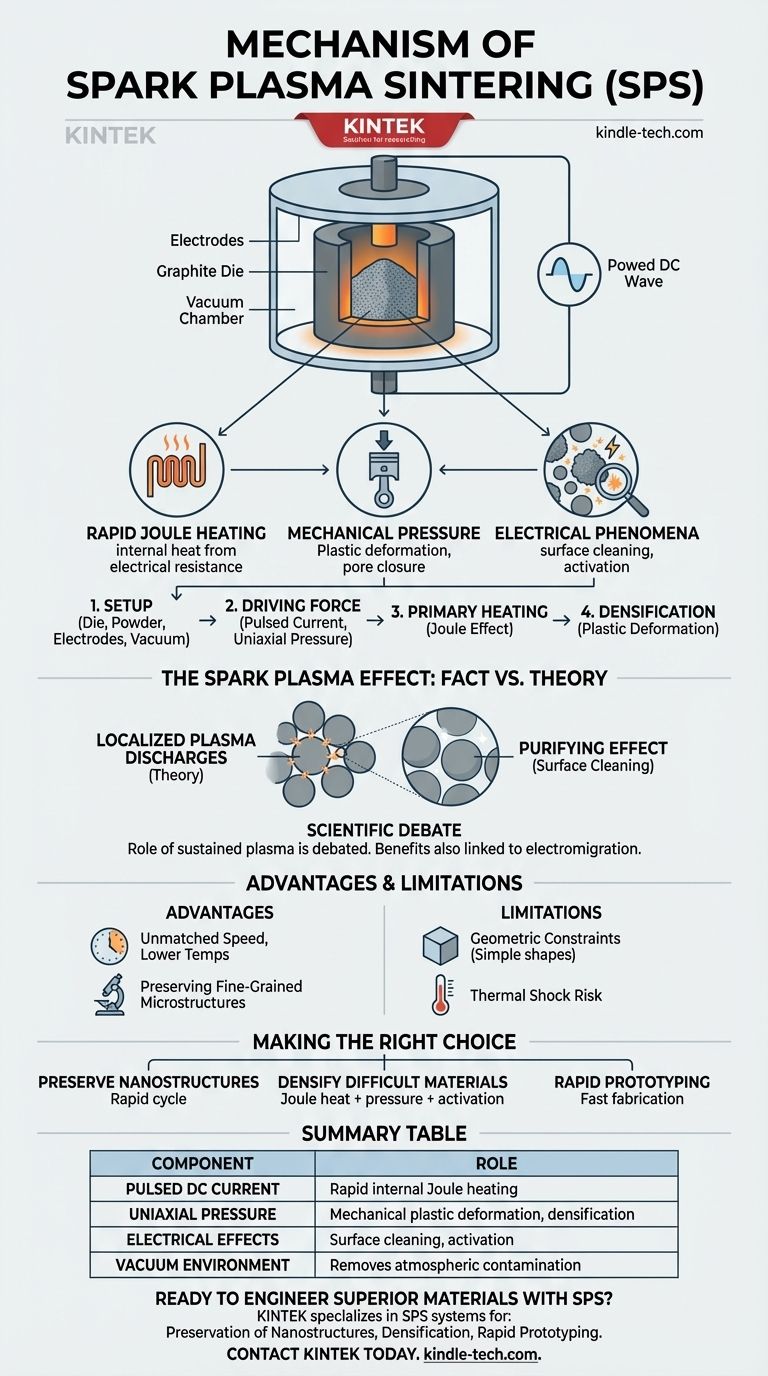
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced sintering technique that uses a pulsed direct electric current and uniaxial pressure to consolidate powders into a dense solid. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat materials externally, SPS passes current directly through the graphite mold and the powder compact itself, generating intense internal heat via electrical resistance. This direct heating is the key to its remarkably fast processing times and lower sintering temperatures.
The true advantage of SPS lies in the powerful synergy of three simultaneous effects: rapid Joule heating, mechanical pressure causing plastic deformation, and unique electrical phenomena that clean and activate particle surfaces to accelerate bonding.

Deconstructing the SPS Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand the mechanism, it's best to visualize the process from start to finish. It is a highly controlled sequence of physical events designed for maximum efficiency.
The Setup: Die, Powder, and Electrodes
The process begins by loading the material powder into a conductive die, which is almost always made of graphite. This entire assembly is placed between two electrodes within a vacuum chamber. Applying a vacuum is the first crucial step, as it removes atmospheric gases that could interfere with the sintering process.
The Driving Force: Pulsed Current and Pressure
Once a vacuum is established, two things happen simultaneously. A large, pulsed DC electric current is sent through the electrodes, passing directly through the graphite die and the powder. At the same time, a mechanical press applies a constant, uniaxial pressure to the powder.
The Primary Heating Mechanism: Joule Effect
The primary source of heat in SPS is the Joule effect, or resistive heating. The graphite die and the powder compact have electrical resistance. As the strong current passes through them, this resistance generates rapid and uniform heat throughout the material, raising its temperature at rates of hundreds of degrees Celsius per minute.
The Densification Mechanism: Plastic Deformation
As the powder particles heat up, they become softer and more malleable. The continuous mechanical pressure forces the particles together, causing them to deform plastically. This deformation closes the pores and voids between particles, dramatically increasing the density of the compact.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect: Fact vs. Theory
The name "Spark Plasma Sintering" points to a more complex phenomenon that contributes to its effectiveness, though its exact nature is still a subject of scientific discussion.
The Theory: Localized Plasma Discharges
The foundational theory suggests that at the microscopic contact points between individual powder particles, the pulsed current generates momentary spark discharges. These discharges are thought to create tiny pockets of extremely high-temperature plasma in the voids.
The Purifying Effect: Surface Cleaning and Activation
This localized plasma is believed to have a critical cleaning effect. It can vaporize and strip away surface contaminants or oxide layers that naturally form on powder particles. This leaves behind highly pure and atomically active surfaces that are primed to bond together, greatly enhancing the diffusion and neck formation that are essential for sintering.
The Scientific Debate: An Evolving Understanding
It is crucial to note that the existence and role of a sustained "plasma" are debated within the materials science community. Some researchers argue that the observed benefits are primarily due to the combination of rapid Joule heating and other electrical effects like electromigration, rather than a true plasma discharge. Regardless of the precise mechanism, the electrical effects at the particle level clearly accelerate densification beyond what heat and pressure alone could achieve.
Understanding the Key Advantages and Limitations
SPS is a powerful tool, but its application requires understanding its distinct characteristics.
Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Lower Temperatures
The most significant benefit of SPS is speed. Sintering cycles are completed in minutes, not hours. This rapid heating allows densification to occur at temperatures 200–500°C lower than conventional methods, which is critical for preventing unwanted grain growth.
Advantage: Preserving Fine-Grained Microstructures
Because the material spends very little time at high temperatures, SPS is exceptionally good at preserving nano-scale or fine-grained microstructures in the starting powder. This allows for the creation of materials with superior mechanical properties.
Limitation: Geometric and Material Constraints
The use of a rigid die and uniaxial pressure generally limits SPS to producing simple shapes like cylinders and blocks. Furthermore, the extreme heating and cooling rates can induce thermal shock, which certain brittle materials may not withstand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The SPS mechanism is not just a scientific curiosity; it directly enables specific material engineering outcomes.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures or fine grains: The rapid cycle time of SPS is its greatest asset, preventing the grain growth that plagues slower, conventional sintering methods.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult-to-sinter materials: The combination of Joule heat, pressure, and electrical surface activation in SPS can achieve near-full density in materials that are otherwise impossible to consolidate.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping of new material compositions: The speed of the SPS process makes it an unparalleled tool for quickly fabricating and testing novel alloys and composites.
By understanding the interplay of these thermal, mechanical, and electrical forces, you can leverage SPS to engineer materials with properties that were previously out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Key Mechanism Component | Role in SPS Process |
|---|---|
| Pulsed DC Current | Generates rapid, internal Joule heating by passing through the conductive die and powder. |
| Uniaxial Pressure | Applies mechanical force to plastically deform and densify the heated powder particles. |
| Electrical Effects | Cleans and activates particle surfaces, accelerating bonding (spark plasma/discharge theory). |
| Vacuum Environment | Removes atmospheric gases to prevent contamination and interference during sintering. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Materials with SPS Technology?
Understanding the mechanism of Spark Plasma Sintering is the first step toward unlocking its potential for your research and development. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment, including SPS systems, to help you achieve:
- Preservation of Nanostructures: Create materials with superior properties by preventing grain growth.
- Densification of Challenging Materials: Achieve near-full density in hard-to-sinter compositions.
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerate your material testing and development cycles significantly.
Let our expertise in lab equipment and consumables support your laboratory's most ambitious projects. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how an SPS system can be tailored to your specific material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification


















