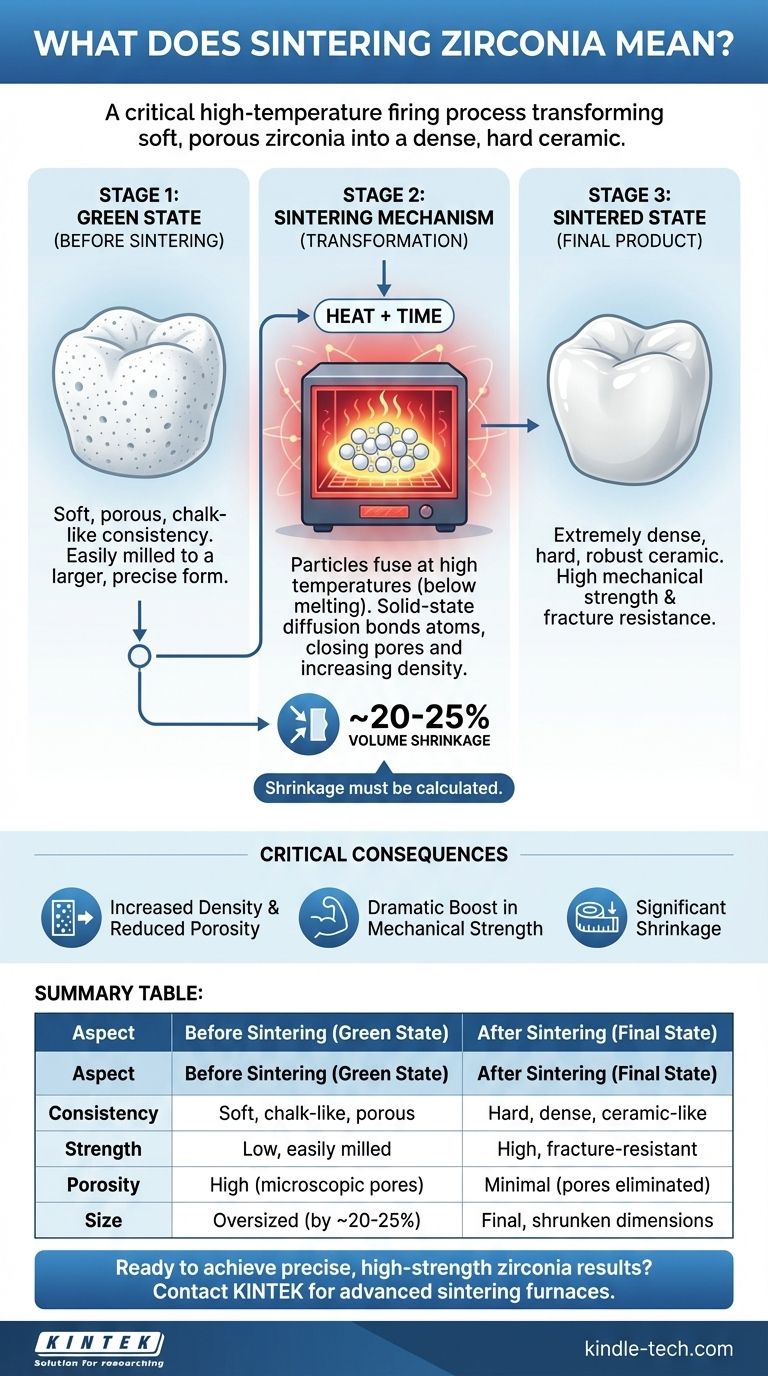
In essence, sintering zirconia is a critical high-temperature firing process that transforms a soft, porous zirconia structure into a dense, incredibly hard, and strong final ceramic. This is achieved by heating the material to a high temperature, causing the individual particles to fuse together without actually melting the material into a liquid.
Sintering is not merely a heating step; it is a fundamental transformation. It closes the microscopic pores within the zirconia, which dramatically increases its density and mechanical strength while causing the entire object to shrink significantly.

From "Chalk" to Ceramic: The Sintering Transformation
To understand sintering, you must first understand the two states of zirconia in the fabrication process: the "green state" before sintering and the final "sintered state."
The "Green State": Zirconia Before Sintering
Before sintering, zirconia exists in a pre-sintered or "green state." In this phase, it has a chalk-like consistency.
This initial state is intentionally soft and porous. This allows it to be easily milled or shaped into a precise, complex form, such as a dental crown.
The Sintering Mechanism: Fusing Without Melting
Once the zirconia is shaped, it is placed in a specialized furnace. As the temperature rises, the atoms at the boundaries of the zirconia particles become highly energized.
This energy allows atoms to diffuse across the particle boundaries, forming strong chemical bonds. The particles essentially merge, pulling closer together and eliminating the empty spaces, or pores, between them.
The "Sintered State": The Final Product
After the sintering cycle is complete, the zirconia has been fundamentally altered. It is now an extremely dense, hard, and robust ceramic.
This final sintered state possesses the high mechanical strength and fracture resistance that zirconia is known for, making it suitable for demanding applications.
The Critical Consequences of Sintering
The changes that occur during sintering are not side effects; they are the entire point of the process. Each one is critical to achieving the material's desired final properties.
Increased Density and Reduced Porosity
The most fundamental change is the reduction of porosity. The elimination of these internal voids is what drives the increase in density.
A fully sintered zirconia component has minimal internal defects, which is the primary source of its strength.
A Dramatic Boost in Mechanical Strength
The increase in density is directly correlated with a massive increase in mechanical strength and hardness.
By fusing the particles and removing the porous weak points, the material becomes highly resistant to cracks and fractures.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
As the pores are eliminated and the particles consolidate, the entire object undergoes significant and predictable shrinkage.
This shrinkage is substantial, often around 20-25% in volume. Manufacturers must precisely account for this by milling the "green state" object at a larger, calculated size.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the concept is straightforward, the practical application requires precision and a clear understanding of the process limitations.
Shrinkage Must Be Perfectly Calculated
The most critical factor in manufacturing with zirconia is managing the shrinkage. The pre-sintered object is digitally designed and milled to be proportionally larger than the final desired part.
Any error in calculating this shrinkage will result in a final component that does not fit, which is especially critical in high-precision dental and medical applications.
Sintering Is Not Melting
It is a common misconception that sintering involves melting. The process occurs entirely in the solid state, at temperatures below zirconia's melting point.
This solid-state diffusion preserves the fine-grained microstructure of the material, which is essential for its superior mechanical properties.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
While high temperature is the primary driver of sintering, some industrial processes may also apply pressure.
Using pressure can help accelerate the densification process or achieve higher densities at slightly lower temperatures, but for many applications like dental zirconia, heat alone is the standard method.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding sintering is key to working with zirconia effectively, whether in a lab or in an industrial setting.
- If your primary focus is dentistry or prosthetics: Recognize that the pre-sintered block is intentionally oversized to precisely compensate for shrinkage, which is the only way to ensure the final dimensional accuracy required for a perfect fit.
- If your primary focus is materials science or engineering: Understand that controlling the sintering parameters—such as peak temperature, heating rate, and hold time—is how you directly manipulate the final density, grain size, and resulting mechanical properties of the zirconia component.
Ultimately, sintering is the essential and transformative process that unlocks the exceptional strength and durability that define zirconia as a high-performance ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Before Sintering (Green State) | After Sintering (Final State) |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Soft, chalk-like, porous | Hard, dense, ceramic-like |
| Strength | Low, easily milled | High, fracture-resistant |
| Porosity | High (microscopic pores) | Minimal (pores eliminated) |
| Size | Oversized (by ~20-25%) | Final, shrunken dimensions |
Ready to achieve precise, high-strength zirconia results?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including sintering furnaces designed for optimal zirconia processing. Whether you're in dentistry, prosthetics, or materials engineering, our solutions ensure controlled sintering for superior density and mechanical properties.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can a broken porcelain tooth be repaired? A Guide to Durable Dental Solutions
- Is ceramic the same as porcelain teeth? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Material
- What is dental ceramic materials? Your Guide to Strong, Natural-Looking Restorations
- What is the temperature of a porcelain furnace? Master Sintering for Perfect Results
- Why are porcelain fired under vacuum? To Eliminate Porosity for Superior Strength & Translucency
- What is the structure and properties of dental ceramics? Mastering the Science Behind Durable, Aesthetic Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















