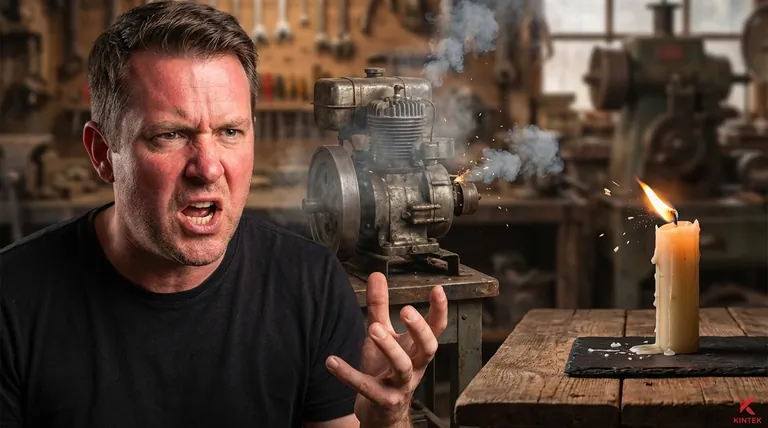
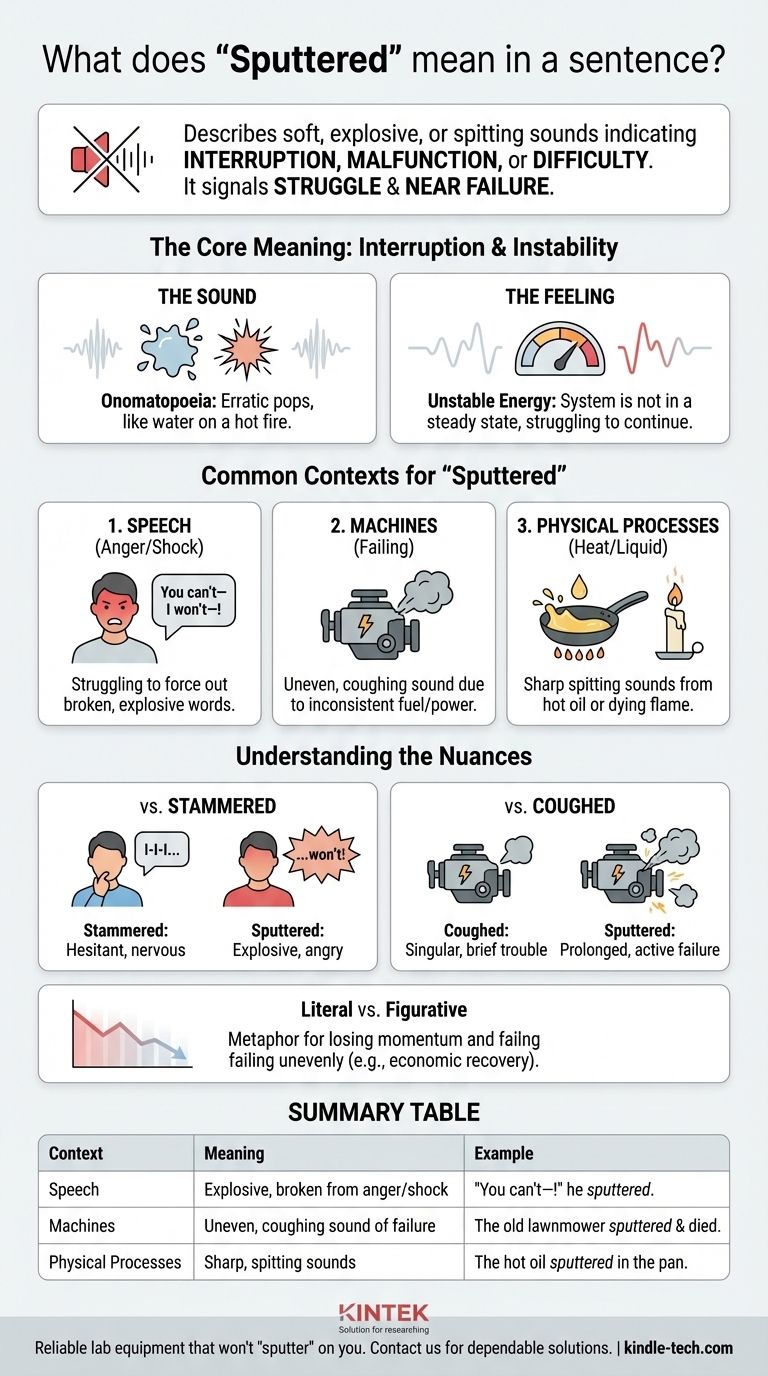
In a sentence, the word "sputtered" describes the act of making a series of soft, explosive, or spitting sounds. It implies a sense of interruption, malfunction, or difficulty, whether used to describe a person speaking, an engine running, or a flame dying out.
The core idea behind "sputtered" is not just the sound itself, but the struggle it represents. It signals that something is not working smoothly and is likely on the verge of failing or stopping completely.

The Core Meaning: Interruption and Instability
The verb "sputter" is evocative, bringing a distinct audio and visual sense to the reader's mind. It's built on the idea of something that is uneven and disjointed.
The Sound of Sputtering
At its heart, sputtering is an onomatopoeia. The sound is one of wet, popping bursts.
Think of bacon grease hitting a hot pan or a few drops of water falling onto a fire. It is not a continuous hiss but a series of small, sharp, and erratic pops.
The Feeling of Sputtering
Beyond the sound, the word conveys a feeling of unstable energy. A system that sputters is not in a steady state; it is struggling to continue.
This is why we use it for engines running out of fuel or for people so overcome with emotion they cannot speak clearly. The common thread is a loss of controlled, continuous output.
Common Contexts for "Sputtered"
Understanding where the word is most often used is the key to mastering its meaning. It appears in three primary contexts: human speech, mechanical failure, and physical processes.
Sputtering in Speech
When a person sputters, they are typically struggling to speak due to a strong, overwhelming emotion like anger, shock, or indignation.
They may spit slightly while trying to force out words, which come out in a broken, explosive rush rather than a coherent sentence. For example: “You can’t—I won’t—!” he sputtered, his face red with rage.
Sputtering in Machines
This is one of the most common uses of the word. An engine or motor sputters when it is failing.
It describes the uneven, coughing sound of a machine that is not getting a consistent supply of fuel or power. For instance: The old lawnmower sputtered for a few moments and then died.
Sputtering in Physical Processes
You will also see "sputtered" used to describe reactions involving heat and liquid, or a dying flame.
A candle flame might sputter just before it goes out, its light flickering and spitting wax. Similarly, hot oil in a skillet will sputter and spit when a piece of food is dropped into it.
Understanding the Nuances
While "sputtered" has a clear meaning, it's often confused with similar words. Clarifying the differences reveals its unique power.
Sputtered vs. Stammered
A person stammers due to nervousness, anxiety, or a speech impediment, often repeating the beginning of words ("I-I-I can't go").
A person sputters out of anger or shock, with the difficulty stemming from being too incensed to speak properly. Sputtering is explosive; stammering is hesitant.
Sputtered vs. Coughed (for engines)
An engine might cough once or twice as a brief, singular sign of trouble.
An engine that sputters is undergoing a more prolonged failure. Sputtering is the sound of the engine actively dying over several moments, not just hiccuping once.
Literal vs. Figurative Use
The concept of a sputtering engine is a powerful metaphor. You may hear that an "economic recovery is sputtering" or that a "political campaign sputtered to a halt."
In these cases, it means the effort is losing momentum and failing in an uneven, faltering way.
How to Use "Sputtered" Correctly
To use the word effectively, connect it to the underlying sense of struggle or failure.
- If you are describing emotional speech: Use "sputtered" to convey anger, shock, or indignation where a person struggles to form explosive, broken phrases.
- If you are describing a failing machine: Use "sputtered" to depict an engine or device that is running unevenly and about to stop completely.
- If you are describing a physical reaction: Use "sputtered" for liquids like hot oil or a dying flame that make sharp, spitting, and popping sounds.
Ultimately, "sputtered" is a powerful verb that brings a sense of audible, disjointed struggle to your writing.
Summary Table:
| Context | Meaning of 'Sputtered' | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Speech | Explosive, broken speech from anger or shock | "You can't—I won't—!" he sputtered. |
| Machines | Uneven, coughing sound of a failing engine | The old lawnmower sputtered and died. |
| Physical Processes | Sharp, spitting sounds from heat/liquid | The hot oil sputtered in the pan. |
Master the nuances of precise language. Whether you're writing reports or documenting processes, clear communication is key. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable tools that won't 'sputter' on you. Contact us today to find the dependable solutions your lab needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



