical composition.
### Heat-Treatable Alloys
Alloys in the 2xxx, 6xxx, and 7xxx series are considered heat-treatable. Their primary alloying elements (like copper or magnesium/silicon) have a decreasing solubility in aluminum as the temperature drops, which is the essential requirement for the precipitation process to work.
### Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys
Alloys in the 1xxx, 3xxx, and 5xxx series cannot be strengthened by heat treatment. They achieve their strength through strain hardening (also known as work hardening), which involves physically deforming the metal through processes like rolling or forging.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Altering a material's properties always involves compromises. Heat treating is no exception, and being aware of the trade-offs is essential for proper material selection.
### Strength vs. Ductility
The primary trade-off is between strength and ductility. As you increase an alloy's hardness and strength through heat treatment, you typically decrease its ductility, making it more brittle and less forgiving of bending or impact.
### The Risk of Over-aging
The aging process is a function of both time and temperature. If an alloy is held at its aging temperature for too long or at too high a temperature, the fine precipitates will begin to grow and coarsen. This over-aging actually reduces the material's strength and hardness, effectively undoing the benefits of the treatment.
### Changes in Corrosion Resistance
Heat treatment can sometimes alter an alloy's resistance to corrosion. The precipitates formed near the material's grain boundaries can create localized galvanic cells, potentially making some high-strength alloys more susceptible to certain types of corrosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct alloy and heat treatment depends entirely on the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Choose a 7xxx or 2xxx series alloy and apply a full solution heat treatment and artificial aging process (e.g., a T6 temper).
- If your primary focus is good formability with moderate strength: Use a non-heat-treatable alloy (like the 5xxx series) in a work-hardened state or a heat-treatable alloy (like 6061) in its annealed, pre-treatment condition.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength, cost, and corrosion resistance: A 6xxx series alloy (like 6061-T6) is often the most versatile and common choice for a wide range of structural applications.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms certain aluminum alloys from a common, lightweight metal into a high-performance engineering material.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treating Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Solution Treatment | Heat alloy to dissolve elements | Creates uniform solid solution |
| Quenching | Rapidly cool the alloy | Traps elements, creates supersaturated solution |
| Aging | Hold at low temperature | Forms strengthening precipitates |
Need precise thermal processing for your aluminum components? KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces and thermal treatment equipment, providing the controlled heating solutions essential for achieving the exact material properties your project demands. From aerospace alloys to automotive parts, our expertise ensures reliable and repeatable results. Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can support your high-performance material needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is pyrolysis gasification in waste management? Transform Waste into Valuable Resources
- What materials can be case hardened? Choosing the Right Steel for a Hard Case and Tough Core
- What is the primary function of large-scale resistance furnaces in the Acheson process? Powering SiC Synthesis
- How is a vacuum furnace heated? The Science of Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the best method of quenching? Choose the Right Quenchant for Maximum Hardness & Integrity
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of annealing? A Guide to Strategic Material Processing
- How does sintering temperature affect grain size? Control Your Material's Microstructure for Optimal Properties
- Why do we need vacuum for thermal evaporation? Ensure High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















