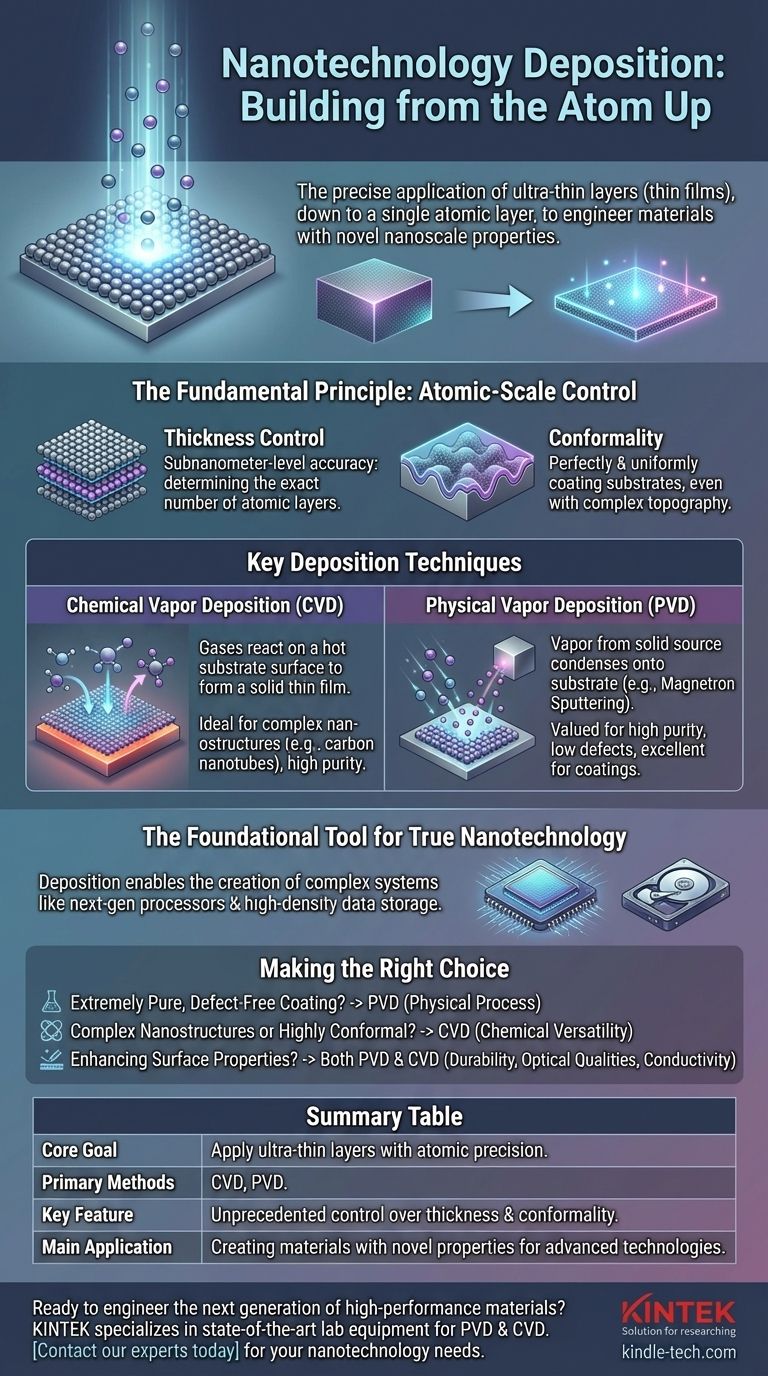
In the context of nanotechnology, deposition is the process of precisely applying an ultra-thin layer of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. These layers, or thin films, can be as thin as a single layer of atoms, allowing engineers to build materials from the ground up and endow them with entirely new properties.
Deposition moves beyond simply coating a surface; it is a foundational technique for engineering material properties at the atomic level. By controlling the exact placement of atoms and molecules, we can create high-performance materials that are impossible to produce using conventional bulk methods.

The Fundamental Principle: Building From the Atom Up
At its core, nanotechnology deposition is about control. Unlike traditional coating methods like painting or electroplating, which apply thick, often imprecise layers, nano-deposition techniques are designed for atomic-scale precision.
From Bulk Material to Nanoscale Properties
The primary reason deposition is so critical is that materials behave differently at the nanoscale. A bulk material's properties (like color, conductivity, or strength) can change dramatically when it is structured as a thin film.
Deposition allows us to access and exploit these unique nanoscale properties. We can make a material more durable, scratch-resistant, transparent, or electrically conductive simply by structuring it as a precisely controlled thin film.
The Importance of the Substrate
The substrate is the base material or object onto which the thin film is deposited. It serves as the foundation for the new material being built. The interaction between the film and the substrate is critical to the final product's performance.
Achieving Unprecedented Control
Two concepts are central to the power of nanodeposition: thickness control and conformality.
Thickness control, often with subnanometer-level accuracy, means engineers can determine the exact number of atomic layers in the film. Conformality refers to the film's ability to perfectly and uniformly coat a substrate, even one with a complex, non-flat surface topography.
Key Deposition Techniques
Different methods are used to achieve deposition, each suited for different materials and outcomes. The two main families are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, precursor gases are introduced into a chamber where they react on the surface of the hot substrate. This chemical reaction forms a solid thin film on the substrate's surface.
This method is highly versatile and is capable of producing very pure, high-performance films, including complex nanostructures like carbon nanotubes.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD techniques work by creating a vapor from a solid source material through physical means, which then condenses onto the substrate.
One common PVD method is magnetron sputtering. In this process, a target of the source material is bombarded with energized ions, which ejects atoms that then travel and deposit onto the substrate. This method is valued for creating films with high purity and a low level of defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Thin Films vs. True Nanotechnology
A nuanced debate exists within the field regarding deposition. Is the creation of a simple thin film truly considered "nanotechnology"?
The Core of the Debate
Some argue that if a thin film merely exhibits smaller-scale versions of its bulk properties, it doesn't represent true nanotechnology. The "true" goal, they contend, is the creation of complex devices and structures with novel functions, like nanomachines or intricate circuits.
The Reality: A Foundational Tool
While a simple film may not be a nanomachine, deposition techniques are the foundational tools that enable the creation of true nanotechnologies. They are the essential first step.
Without the ability to lay down atomically precise layers, it would be impossible to build the more complex systems that define the cutting edge of the field, such as next-generation processors and high-density data storage systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The deposition method you choose depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material or device.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely pure, defect-free coating: PVD methods like magnetron sputtering are an excellent choice for their clean and controlled physical process.
- If your primary focus is growing complex nanostructures or highly conformal layers: CVD offers the chemical versatility to build structures like carbon nanotubes from gaseous precursors.
- If your primary focus is enhancing a bulk material's surface properties: Both PVD and CVD are powerful tools for adding durability, new optical qualities, or conductivity to a substrate.
Ultimately, deposition is the critical bridge that translates the science of the nanoscale into tangible, high-performance technologies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Goal | Apply ultra-thin layers of material with atomic-scale precision. |
| Primary Methods | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). |
| Key Feature | Unprecedented control over thickness and conformality. |
| Main Application | Creating materials with novel properties for advanced technologies. |
Ready to engineer the next generation of high-performance materials?
The precise control of nanoscale deposition is key to developing advanced electronics, durable coatings, and innovative optical devices. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment and consumables for your deposition needs, whether you're exploring new materials or scaling up production.
Our expertise in PVD and CVD systems can help you achieve the atomic-level precision your research demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's nanotechnology goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















