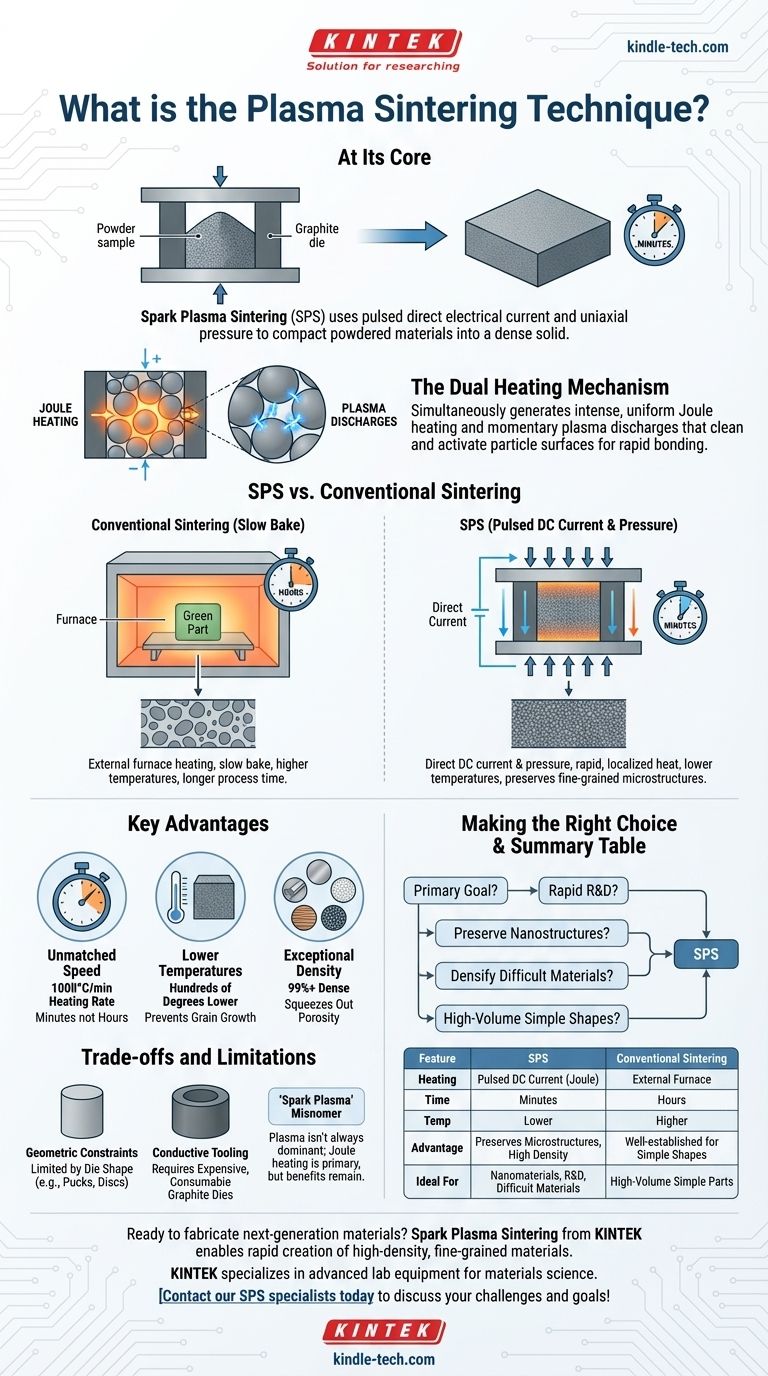
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced manufacturing technique that uses a pulsed direct electrical current and uniaxial pressure to compact powdered materials into a dense solid. Unlike conventional sintering which slowly bakes materials in a furnace, SPS passes electricity directly through the powder and its conductive die, creating rapid, localized heat that dramatically shortens the entire process from hours to minutes.
The central advantage of plasma sintering is not just speed, but control. By combining electrical heating with mechanical pressure, it achieves superior material density at significantly lower temperatures, preserving fine-grained microstructures that are critical for high-performance materials.
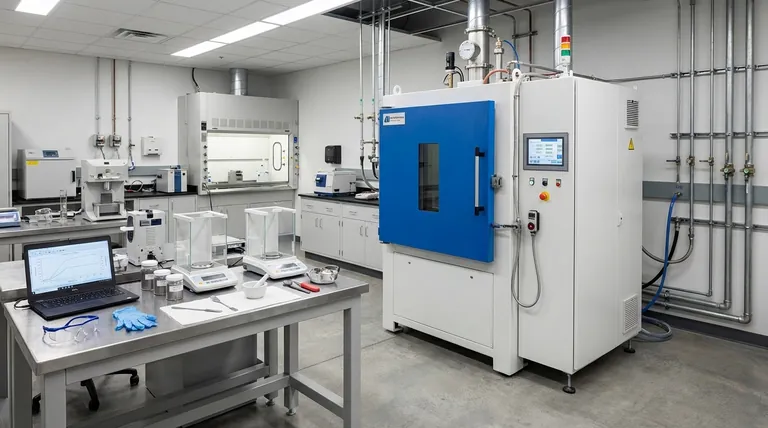

How Plasma Sintering Radically Differs from Traditional Methods
To understand the innovation of SPS, it's essential to first understand the conventional process it improves upon.
The Conventional Sintering Process: A Slow Bake
Traditional sintering involves forming a "green" part from a powder mixed with a binder. This part is then placed in a furnace and heated for an extended period.
The heat burns off the binder and causes the material particles to slowly fuse at their contact points, gradually reducing the empty space between them until a solid object is formed. This process is effective but slow and energy-intensive.
The SPS Revolution: Direct Current and Pressure
Spark Plasma Sintering, also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), completely changes the heating method.
The powdered sample is loaded into a conductive graphite die. This entire assembly is placed between two electrodes and subjected to mechanical pressure.
A powerful, pulsed DC current is then passed directly through the electrodes, the die, and often, the sample itself.
The Dual Heating Mechanism
The genius of SPS lies in its dual heating effect. The electrical resistance of the graphite die and the powder generates intense, uniform heat throughout the material, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
Simultaneously, the pulsed current can generate momentary plasma discharges in the microscopic spaces between powder particles. This plasma cleans and activates the particle surfaces, promoting exceptionally fast and efficient bonding.
Key Advantages of the SPS Technique
This unique mechanism delivers several transformative benefits for materials science and engineering.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
SPS systems can achieve heating rates of up to 1000°C per minute, compared to the 5-20°C per minute of conventional furnaces. This reduces total processing time from many hours to just a few minutes.
Lower Temperatures, Superior Results
Because the heating is so efficient and localized at the particle surfaces, densification occurs at much lower overall temperatures—often hundreds of degrees lower than conventional methods.
This prevents unwanted grain growth, allowing for the creation of materials with extremely fine, nanometer-scale structures that possess superior mechanical properties.
Exceptional Material Density and Purity
The combination of pressure and rapid, surface-activated heating squeezes out porosity with remarkable efficiency, routinely producing materials that are over 99% dense.
The process is typically conducted in a vacuum, which prevents oxidation and ensures high material purity.
Versatility for Advanced Materials
SPS is exceptionally well-suited for processing difficult-to-sinter materials. This includes metals with very high melting points, advanced ceramics, and composite materials that would not consolidate properly using traditional techniques.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Constraints on Geometry and Size
The process is limited by the shape of the graphite die, which is typically a simple cylinder. This makes SPS ideal for producing basic shapes like pucks or discs but less suitable for creating complex, near-net-shape parts directly.
Requirement for Conductive Tooling
The entire process relies on the electrical conductivity of the graphite die. These dies are consumable items that can be expensive and limit the maximum size of the component being sintered.
The "Spark Plasma" Misnomer
While the name is catchy, recent research indicates that a sustained, widespread plasma is not always the dominant mechanism. The primary effect is often the rapid resistive (Joule) heating. However, the name "Spark Plasma Sintering" has stuck, and its benefits remain undisputed regardless of the exact terminology.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
SPS is a specialized tool. Deciding whether it fits your project depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid research and development: SPS is unmatched for quickly producing and iterating on small batches of novel materials and alloys.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures: The low-temperature, short-duration process is essential for creating dense nanomaterials without destroying their unique properties.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult-to-sinter materials: SPS is the go-to technique for high-melting-point metals, ceramics, and composites that fail in conventional furnaces.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of simple shapes: The speed of SPS can make it a viable, high-throughput production method for specific components.
Spark Plasma Sintering is a transformative tool that empowers engineers and scientists to create next-generation materials that were previously impossible to fabricate.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Pulsed DC current (Joule heating) | External furnace heating |
| Process Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Typical Temperature | Lower (by hundreds of degrees) | Higher |
| Key Advantage | Preserves fine microstructures, high density | Well-established for simple shapes |
| Ideal For | Nanomaterials, R&D, difficult-to-sinter materials | High-volume production of simple parts |
Ready to fabricate next-generation materials?
Spark Plasma Sintering from KINTEK enables you to rapidly create high-density, fine-grained materials that are impossible with conventional methods. Whether you are developing new ceramics, metal composites, or nanostructured materials, our SPS solutions provide the speed, control, and low-temperature processing you need to preserve critical material properties.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment for materials science. Let our experts help you integrate SPS technology into your R&D or production workflow.
Contact our SPS specialists today to discuss your specific material challenges and goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application



















