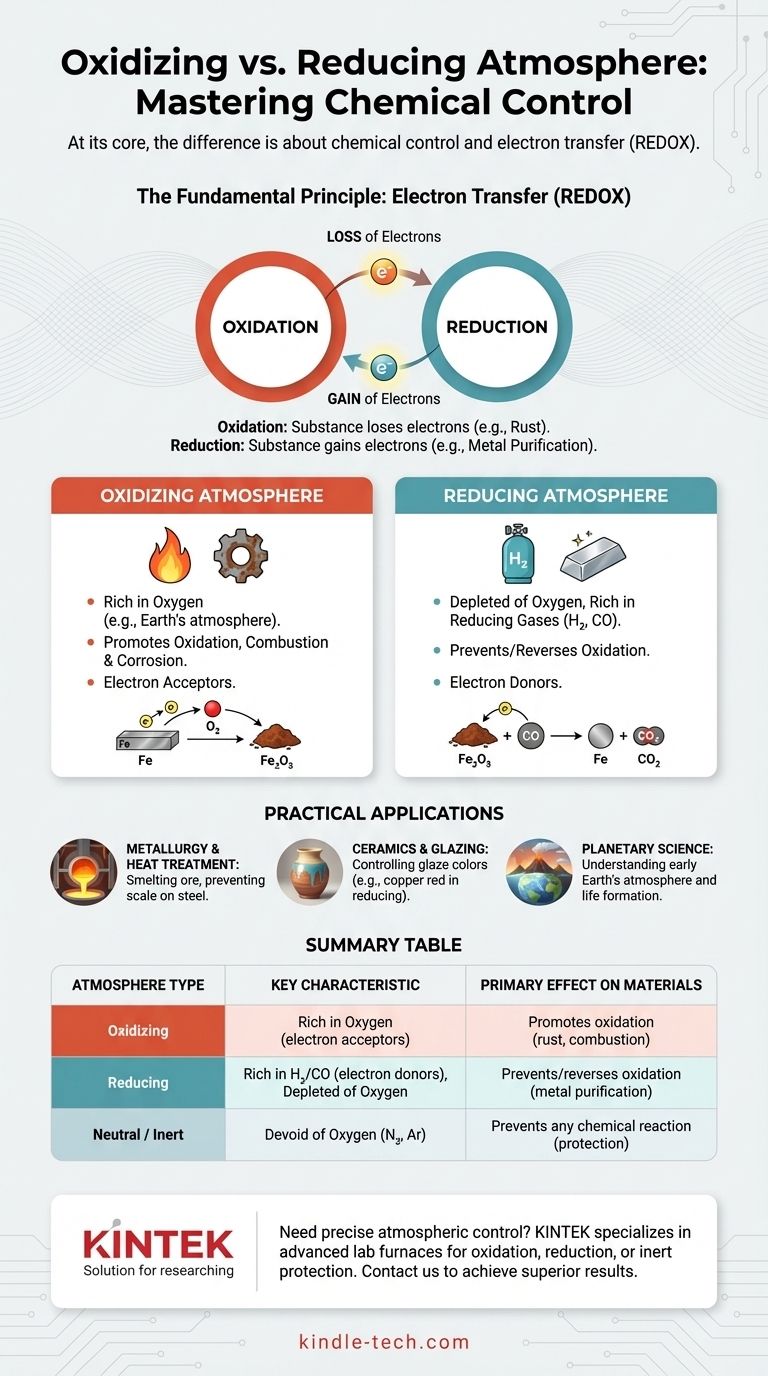
At its core, the difference is about chemical control. An oxidizing atmosphere is rich in oxygen or other substances that accept electrons, promoting reactions like combustion and corrosion. In direct contrast, a reducing atmosphere is intentionally depleted of oxygen and often contains gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide that donate electrons, which prevents or even reverses oxidation.
The key distinction isn't just the presence of oxygen, but whether the atmosphere's chemistry causes a material to lose electrons (oxidation) or gain electrons (reduction). Choosing the right atmosphere is fundamental to controlling the outcome of high-temperature processes, from manufacturing steel to firing artistic pottery.

The Fundamental Principle: Electron Transfer
To truly understand the difference, you must look past the gases and focus on the underlying chemistry of electron exchange. This is known as REDOX (Reduction-Oxidation).
Understanding Oxidation: The Loss of Electrons
Oxidation is a chemical process where a substance loses electrons. While oxygen is the most famous oxidizing agent, it's not the only one.
The classic example is rust. When iron is exposed to an oxygen-rich atmosphere, the iron atoms lose electrons to the oxygen atoms, forming iron oxide. The material has been oxidized.
Understanding Reduction: The Gain of Electrons
Reduction is the exact opposite process: a substance gains electrons. This "reduces" its oxidation state.
In a reducing atmosphere, gases like hydrogen (H₂) or carbon monoxide (CO) are present. These gases are electron donors; they readily give their electrons to other substances, reversing the process of oxidation.
Characteristics of Each Environment
The composition of the atmosphere directly dictates its chemical behavior and its effect on materials within it.
The Oxidizing Atmosphere
An oxidizing environment is characterized by an abundance of free oxygen or other oxidizing agents. Earth’s atmosphere is the most common example.
This environment supports and accelerates combustion. It is also the primary driver of corrosion and degradation for many materials, especially metals at high temperatures.
The Reducing Atmosphere
A reducing atmosphere is defined by the near-total absence of oxygen. To be actively "reducing," it must also contain reducing gases.
These gases, such as hydrogen or carbon monoxide, will chemically strip oxygen atoms from materials they come into contact with. This is essential for processes like smelting ore into pure metal.
The Neutral (or Inert) Atmosphere
It is important to recognize a third state: a neutral or inert atmosphere. This environment, typically composed of nitrogen or argon, is also devoid of oxygen.
However, unlike a reducing atmosphere, these gases do not actively donate electrons. Their purpose is simply to displace oxygen and prevent any chemical reactions from occurring, protecting the material without altering it.
Practical Implications and Why It Matters
The choice between these atmospheres is not academic; it is a critical decision in countless industrial and scientific processes.
In Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
When smelting iron ore, a blast furnace is filled with coke (a form of carbon), which burns to create a carbon monoxide-rich, oxygen-poor reducing atmosphere. The CO strips oxygen from the iron oxide ore, reducing it to pure liquid iron.
Similarly, when heat-treating steel, a reducing atmosphere is used to prevent the formation of "scale" (a layer of iron oxide) on the hot surface of the metal.
In Ceramics and Glazing
The atmosphere inside a kiln has a profound effect on the final color of pottery glazes.
A copper carbonate glaze, for example, will turn green in an oxidizing atmosphere. In a reducing atmosphere, the same glaze will produce a brilliant red as the copper oxide is chemically "reduced" back to pure copper.
In Planetary Science
The distinction is also crucial to understanding planetary formation. The early Earth had a reducing atmosphere, which was a necessary condition for the formation of the complex organic molecules that led to life.
Only after the evolution of photosynthetic organisms did our planet develop the oxygen-rich, oxidizing atmosphere we depend on today.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice is dictated entirely by the chemical transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preventing corrosion or removing oxygen from a compound (like smelting ore): You require a reducing atmosphere rich in agents like carbon monoxide or hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is complete combustion or creating a specific chemical oxide: You need an oxidizing atmosphere with a controlled supply of oxygen.
- If your primary focus is simply protecting a material from any chemical change at high temperatures: You should use a neutral or inert atmosphere, such as pure argon or nitrogen.
Ultimately, mastering the atmospheric conditions means you are mastering the final state and integrity of your material.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Effect on Materials | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing | Rich in oxygen (electron acceptors) | Promotes oxidation (e.g., rust, combustion) | Complete combustion, creating specific oxides |
| Reducing | Depleted of oxygen, rich in H₂/CO (electron donors) | Prevents/reverses oxidation (e.g., metal purification) | Smelting ore, preventing scale on steel, ceramic color effects |
| Neutral/Inert | Devoid of oxygen (e.g., N₂, Ar) | Prevents any chemical reaction | Protecting materials from change at high temperatures |
Need precise atmospheric control for your lab processes? The right furnace atmosphere is critical for achieving your desired material properties, whether you're heat-treating metals, developing new ceramics, or protecting sensitive samples. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and equipment designed for exact atmospheric control. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to ensure oxidation, reduction, or inert protection for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















