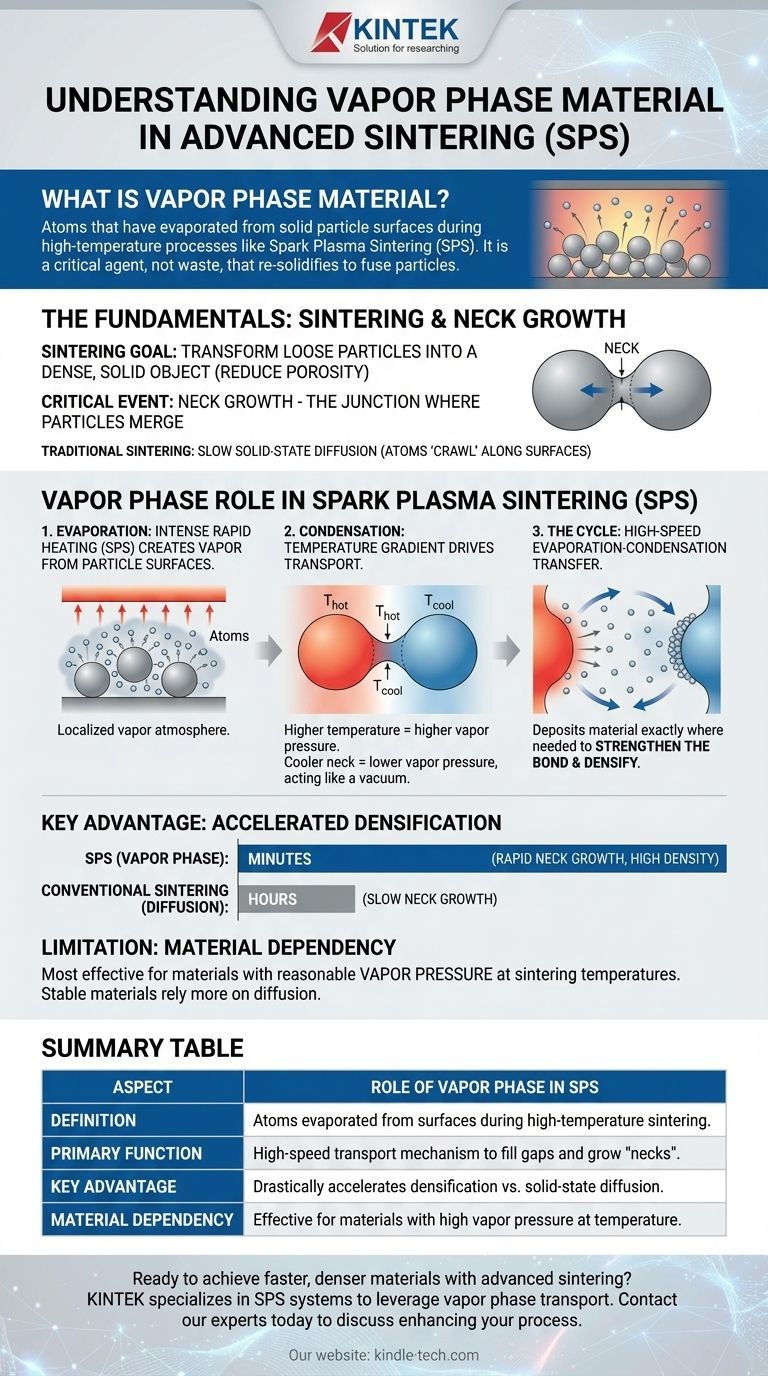
In the context of advanced materials processing, the vapor phase material refers to atoms that have evaporated from the surface of solid particles during a high-temperature process like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). This gas-like material is not lost; it is a critical agent that re-solidifies, or condenses, onto specific areas to help fuse the particles together more efficiently.
The vapor phase is best understood as a high-speed transport mechanism. It moves material from hotter particle surfaces to cooler junction points ("necks") between them, accelerating the bonding process far beyond what traditional methods can achieve.

The Fundamentals of Sintering and Mass Transport
To grasp the importance of the vapor phase, we must first understand the fundamental goal of sintering: to transform a collection of loose particles into a dense, solid object.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a process that uses heat and pressure to bond particles together without melting them completely. The primary objective is to reduce the empty space (porosity) between particles, resulting in a strong, consolidated component.
The "Neck": Where Particles Join
When two particles touch and begin to fuse, the small bridge that forms between them is called a neck. The growth of these necks is the most critical event in sintering, as it is how individual particles merge into a solid mass.
Traditional Mass Transport
In conventional sintering, necks grow through solid-state diffusion. This is a relatively slow process where atoms essentially "crawl" along the particle surfaces or through their bulk to fill in the gaps.
The Vapor Phase Role in Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Spark Plasma Sintering is an advanced technique that introduces a much faster transport mechanism: evaporation and condensation.
Evaporation: Creating the Vapor Phase
The intense, rapid heating in SPS provides enough energy for atoms on the particle surfaces to escape, turning into a gas or vapor. This creates a localized atmosphere of material vapor surrounding the solid particles.
Condensation: The Driving Force for Neck Growth
The key to this process is a temperature difference. The area at the neck between two particles is often slightly cooler than the exposed surfaces of the particles. This temperature difference creates a vapor pressure gradient.
A higher temperature on the particle surface leads to a higher vapor pressure (more evaporation), while the cooler neck has a lower vapor pressure. This pressure difference acts like a vacuum, pulling the vaporized atoms toward the neck.
The Evaporation-Condensation Cycle
This creates a highly efficient cycle. Atoms evaporate from hotter regions and are immediately drawn to condense and solidify on the cooler necks. This "evaporation-solidification transfer" deposits material exactly where it is needed most to strengthen the bond and densify the component.
Understanding the Key Advantage
The vapor phase mechanism offers a distinct benefit but is not universally applicable. Understanding its nature is key to leveraging it correctly.
Benefit: Accelerated Densification
Vapor transport is orders of magnitude faster than solid-state diffusion. This is why SPS can consolidate materials and achieve high densities in minutes, whereas conventional sintering can take many hours.
Limitation: Material Dependency
This mechanism is most effective for materials that have a reasonably high vapor pressure at their sintering temperature. Materials that are extremely stable and do not readily evaporate will rely more on traditional, slower diffusion mechanisms even during SPS.
Control is Critical
The effectiveness of vapor phase transport relies on the precise temperature gradients established by the SPS process. The ability to create rapidly cooled necks, as mentioned in the process description, is what makes the vapor pressure difference significant enough to drive this rapid material transfer.
Applying This to Your Material Goals
Your understanding of the vapor phase directly impacts how you select and optimize a manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing: Leveraging materials with a suitable vapor pressure in an SPS system can dramatically shorten manufacturing times.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density: For suitable materials, optimizing SPS parameters to enhance the evaporation-condensation cycle is the most effective way to eliminate porosity and strengthen inter-particle necks.
- If you are choosing a sintering method: For materials prone to evaporation-condensation, SPS offers a clear advantage over conventional furnace sintering, which cannot effectively utilize this rapid transport mechanism.
By controlling these atomic-level transport phenomena, engineers can create stronger, denser materials in a fraction of the time.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Vapor Phase in SPS |
|---|---|
| Definition | Atoms evaporated from particle surfaces during high-temperature sintering. |
| Primary Function | High-speed transport mechanism to fill gaps and grow 'necks' between particles. |
| Key Advantage | Drastically accelerates densification compared to solid-state diffusion. |
| Material Dependency | Most effective for materials with high vapor pressure at sintering temperatures. |
Ready to achieve faster, denser materials with advanced sintering?
KINTEK specializes in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems, to help you leverage mechanisms like vapor phase transport for superior material consolidation. Our expertise ensures you can optimize parameters to accelerate your R&D and production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sintering process and meet your specific material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the synthesis and purification methods for carbon nano tubes? Scaling Quality and Purity for Your Application
- What are the advantages of carbon nanotubes over steel? Unmatched Strength & Conductivity
- What is the thickness of CVD graphene? From Single-Atom Layers to Precise Multi-Layer Control
- What are the applications of thin-film in renewable energy? Beyond Solar Panels to Energy Storage & Hydrogen
- What is the process of thin film making? A Guide to Controlled Deposition Techniques
- What are the applications of thin film in nanotechnology? Building the Future, One Atom at a Time
- What are the advantages of sputtering based thin film deposition? Achieve Superior Film Quality & Material Versatility
- What are thin films made of? Metals, Ceramics, Semiconductors, and Polymers



















