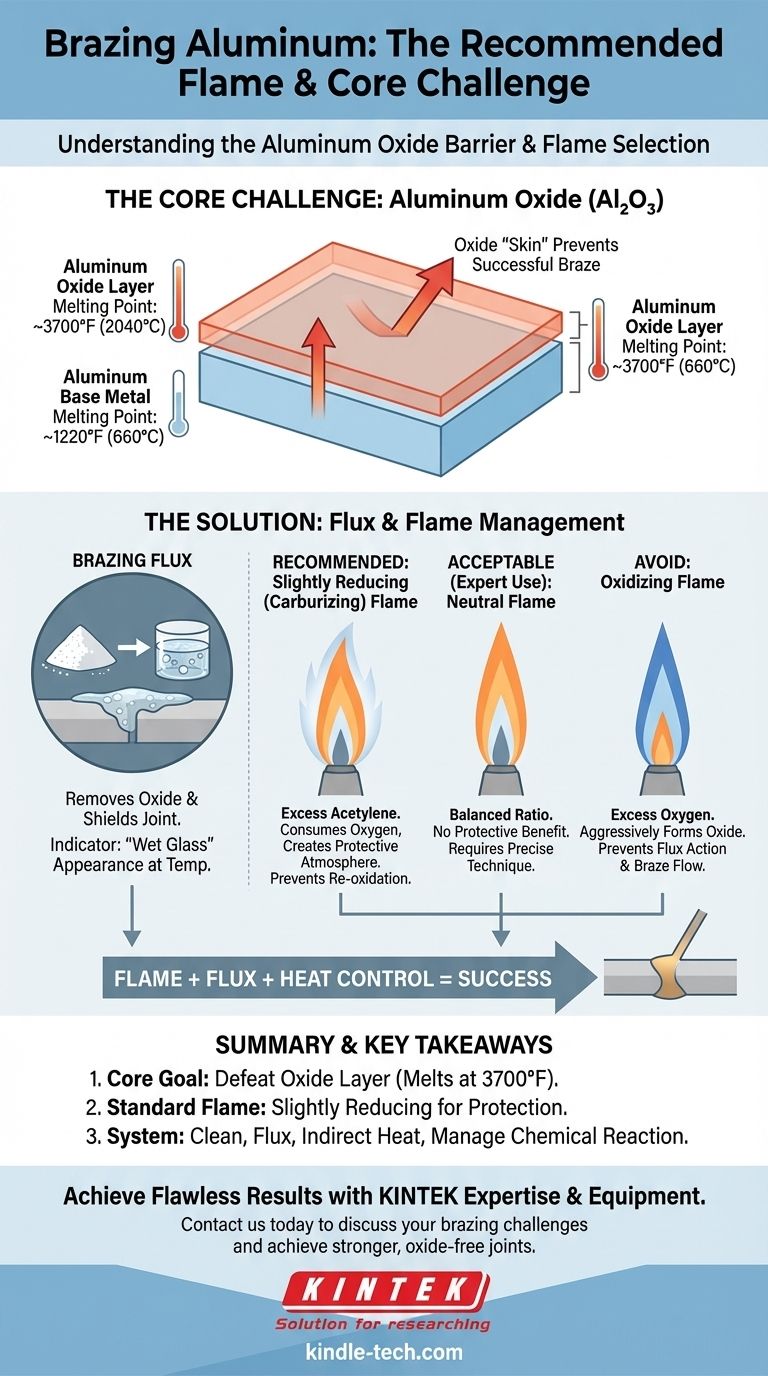
For brazing aluminum, the standard recommendation is a slightly reducing (carburizing) flame from an oxy-acetylene torch. This type of flame has a slight excess of fuel, which helps protect the aluminum from excessive oxidation during the heating process. A neutral flame can sometimes be used, but a reducing flame provides an extra margin of safety against forming the stubborn aluminum oxide layer that prevents a successful braze.
The key to brazing aluminum is not just selecting a flame, but understanding that your primary challenge is defeating the aluminum oxide layer. Your choice of flame, flux, and heat control are all tools dedicated to managing this invisible barrier.

The Core Challenge: Understanding Aluminum Oxide
Brazing aluminum is fundamentally different from brazing steel or copper because of a chemical reality you cannot see. Success depends entirely on how you manage this reality.
The Aluminum Oxide Problem
All aluminum is covered by a thin, transparent, and incredibly tough layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). This layer melts at around 3700°F (2040°C), while the aluminum underneath melts at a much lower temperature of about 1220°F (660°C).
If you try to heat aluminum to brazing temperature without addressing this oxide layer, you will melt the base metal into a puddle long before you ever break through the oxide "skin" holding it together.
The Role of Flux
Brazing flux is the chemical solution to the oxide problem. When heated, the flux becomes active and performs two critical jobs: it removes the existing oxide layer and shields the joint from oxygen in the air, preventing new oxide from forming.
The appearance of the flux is your most important temperature indicator. It will turn clear and liquid, looking like "wet glass," when the workpiece has reached the correct brazing temperature.
Selecting the Right Flame for Aluminum
Your flame is the tool you use to apply heat, and its chemical properties have a direct impact on the aluminum oxide you are trying to defeat.
Why a Slightly Reducing (Carburizing) Flame is Standard
A reducing flame is created with a slight excess of acetylene fuel. You can identify it by the primary inner cone and a secondary, whitish-blue "feather" at the tip.
The excess, unburnt fuel in this flame consumes oxygen in the immediate vicinity of the joint. This creates a protective atmosphere that helps prevent the rapid re-formation of aluminum oxide, giving your flux an easier job.
What is a Neutral Flame?
A neutral flame has a perfectly balanced ratio of oxygen and acetylene. It has a clear, well-defined inner cone and no secondary feather.
While it can be used for aluminum brazing by a skilled operator, it offers no protective benefit against oxidation. It is less forgiving than a reducing flame if your technique is not perfect.
Why to Avoid an Oxidizing Flame
An oxidizing flame, which has an excess of oxygen, is actively harmful when brazing aluminum. This flame is characterized by a short, pointed inner cone and a loud hissing sound.
The excess oxygen will aggressively and rapidly form more aluminum oxide on the workpiece, working directly against your flux and making a successful braze nearly impossible.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
The flame is only one part of a three-part system: clean, flux, heat. A mistake in any one area will lead to failure.
Overheating and Melting the Base Metal
Aluminum gives very little warning before it melts. Unlike steel, it does not glow red. The melting point of the brazing filler is often very close to the melting point of the aluminum itself, leaving a very narrow window for success.
Incorrect Heat Application
Focus on heating the workpiece evenly and broadly. Do not point the flame directly at the brazing filler rod. Allow the heat of the base metal to melt the filler, which will then be drawn into the joint by capillary action.
Poor Cleaning or Flux Application
The flame cannot overcome a dirty or poorly fluxed joint. The base metal must be mechanically cleaned with a stainless steel brush right before applying flux. The flux must cover all surfaces of the joint completely.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach should be guided by the precision required and your experience level.
- If your primary focus is precision on small parts: Use a slightly reducing flame and a smaller torch tip. Pay close attention to the flux; as soon as it turns clear and liquid, introduce the filler rod to the joint.
- If your primary focus is learning the process: Practice on scrap pieces of the same aluminum alloy. Deliberately create reducing, neutral, and oxidizing flames to see their effects. Your goal is to learn to recognize the "wet glass" appearance of the active flux.
- If your primary focus is achieving a strong, oxide-free joint: Remember that the flame is just one part of the system. Meticulous cleaning, complete flux coverage, and indirect heating are just as critical as choosing a reducing flame.
Mastering this process comes from understanding that you are not just melting metal, but managing a chemical reaction at the surface of the joint.
Summary Table:
| Flame Type | Acetylene/Oxygen Ratio | Key Characteristic | Effect on Aluminum Brazing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slightly Reducing (Recommended) | Slight excess of acetylene | Whitish-blue "feather" at tip | Protects against oxidation, safer for flux |
| Neutral | Balanced ratio | Clear, defined inner cone | Can be used by experts, less forgiving |
| Oxidizing (Avoid) | Excess of oxygen | Short, pointed cone, hissing sound | Rapidly forms oxide, prevents successful braze |
Achieve flawless aluminum brazing results with the right equipment and expertise. Brazing aluminum requires precise heat control to manage the stubborn oxide layer. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable heating tools and expert support. Let our team help you select the perfect torch and provide guidance for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your brazing challenges and how we can help you achieve stronger, oxide-free joints.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?



















