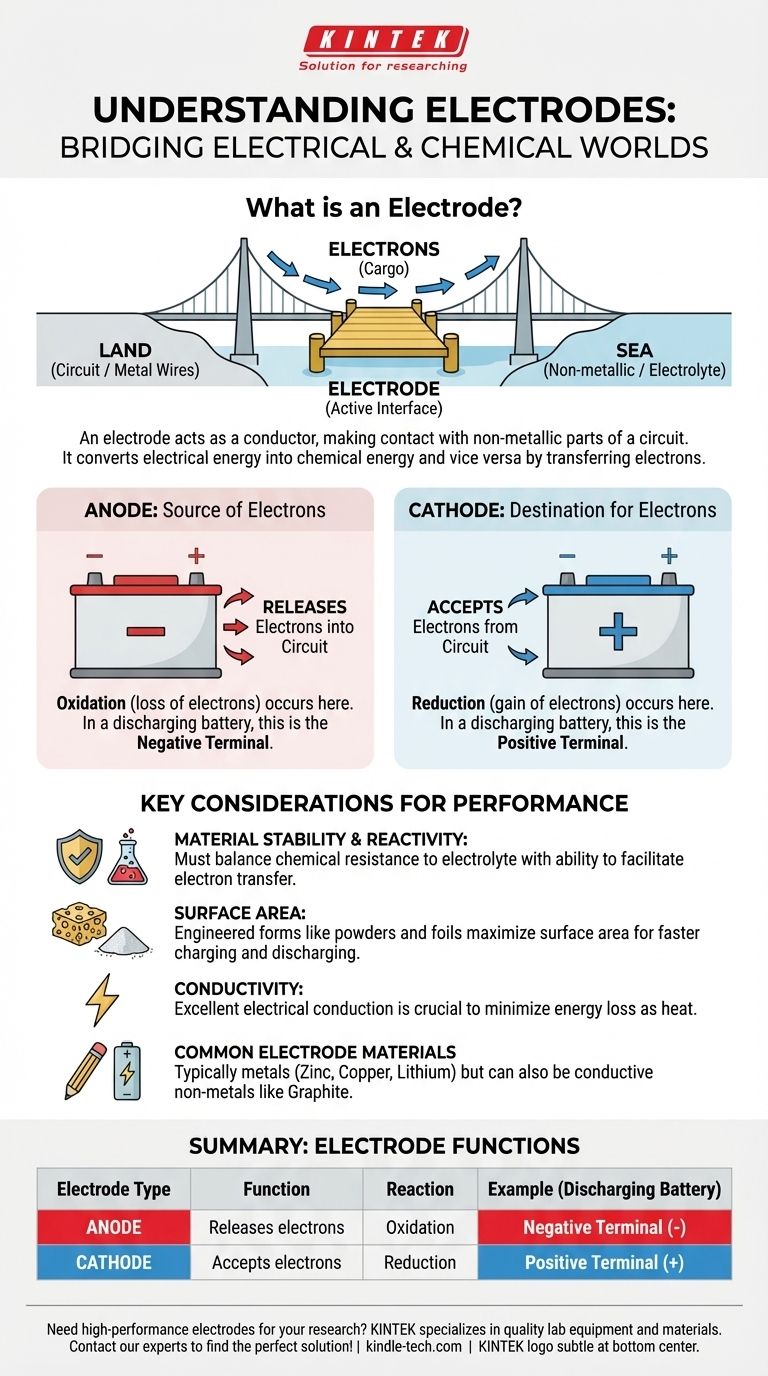
At its core, an electrode is a bridge. It is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a non-metallic part of a circuit, allowing current to flow between them. For example, the positive and negative terminals of any battery are the external connection points for two internal electrodes submerged in a chemical solution.
An electrode's essential job is not just to conduct electricity, but to serve as the physical interface where electrical energy is converted into chemical energy (and vice versa) by either releasing or accepting electrons.

The Fundamental Role of an Electrode
An electrode’s primary function is to solve a fundamental problem: how to get electricity to flow through a material that isn't a simple metal wire.
Bridging Two Worlds
Think of an electrode as a specialized dock. The metal wires in a circuit are the "land," and a non-metallic substance like a liquid electrolyte in a battery is the "sea." The electrode is the dock where electrons (the "cargo") are transferred between the land and the sea.
These non-metallic substances can include electrolytes (in batteries), semiconductors (in transistors), gases (in neon signs), or even a vacuum (in old vacuum tubes).
A Site for Chemical Reactions
In many applications, especially batteries, electrodes are not passive conductors. They are active participants in chemical reactions.
The surface of an electrode is where oxidation (the loss of electrons) or reduction (the gain of electrons) takes place. This controlled chemical reaction is what allows a battery to store and release energy.
Common Electrode Materials
While typically made of metals like zinc, copper, or lithium, electrodes are not exclusively metallic. Any good electrical conductor can serve.
For instance, graphite (a form of carbon) is a very common electrode material used in batteries and industrial electrolysis because it is an excellent conductor and is chemically stable.
Anodes and Cathodes: The Two Key Types
In any system with two electrodes, they are given specific names based on the chemical reaction that occurs on their surface. These labels are crucial for understanding how electrochemical cells work.
The Anode: The Source of Electrons
The anode is defined as the electrode where oxidation occurs. In simple terms, it is the electrode that releases electrons into the circuit.
In a battery that is powering a device (discharging), the anode is the negative terminal.
The Cathode: The Destination for Electrons
The cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs. It is the electrode that accepts electrons coming from the circuit.
In a battery that is discharging, the cathode is the positive terminal.
Understanding the Key Considerations
Choosing an electrode material is a critical design decision that involves balancing several competing factors.
Material Stability and Reactivity
An electrode must be chemically stable enough to survive its environment, which is often a corrosive electrolyte. If it degrades too quickly, the device will fail.
At the same time, it must be reactive enough to facilitate the desired electron transfer. This balance between stability and reactivity is key to performance.
Surface Area and Performance
The rate of a chemical reaction is often limited by the available surface area. Because of this, many modern electrodes are not solid blocks of metal.
Instead, they are engineered from powders, foils, or foams to create a massive surface area in a small volume. This increases the device's power output, allowing it to charge and discharge more quickly.
Conductivity is Non-Negotiable
Above all, the material must be an excellent electrical conductor. Any resistance in the electrode itself wastes energy as heat, reducing the overall efficiency of the device.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The terms anode and cathode are tied to the direction of electron flow, so their physical location depends on the context.
- If you are looking at a battery: The positive (+) terminal is the external connection for the cathode, and the negative (-) terminal is the connection for theanode.
- If you are studying electrolysis (using electricity to drive a reaction): The electrode connected to the positive side of the power supply is the anode, and the one connected to the negative side is the cathode.
- If you are working with a semiconductor device: The electrodes are the named metal contacts (e.g., source, drain, gate) that allow you to control the flow of current through the silicon.
Understanding the role of an electrode is the first step to mastering how modern technology stores, releases, and controls electrical energy.
Summary Table:
| Electrode Type | Function | Reaction | Example (Discharging Battery) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anode | Releases electrons into the circuit | Oxidation (loss of electrons) | Negative Terminal (-) |
| Cathode | Accepts electrons from the circuit | Reduction (gain of electrons) | Positive Terminal (+) |
Need high-performance electrodes or lab equipment for your research? Choosing the right electrode material is critical for the efficiency and longevity of your devices. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including stable and conductive electrode materials, to power your innovations. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- How should carbon cloth used for high-temperature electrolysis be handled after operation? Prevent Irreversible Oxidative Damage
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What are 3 products that carbon nanotubes can be used in? Enhancing Batteries, Tires, and Composites
- What are the material properties of carbon paper? Unlocking High Conductivity & Porosity for Your Lab
- Why are high surface area materials preferred for BES anodes? Maximize Microbial Power and Efficiency



















