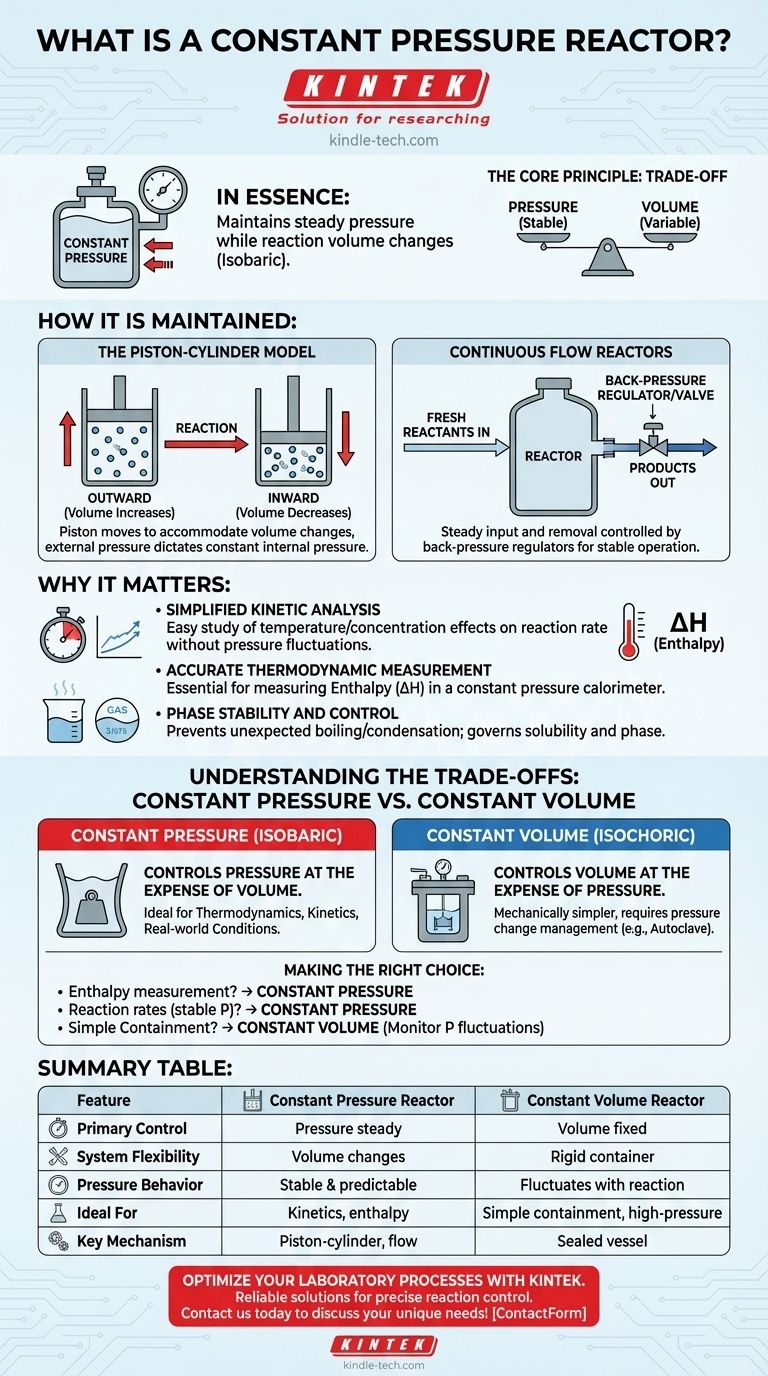
In essence, a constant pressure reactor is a system designed to maintain a steady, unchanging pressure while a chemical reaction occurs within it. Also known as an isobaric reactor, its primary characteristic is that it allows the volume of the system to change in order to keep the internal pressure constant, even if the reaction produces or consumes gas.
The core principle to grasp is the trade-off between pressure and volume. Unlike a sealed, rigid container where pressure builds up (constant volume), a constant pressure reactor sacrifices a fixed volume to achieve a stable, predictable pressure environment.
How Constant Pressure is Maintained
The mechanism for maintaining constant pressure can be physical or operational, depending on the scale and type of the reactor.
The Piston-Cylinder Model
For conceptual understanding, the simplest model is a gas-phase reaction occurring in a cylinder sealed by a frictionless, movable piston.
As the reaction proceeds, if the number of gas molecules increases, the piston moves outward. This increases the system's volume, preventing a rise in pressure.
Conversely, if gas molecules are consumed, the piston moves inward, decreasing the volume to prevent a pressure drop. The external pressure on the piston dictates the constant internal pressure.
Continuous Flow Reactors
In many industrial settings, large-scale reactors operating in a continuous flow mode approximate constant pressure conditions.
Fresh reactants are continuously fed in and products are removed at a steady rate. The system is controlled by back-pressure regulators and valves that ensure the overall operating pressure remains stable.
Why Constant Pressure Matters
Maintaining constant pressure isn't just an operational choice; it's fundamental to understanding and controlling chemical reactions for several key reasons.
For Simplified Kinetic Analysis
The rate of many chemical reactions depends on the concentration (or partial pressure) of the reactants.
By holding the total pressure constant, it becomes much easier to study how changes in temperature or reactant concentration independently affect the reaction rate without the complicating factor of a fluctuating pressure.
For Accurate Thermodynamic Measurement
Key thermodynamic quantities, most notably enthalpy (ΔH), are defined under constant pressure conditions. Enthalpy represents the heat absorbed or released by a reaction.
Running a reaction in a constant pressure calorimeter allows for the direct measurement of this crucial value, which is essential for process design and safety analysis.
For Phase Stability and Control
In reactions involving multiple phases (e.g., gas-liquid), pressure is a critical variable that governs solubility and boiling points.
Maintaining a constant pressure ensures that materials remain in their desired phase, preventing unexpected boiling or condensation that could disrupt the reaction or create a safety hazard.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Constant Pressure vs. Constant Volume
The choice of reactor conditions creates a fundamental trade-off. It is critical to distinguish a constant pressure system from its opposite.
Constant Volume Reactors (Isochoric)
A constant volume reactor is a rigid, sealed container, like a bomb calorimeter or a simple sealed autoclave. Here, the volume cannot change.
If a reaction inside this sealed vessel produces gas, the pressure will increase, sometimes dramatically. If gas is consumed, the pressure will drop.
While structurally simple, the changing pressure during the reaction complicates the analysis of reaction kinetics and thermodynamics. The "high pressure autoclave" mentioned in some contexts for sterilization is typically a constant volume system where pressure and temperature rise together.
The Key Distinction
The choice depends entirely on what you need to control.
A constant pressure (isobaric) system controls pressure at the expense of volume. It is ideal for studying thermodynamics and kinetics under real-world atmospheric or industrial conditions.
A constant volume (isochoric) system controls volume at the expense of pressure. It is mechanically simpler but requires careful management and analysis of pressure changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct experimental or industrial setup, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is measuring the heat of reaction (enthalpy): A constant pressure (isobaric) system is the standard and correct choice.
- If your primary focus is studying reaction rates without pressure as a variable: A constant pressure reactor simplifies your analysis by providing a stable environment.
- If your primary focus is simply containing a reaction in a strong, sealed vessel: You are using a constant volume system and must be prepared to monitor and account for pressure fluctuations.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between constant pressure and constant volume systems allows you to control your experiment, rather than letting it control you.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Constant Pressure Reactor | Constant Volume Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Control | Pressure remains steady | Volume remains fixed |
| System Flexibility | Volume changes to maintain pressure | Rigid, sealed container |
| Pressure Behavior | Stable and predictable | Fluctuates with reaction |
| Ideal For | Kinetic studies, enthalpy measurement | Simple containment, high-pressure processes |
| Key Mechanism | Piston-cylinder or continuous flow | Sealed vessel (e.g., autoclave) |
Optimize your laboratory processes with the right reactor setup. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for precise reaction control. Whether you need constant pressure systems for accurate thermodynamic measurements or robust constant volume reactors for high-pressure applications, our expertise ensures safety, efficiency, and reproducible results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's unique needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- Does a batch reactor have constant volume? Understanding Volume, Pressure, and Reactor Design
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined high-pressure reactor? Enhance Your Perovskite Oxide Synthesis
- How do you remove heat from a bioreactor? Master Temperature Control for Stable Bioprocessing
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in CFRP recycling? Unlocking Efficient Carbon Fiber Recovery
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What are the different types of pyrolysis equipment? Choose the Right Reactor for Your Process
- How does rapid decompression in AFEX affect biomass quality? Unlock Maximum Surface Area for Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- Why must a high-pressure reactor be used for the hydrogenolysis of cellulose? Optimize Sorbitol Yield Safely



















