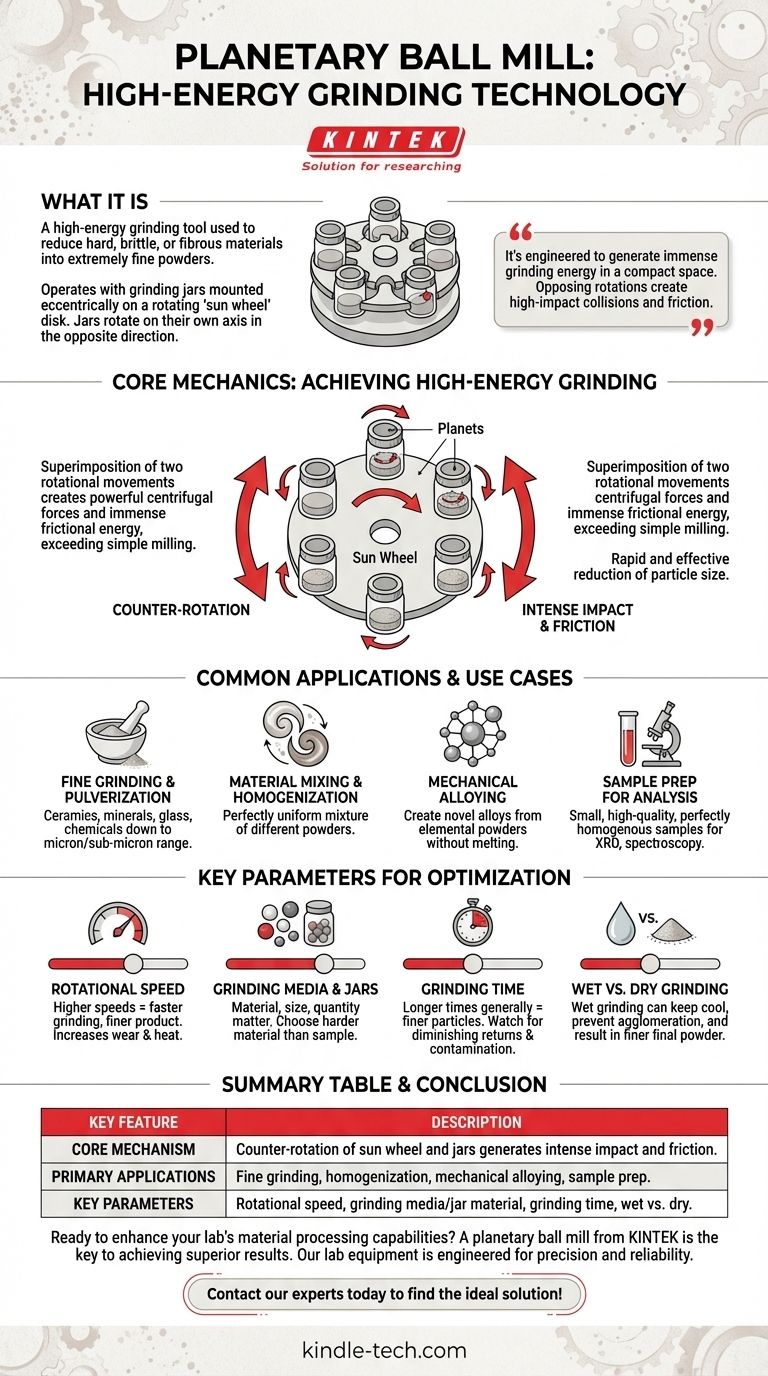
At its core, a planetary ball mill is a high-energy grinding tool used to reduce hard, brittle, or fibrous materials into extremely fine powders. It operates using grinding jars mounted eccentrically on a rotating disk, called a "sun wheel." The critical design feature is that the jars rotate on their own axis in the opposite direction of the sun wheel's rotation, creating a unique and powerful grinding effect.
The planetary ball mill's design is not arbitrary; it's engineered to generate immense grinding energy in a compact space. The opposing rotations create a combination of high-impact collisions and friction, far exceeding the energy levels of simpler milling methods.

The Core Mechanics: How It Achieves High-Energy Grinding
To understand why a planetary mill is so effective, we need to look at the forces it generates. The entire process is a result of its unique dual-rotation system.
The "Sun Wheel" and "Planets"
The central component is the main rotating disk, or sun wheel.
Mounted on this wheel are one or more grinding jars, which act as the planets. These jars contain the material to be ground along with the grinding media, which are typically hardened balls.
The Power of Counter-Rotation
The defining feature is the superimposition of two rotational movements. The sun wheel rotates in one direction, while the grinding jars rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction.
This counter-rotation is the key to the mill's high efficiency.
Generating Intense Grinding Forces
This complex movement subjects the grinding media and sample material to two primary forces. First, powerful centrifugal forces cause the balls and material to be thrown against the inner wall of the jar at high speed.
Simultaneously, the counter-rotation causes the balls to cascade and rub against each other and the jar wall with immense frictional energy. This combination of intense impact and friction is what enables the rapid and effective reduction of particle size.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The high energy input makes planetary ball mills versatile tools for a range of demanding applications, particularly in laboratory settings for preparing small quantities of material.
Fine Grinding and Pulverization
This is the most common use. They excel at grinding materials down to the micron or even sub-micron range, which is often difficult or impossible with other methods. This is ideal for ceramics, minerals, glass, and chemicals.
Material Mixing and Homogenization
The intense motion is extremely effective for creating a perfectly uniform mixture of different powders. The constant tumbling and collisions ensure that all particles are thoroughly distributed.
Mechanical Alloying
In materials science, the high kinetic energy can be used for mechanical alloying. The repeated impact and cold-welding of powder particles can be used to create novel alloys from elemental powders without melting them.
Sample Preparation for Analysis
For analytical techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD) or spectroscopy, a perfectly homogenous and fine powder sample is essential. The planetary mill is an ideal tool for preparing these small, high-quality samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
Achieving the desired result depends on controlling several key variables. The process is not one-size-fits-all.
Rotational Speed
Higher speeds impart more energy into the system, leading to faster grinding and a finer end product. However, this also increases wear on the grinding jars and balls, and can generate significant heat.
Grinding Media and Jars
The material, size, and quantity of the grinding balls are critical. The ball material (e.g., hardened steel, zirconia, agate) must be harder than the sample to be effective and should be chosen to minimize sample contamination.
Grinding Time
Longer grinding times generally result in finer particles. However, there is a point of diminishing returns where milling for longer does not significantly reduce particle size and may even introduce unwanted effects from excess heat or contamination.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Grinding can be done dry or wet by adding a liquid (like water or ethanol). Wet grinding can help keep the sample cool, prevent particles from clumping together (agglomerating), and often results in a finer final powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates how you should approach the milling process.
- If your primary focus is maximum particle fineness: Utilize high rotational speeds, smaller grinding media to increase impact frequency, and consider wet grinding to prevent agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample contamination: Carefully match the material of your grinding jar and balls to your sample. For sensitive materials, use inert options like zirconia or agate instead of steel.
- If your primary focus is rapid mixing or homogenization: Use larger balls to promote greater tumbling action within the jar and ensure the jar is not overfilled, allowing room for the material to move freely.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively leverage the planetary ball mill as a powerful tool for your material processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Counter-rotation of sun wheel and grinding jars generates intense impact and friction. |
| Primary Applications | Fine grinding, homogenization, mechanical alloying, and sample preparation for analysis. |
| Key Parameters | Rotational speed, grinding media/jar material, grinding time, and wet vs. dry grinding. |
Ready to enhance your lab's material processing capabilities?
A planetary ball mill from KINTEK is the key to achieving superior fine grinding, perfect homogenization, and advanced mechanical alloying for your research and development. Our lab equipment is engineered for precision, reliability, and to meet the demanding needs of laboratories like yours.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal planetary ball mill solution for your specific materials and goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Ni-Co-Al Superalloy Powders
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis
- What is the primary function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Nickel Nanoparticles
- What role does a high-energy planetary ball mill play in Mo-La2O3 alloying? Achieve Superior Microstructure Control
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?



















