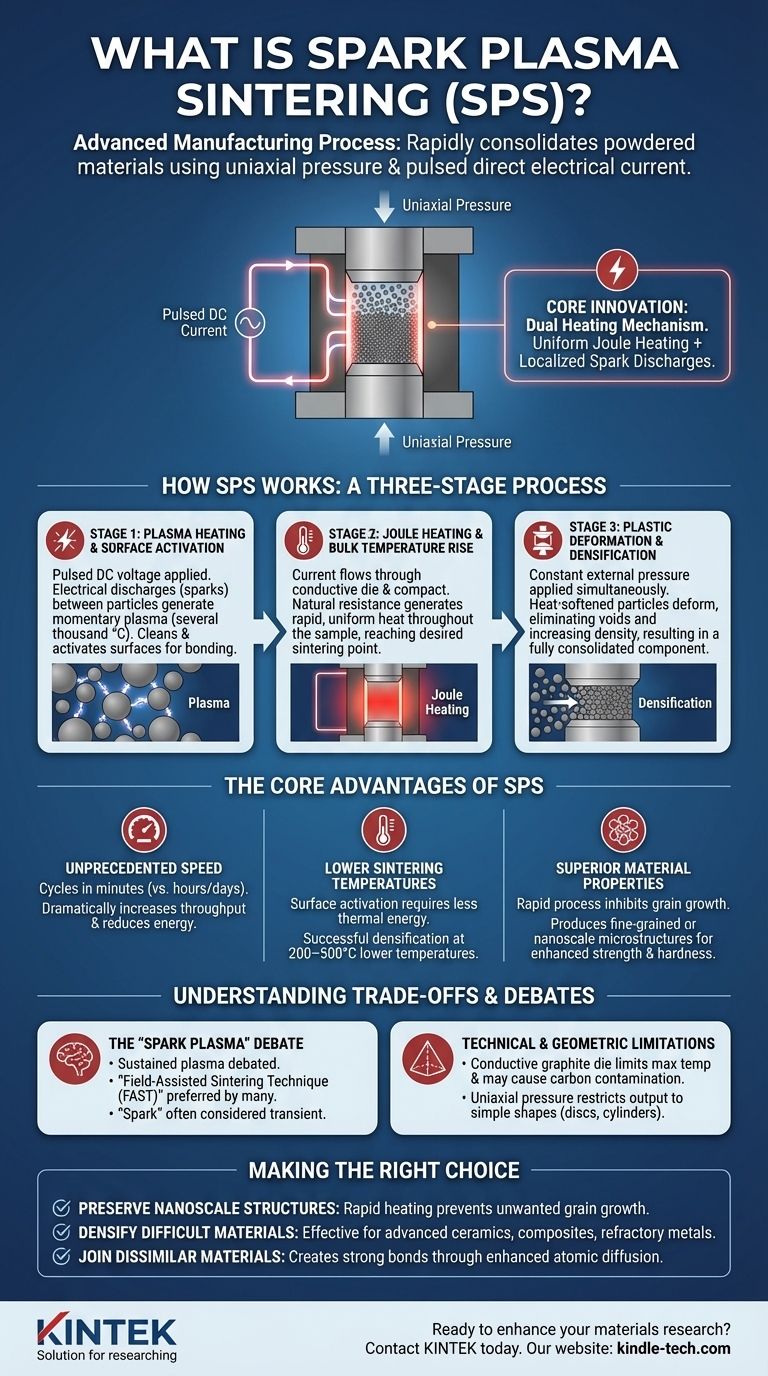
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced manufacturing process that uses a combination of uniaxial pressure and a pulsed direct electrical current to rapidly consolidate powdered materials into a dense solid. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat materials slowly from the outside, SPS passes current directly through the powder and its container, generating intense heat internally and at the contact points between particles. This method achieves full densification in minutes at temperatures 200–500°C lower than traditional sintering techniques.
The central innovation of SPS is its dual heating mechanism. It combines uniform, bulk Joule heating with localized, high-temperature spark discharges between powder particles, a synergy that dramatically accelerates the sintering process while preserving the material's fine-grained microstructure.

How SPS Works: A Three-Stage Process
The SPS process is a sophisticated evolution of traditional hot pressing. By introducing an electrical current, it fundamentally changes how energy is delivered to the material, leading to a highly efficient and controlled densification cycle.
Stage 1: Plasma Heating and Surface Activation
The process begins as a pulsed DC voltage is applied to the loose powder compact. In the initial moments, electrical discharges (sparks) arc across the tiny gaps between individual powder particles.
These discharges generate a momentary, localized plasma with temperatures reaching several thousand degrees Celsius. This intense heat purifies the particle surfaces by vaporizing contaminants and activates the material, creating the ideal conditions for bonding to occur.
Stage 2: Joule Heating and Bulk Temperature Rise
As the electrical current continues to flow, it passes through both the conductive graphite die and, if conductive, the material compact itself. The natural electrical resistance of these components generates rapid and uniform heat throughout the bulk of the sample.
This effect, known as Joule heating, is responsible for raising the overall temperature of the material to the desired sintering point, making it soft and malleable.
Stage 3: Plastic Deformation and Densification
Simultaneously with the heating stages, a constant external pressure is applied. This force, combined with the heat-softened material, causes the powder particles to deform and squeeze together.
This plastic deformation eliminates the voids and pores between particles, forcing them into intimate contact. This final mechanical step rapidly increases the material's density, resulting in a solid, fully consolidated component.
The Core Advantages of the SPS Method
The unique mechanisms of SPS provide significant benefits over conventional furnace-based sintering, enabling the creation of materials that were previously difficult or impossible to fabricate.
Unprecedented Speed
SPS cycles are completed in a matter of minutes, whereas conventional sintering can take many hours or even days. This dramatically increases throughput and reduces energy consumption.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
The surface activation from the initial plasma effect means less thermal energy is required to bond the particles. This allows for successful densification at significantly lower overall temperatures, which is crucial for temperature-sensitive materials.
Superior Material Properties
The extreme speed of the SPS process inhibits grain growth—a common issue in slow, high-temperature sintering that can degrade mechanical properties. SPS consistently produces materials with fine-grained or even nanoscale microstructures, leading to enhanced strength, hardness, and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Debates
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution, and its precise mechanisms are still a subject of scientific discussion.
The "Spark Plasma" Debate
The existence of a sustained "plasma" throughout the process is highly debated. Many researchers prefer the more descriptive term Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), as the effects of the electric field and Joule heating are undisputed. The "spark" is largely considered a transient phenomenon that occurs only at the very beginning of the process.
Technical and Geometric Limitations
The SPS process relies on a conductive die, which is typically made of graphite. This can limit the maximum processing temperature and may cause carbon contamination with certain reactive materials. Furthermore, the use of uniaxial pressure generally restricts the output to simple geometric shapes like discs and cylinders.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
SPS technology excels in specific scenarios, offering unique capabilities for advanced material development.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanoscale or fine-grained structures: SPS is ideal due to its rapid heating and short cycle times that prevent unwanted grain growth.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult-to-sinter materials: The combination of pressure, Joule heat, and surface activation makes SPS highly effective for advanced ceramics, composites, and refractory metals.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials: SPS offers a unique capability for creating strong ceramic-metal or ceramic-ceramic bonds through enhanced atomic diffusion.
By leveraging a unique combination of heat, pressure, and electrical effects, Spark Plasma Sintering provides a powerful tool for fabricating next-generation materials with superior properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | How SPS Achieves It | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Direct internal Joule heating & plasma activation | Cycle times of minutes vs. hours/days |
| Temperature | Efficient surface activation & bulk heating | Sintering at 200–500°C lower temperatures |
| Microstructure | Rapid process inhibits grain growth | Preserves fine-grained or nanoscale structures |
| Materials | Effective for ceramics, composites, refractory metals | Enables densification of hard-to-sinter materials |
Ready to enhance your materials research with advanced sintering? KINTEK specializes in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including sintering solutions, to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories. Our expertise can help you achieve superior material properties with efficiency and precision. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and accelerate your development process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts


















