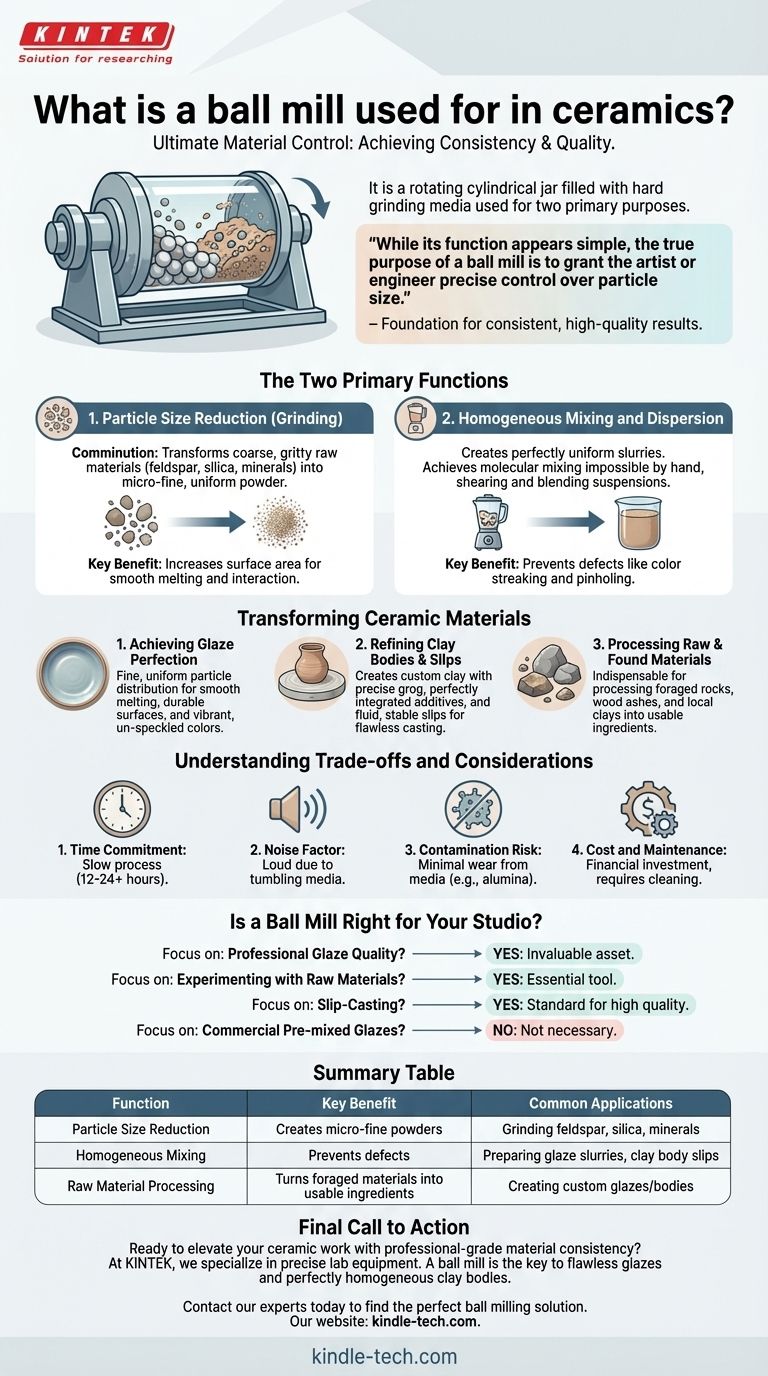
At its core, a ball mill is a ceramicist's tool for ultimate material control. It is a rotating cylindrical jar filled with hard grinding media used for two primary purposes: grinding raw, dry materials into an exceptionally fine powder and intimately mixing the components of a liquid slurry for glazes or clay bodies.
While its function appears simple, the true purpose of a ball mill is to grant the artist or engineer precise control over particle size. This single variable is the foundation for achieving consistent, high-quality results and unlocking the full potential of ceramic materials.
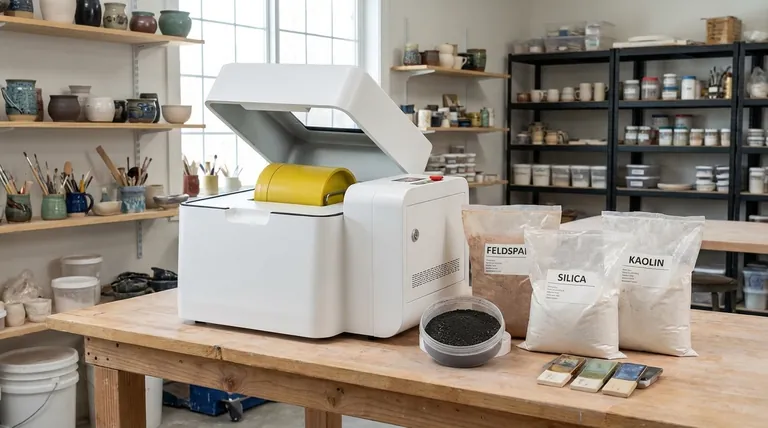

The Two Primary Functions of a Ball Mill
A ball mill is not just a mixer; it is a processing machine that fundamentally changes the physical properties of your ingredients. Its utility comes from performing two critical jobs far more effectively than any manual method.
Particle Size Reduction (Grinding)
The most fundamental use of a ball mill is to take coarse, gritty, or crystalline raw materials and reduce them to a micro-fine, uniform powder. This process is known as comminution.
Materials like feldspar, silica, and various minerals are often supplied in granular forms. By tumbling them for hours with hard grinding media (such as high-alumina porcelain or zirconia balls), the mill pulverizes these particles through impact and attrition.
This dramatic increase in surface area is critical for how the material behaves in a glaze or clay body, enabling it to melt more completely and interact more readily with other ingredients.
Homogeneous Mixing and Dispersion
The second key function is creating a perfectly uniform slurry. While a whisk or drill mixer can combine ingredients, a ball mill achieves a level of molecular mixing that is impossible by hand.
As the jar rotates, the grinding media continuously shears and blends the suspension. This action breaks down any agglomerated clumps of material and ensures every particle is evenly dispersed throughout the liquid.
This process is essential for creating stable suspensions that don't settle out quickly, preventing issues like color streaking in glazes or inconsistent properties in a castable clay body.
How Ball Milling Transforms Ceramic Materials
Understanding the "what" is simple, but the "why" reveals the tool's true power. Ball milling is the step that separates commercial-grade material refinement from standard studio practice.
Achieving Glaze Perfection
Most glaze defects, such as pinholing, crawling, and rough surfaces, can be traced back to inconsistent particle size or inadequate mixing.
Ball milling a glaze recipe creates an incredibly fine and uniform particle distribution. This allows the glaze to melt more smoothly and at a lower effective temperature, resulting in a more durable, glassy, and professional surface. It is the key to creating crystal-clear glazes and vibrant, un-speckled colors.
Refining and Creating Clay Bodies
While less common for hobbyists, ball milling is used to create custom clay bodies with specific properties. It can be used to grind grog to a precise size or to ensure plasticizers and other additives are perfectly integrated.
For slip-casting, ball milling is essential for producing a fluid, stable, and completely homogeneous slip that results in flawless casts.
Processing Raw and Found Materials
For the ceramicist interested in creating their own unique materials, a ball mill is indispensable. It is the only practical way to process foraged rocks, wood ashes, and local clays into usable, refined ingredients for custom glazes and bodies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a ball mill is a significant piece of equipment that comes with practical considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
The Time Commitment
Ball milling is not a fast process. Grinding hard raw materials can take 12, 24, or even more hours of continuous operation. Mixing a glaze slurry may still take several hours to achieve perfect homogeneity.
The Noise Factor
Ball mills are loud. The constant tumbling of ceramic media inside a jar creates a significant amount of noise, requiring a dedicated space like a garage, basement, or outbuilding where it will not be a disturbance.
Contamination Risk
The grinding media and the jar itself wear down over time. This wear introduces a small amount of material from the media (e.g., alumina from porcelain balls) into your batch. For most applications this is negligible, but for high-purity materials science, it is a critical variable to manage.
Cost and Maintenance
Ball mills and the associated high-quality grinding media are a financial investment. They are durable machines but represent a step up in studio infrastructure beyond the basics. Jars and lids require regular cleaning and inspection.
Is a Ball Mill Right for Your Studio?
Choosing to integrate a ball mill depends entirely on your ceramic goals. It is a tool that solves specific problems related to material quality and consistency.
- If your primary focus is professional glaze quality and repeatability: A ball mill is an invaluable asset for eliminating defects and ensuring your results are consistent from batch to batch.
- If your primary focus is experimenting with raw materials: It is an essential tool for processing foraged rocks, ashes, and local clays into usable ingredients for truly unique work.
- If your primary focus is slip-casting: A ball mill is the standard for producing high-quality, stable slips that yield excellent results.
- If you are a hobbyist using pre-mixed commercial glazes and clays: You do not need a ball mill, as the manufacturer has already performed this processing for you.
Ultimately, a ball mill is a tool that transitions you from a user of ceramic materials to a creator and refiner of them.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Creates micro-fine powders for smooth melting | Grinding feldspar, silica, minerals |
| Homogeneous Mixing | Prevents defects like pinholing and streaking | Preparing glaze slurries, clay body slips |
| Raw Material Processing | Turns foraged rocks/ashes into usable ingredients | Creating custom glazes and unique clay bodies |
Ready to elevate your ceramic work with professional-grade material consistency?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment that serious ceramic artists and studios rely on. A ball mill is the key to unlocking the full potential of your materials, ensuring your glazes are flawless and your clay bodies are perfectly homogeneous.
Our high-quality ball mills and durable grinding media are designed for the demanding needs of laboratory and studio environments, helping you achieve the repeatable, high-quality results you demand.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect ball milling solution for your ceramic studio.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results



















