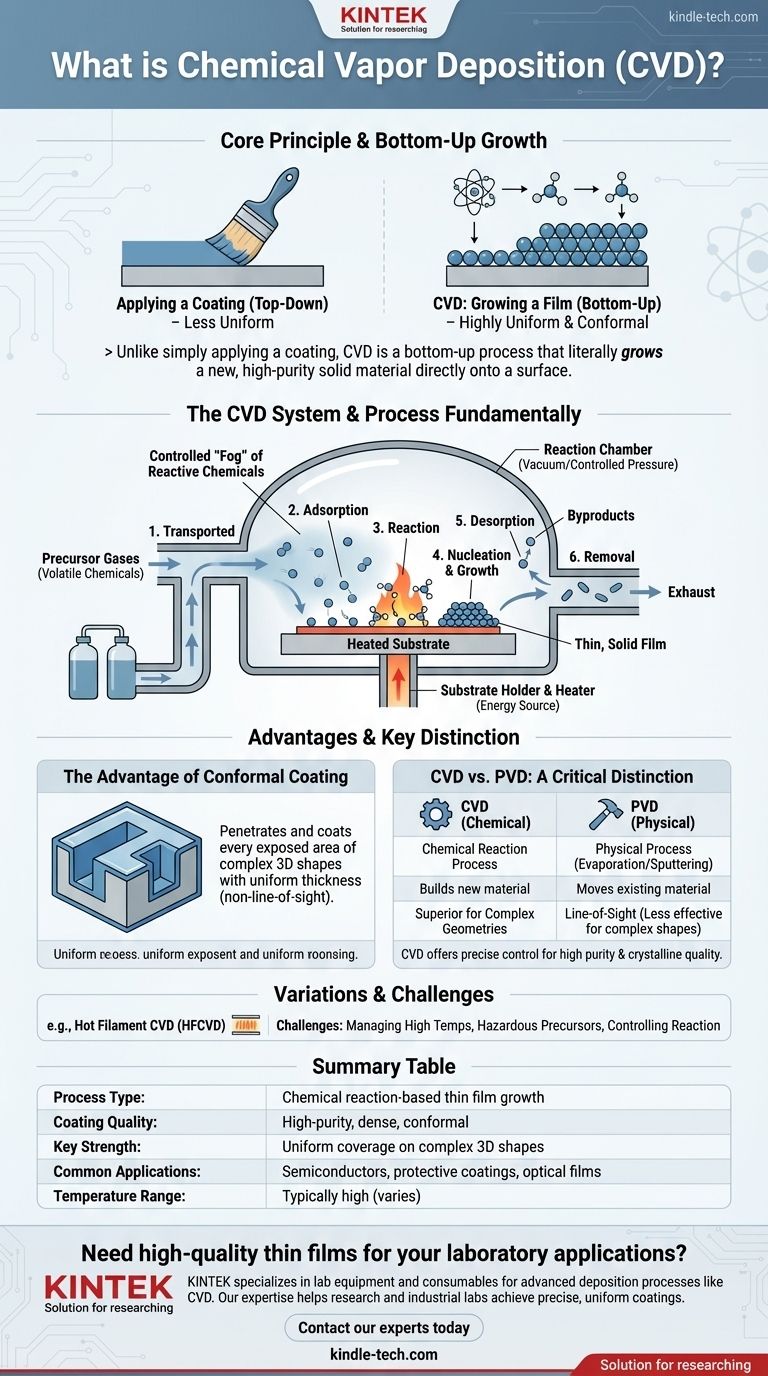
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly controlled manufacturing process used to create thin, solid films on the surface of a workpiece, known as a substrate. It achieves this by introducing precursor gases into a reaction chamber, which then undergo a chemical reaction at or near the substrate's surface, depositing a new, solid layer that chemically bonds to it.
Unlike simply applying a coating, CVD is a bottom-up process that literally grows a new, high-purity solid material directly onto a surface. This allows it to create exceptionally uniform and dense films that conform perfectly to even the most complex shapes.

How CVD Fundamentally Works
The core principle of CVD is transforming a gas into a solid through a chemical reaction. Think of it as a precisely controlled "fog" of reactive chemicals that solidifies only when it touches the target surface.
The Key Components of a CVD System
A typical CVD setup consists of several critical parts:
- Reaction Chamber: An enclosed, sealed environment (often under vacuum) where the deposition takes place. The vacuum removes contaminants and allows for precise control of pressure.
- Precursor Gases: These are volatile chemical compounds that contain the atoms needed for the final film. They are injected into the chamber in a gaseous state.
- Substrate: This is the workpiece or material onto which the thin film will be grown. It is heated to a specific temperature to drive the chemical reaction.
- Energy Source: Heat is the most common energy source, used to raise the substrate and/or chamber temperature to the point where the precursor gases react or decompose.
The Step-by-Step Deposition Process
While the specifics vary, the process generally follows a sequence of well-defined physical and chemical steps:
- Transport: The precursor gases are transported into the reaction chamber and flow towards the substrate.
- Adsorption: The gas molecules land on and stick to the heated substrate surface.
- Reaction: Driven by the high temperature, the adsorbed molecules undergo chemical reactions. This can be decomposition (breaking down) or reaction with other gases.
- Nucleation and Growth: The solid products of the reaction begin to form stable clusters (nucleation) on the surface, which then grow into a continuous film.
- Desorption: Gaseous byproducts from the reaction are released from the surface.
- Removal: These byproduct gases are transported away from the substrate and exhausted from the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
CVD is a powerful and versatile technology, but it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its advantages and disadvantages is key to its proper application.
The Advantage of Conformal Coating
The defining strength of CVD is its ability to produce conformal coatings. Because the precursor is a gas, it can penetrate and coat every exposed area of a complex, three-dimensional object with a uniform thickness. This is extremely difficult to achieve with line-of-sight methods.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The primary challenge in CVD is managing the high temperatures required, which can damage sensitive substrates. The precursor chemicals can also be hazardous and expensive, and controlling the reaction to avoid unwanted gas-phase particle formation is a constant technical challenge.
Key CVD Variations
The term CVD covers a family of related techniques. For example, Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) uses a heated wire made of a material like tungsten to thermally break down the precursor gases above the substrate. This allows for dissociation at lower substrate temperatures but introduces the risk of filament degradation over time.
CVD vs. PVD: A Critical Distinction
Another common thin-film method is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The fundamental difference is chemical versus physical action.
- CVD is a chemical process: It builds a new material via reaction.
- PVD is a physical process: It moves an existing material from a source (target) to the substrate via evaporation or sputtering. It is a line-of-sight process, making it less effective for coating complex geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right deposition technique depends entirely on your project's specific goals and constraints.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight surfaces: CVD is the superior choice due to the penetrating nature of its gas-phase precursors.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film purity and crystalline quality: The precise control over chemical reactions in CVD offers unparalleled results for materials like semiconductors.
- If your primary focus is speed, or if your substrate is temperature-sensitive: You should evaluate if PVD or another lower-temperature deposition method is a more suitable alternative.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of CVD empowers you to select the right tool for building functional materials from the molecule up.
Summary Table:
| CVD Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction-based thin film growth |
| Coating Quality | High-purity, dense, and conformal |
| Key Strength | Uniform coverage on complex 3D shapes |
| Common Applications | Semiconductors, protective coatings, optical films |
| Temperature Range | Typically high (varies by method) |
Need high-quality thin films for your laboratory applications? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced deposition processes like CVD. Our expertise helps research and industrial labs achieve precise, uniform coatings for semiconductors, electronics, and material science projects. Contact our experts today to discuss how our CVD solutions can enhance your research and manufacturing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















