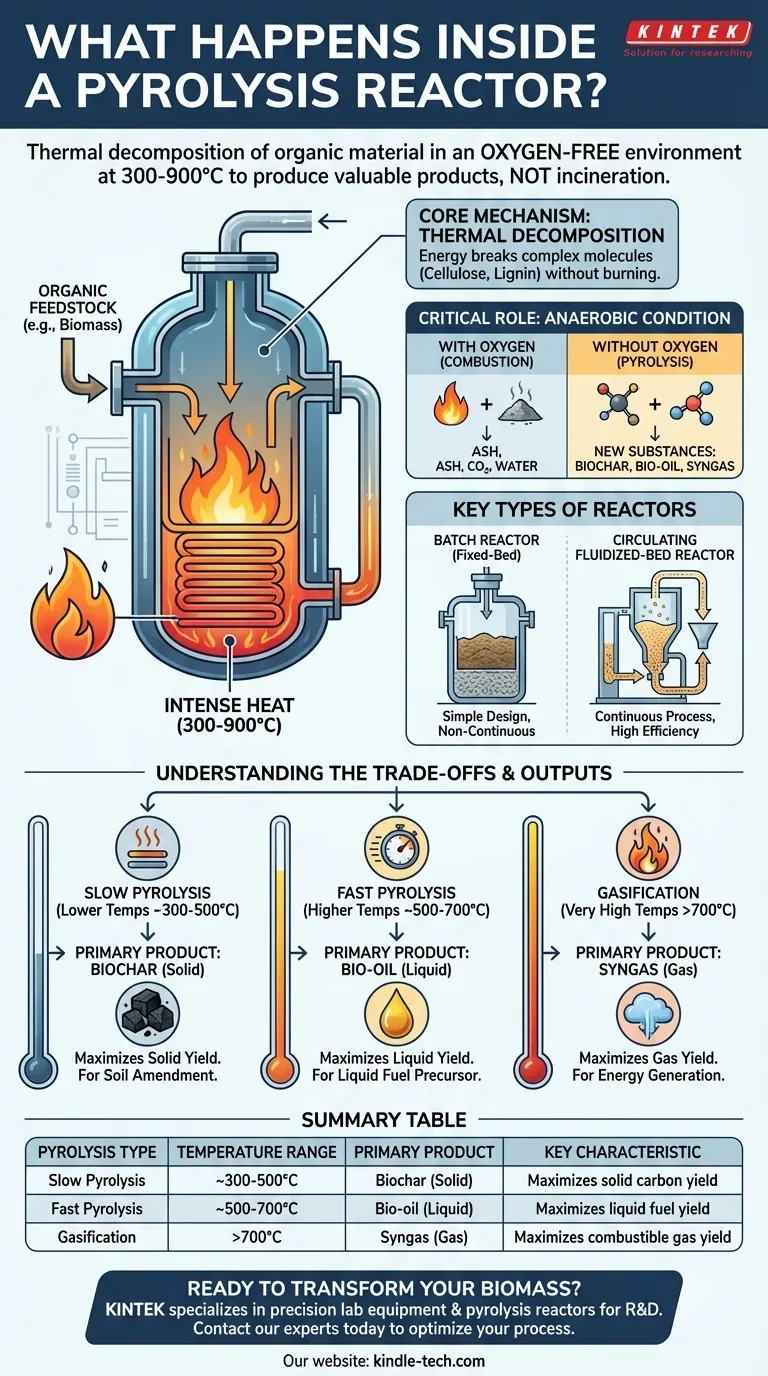
Inside a pyrolysis reactor, organic material is subjected to intense heat in a completely oxygen-free environment. This process, known as thermal decomposition, occurs at temperatures between 300-900°C, breaking down the complex molecular structure of the feedstock into simpler, more valuable products without allowing it to burn.
A pyrolysis reactor is fundamentally a chemical processing vessel, not an incinerator. By precisely controlling heat and eliminating oxygen, it deconstructs materials like biomass to intentionally produce a specific mix of solid (biochar), liquid (bio-oil), and gas (syngas) outputs.

The Core Mechanism: Thermal Decomposition
The function of a pyrolysis reactor is best understood by its two defining operational parameters: the absence of oxygen and the application of high heat.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the anaerobic (oxygen-free) condition inside the reactor.
When oxygen is present, heating organic material causes combustion—burning—which releases energy but primarily produces ash, carbon dioxide, and water.
By removing oxygen, the reactor prevents combustion. Instead, the applied energy breaks the chemical bonds within the material itself, reforming it into new substances.
How High Temperature Drives the Transformation
Heat is the engine of pyrolysis. It provides the necessary energy to break down large, complex molecules found in biomass, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
The specific temperature used inside the reactor is a critical control parameter, as it directly influences the final product yields.
Key Types of Pyrolysis Reactors
While the core principle remains the same, reactors are designed differently to accommodate various scales and operational needs.
The Batch Reactor
A batch pyrolysis reactor, sometimes called a fixed-bed reactor, is the simplest design. It operates like an oven.
Feedstock is loaded into a sealed vessel, the vessel is heated to the target temperature for a set duration, and then it is cooled before the products are removed. This design is robust and well-suited for operations that do not require continuous output.
The Circulating Fluidized-Bed Reactor
For larger, industrial-scale operations, a circulating fluidized-bed reactor offers a continuous process.
In this system, a hot, fluid-like bed of material (such as sand) is circulated within the reactor. When the biomass feedstock is introduced, this hot circulating medium ensures extremely rapid and uniform heat transfer, making the process highly efficient for continuous production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a pyrolysis reactor is measured by its ability to produce a desired output. This is determined by a trade-off between temperature, heating rate, and reactor type.
Temperature Dictates the Product
The most significant variable is temperature. Different temperature ranges favor different products.
- Slow Pyrolysis (Lower Temps, ~300-500°C): Slower heating rates at lower temperatures maximize the yield of the solid product, biochar.
- Fast Pyrolysis (Higher Temps, ~500-700°C): Very rapid heating to higher temperatures maximizes the yield of the liquid product, bio-oil.
- Gasification (Very High Temps, >700°C): At the highest temperatures, the process favors the production of syngas, the gaseous product.
Reactor Design Influences Efficiency and Scale
The choice between a batch or circulating reactor involves a trade-off between simplicity and throughput.
A batch reactor is simpler to build and operate but is less efficient for large-scale, continuous production. A circulating reactor is more complex and expensive but is essential for the high-efficiency throughput required for renewable energy generation.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Selecting the right pyrolysis conditions is entirely dependent on your desired end product.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment: Utilize a slow pyrolysis process at lower temperatures, often in a simpler batch reactor.
- If your primary focus is generating bio-oil as a liquid fuel precursor: Employ a fast pyrolysis process at moderate-to-high temperatures in a system that allows for rapid heat transfer, like a fluidized-bed reactor.
- If your primary focus is creating syngas for energy generation: Operate at very high temperatures to maximize the conversion of the feedstock into a combustible gas.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis reactor is a precise thermal tool designed to unlock specific value from organic materials by carefully managing their decomposition.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Primary Product | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | ~300-500°C | Biochar (Solid) | Maximizes solid carbon yield |
| Fast Pyrolysis | ~500-700°C | Bio-oil (Liquid) | Maximizes liquid fuel yield |
| Gasification | >700°C | Syngas (Gas) | Maximizes combustible gas yield |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable products?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and pyrolysis reactors designed for research and development. Whether you're focusing on biochar production for agriculture, bio-oil for renewable energy, or syngas for power generation, our reactors provide the precise temperature control and oxygen-free environment essential for successful pyrolysis.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can optimize your pyrolysis process and help you achieve your sustainability and energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















