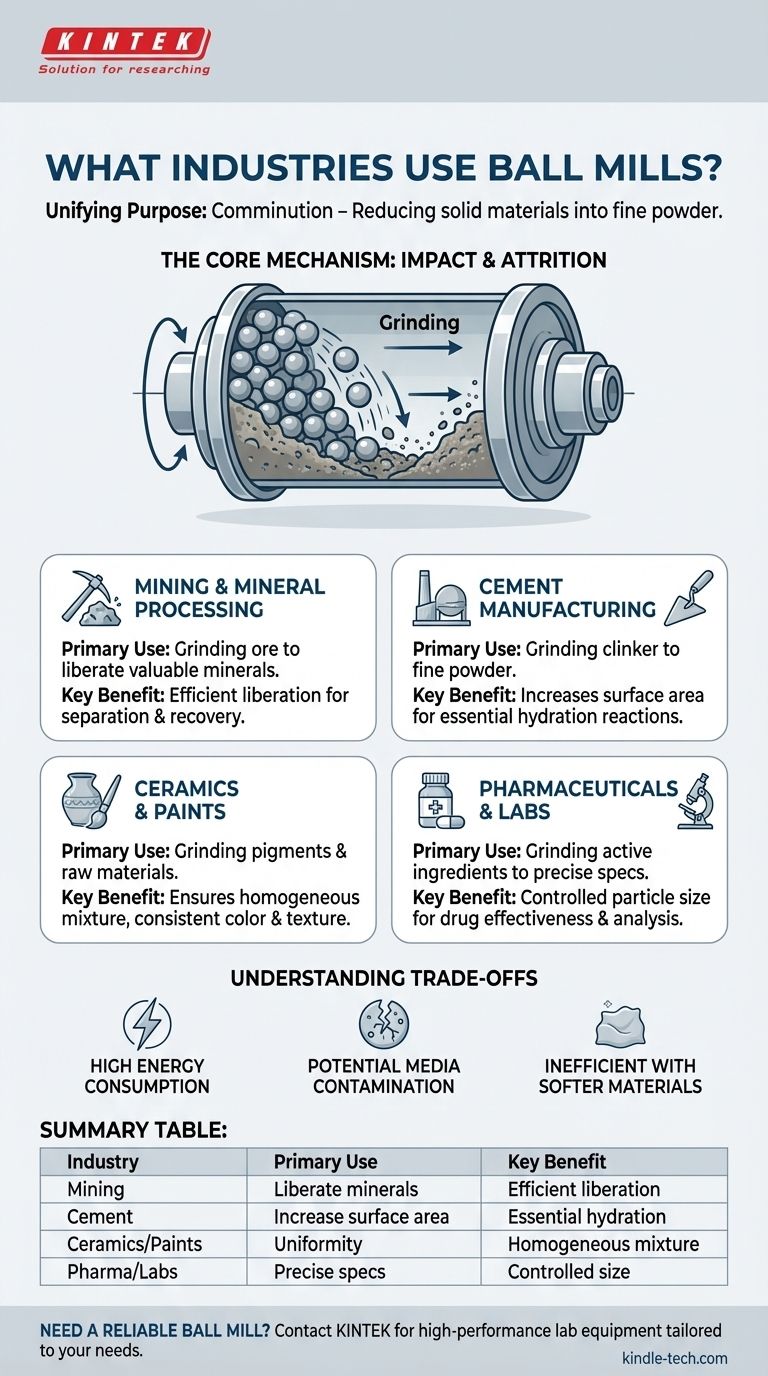
At their core, ball mills are used across a diverse range of heavy and precision industries, most notably in mining and mineral processing, cement manufacturing, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals. They are also a foundational tool in research laboratories where precise material grinding is required for analysis.
The unifying purpose of a ball mill across all applications is comminution, or the reduction of solid materials into a finer powder. The specific reason for this size reduction is what defines its role within each industry.

The Core Function: Why Ball Mills Are So Versatile
A ball mill is fundamentally a simple but powerful device. Its value comes from its ability to reliably and consistently reduce the particle size of hard materials, a critical step in countless industrial processes.
The Principle of Impact and Attrition
Inside a rotating cylindrical shell, the material to be ground is mixed with a grinding media, typically steel or ceramic balls. As the shell rotates, the balls are lifted up and then cascade down, crushing and grinding the material through impact and attrition.
Achieving Precise Particle Size
The final particle size is controlled by factors like the size and material of the grinding media, the rotation speed of the drum, and the duration of the milling process. This control is essential for ensuring the quality and performance of the end product.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
While the mechanism is the same, the goal of particle reduction varies significantly between industries. Understanding these goals reveals why the ball mill is such a widely adopted technology.
Mining and Mineral Processing
In the mining sector, valuable minerals are often locked within large, worthless rock, known as ore. A ball mill is the primary tool used to grind this ore down, liberating the fine mineral particles so they can be separated and recovered.
Cement Manufacturing
After raw materials are heated in a kiln to form a hard substance called clinker, a ball mill grinds it into an extremely fine powder. This process dramatically increases the surface area of the material, which is essential for the chemical reactions (hydration) that allow cement to harden.
Ceramics and Paints
For products like ceramics, glazes, and paints, consistency is paramount. Ball mills are used to grind pigments and raw ceramic materials to a uniform, fine powder. This ensures a homogenous mixture, smooth application, and consistent color and texture in the final product.
Pharmaceuticals and Laboratories
In pharmaceuticals, the effectiveness of a drug can depend on its particle size, which affects its dissolution rate and bioavailability. Ball mills provide a reliable method for grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients to precise specifications. In labs, they are used to prepare samples for analysis where a fine, uniform powder is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite their versatility, ball mills are not the optimal solution for every scenario. Their selection requires understanding key limitations.
High Energy Consumption
Ball milling is an energy-intensive process. The continuous rotation of a heavy drum filled with steel media consumes a significant amount of power, representing a major operational cost, especially in large-scale operations like mining and cement.
Potential for Media Contamination
The constant impact and attrition cause the grinding media itself to wear down over time. These fine particles of steel or ceramic can mix with the product, which is a critical concern in high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals or specialty ceramics.
Inefficiency with Softer Materials
Ball mills excel at grinding hard, brittle materials. They are generally less effective or efficient for processing soft, sticky, or fibrous materials, for which other grinding technologies are better suited.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right grinding technology depends entirely on the material properties and the desired outcome of the process.
- If your primary focus is liberating minerals from hard ore: A ball mill is the industry standard and one of the most effective tools available.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-fine powder for chemical reactions: A ball mill provides the necessary surface area increase required for processes like cement production.
- If your primary focus is achieving high purity without contamination: You must select specialized, non-contaminating grinding media or consider alternative milling technologies.
Ultimately, the ball mill's enduring presence in industry is a testament to its simple, robust, and effective method for breaking big things into smaller, more useful things.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use of Ball Mill | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Grinding ore to liberate valuable minerals | Efficient liberation of fine particles |
| Cement Manufacturing | Grinding clinker to increase surface area | Essential for cement hydration reactions |
| Ceramics & Paints | Grinding pigments and raw materials for uniformity | Homogeneous mixture and consistent color/texture |
| Pharmaceuticals & Labs | Grinding active ingredients to precise specifications | Controlled particle size for drug effectiveness |
Need a reliable ball mill for your industry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions tailored to your grinding needs—whether in mining, pharmaceuticals, or research. Contact us today to enhance your material processing efficiency and achieve precise particle size control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- Why is a high-energy planetary ball mill preferred over traditional casting for nanocrystalline HEAs?
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of NiCr-Al2O3-SrCO3 composite powders? Enhanced Homogeneity
- How does a planetary high-energy ball mill contribute to the top-down preparation of layered materials? Optimize Yield



















