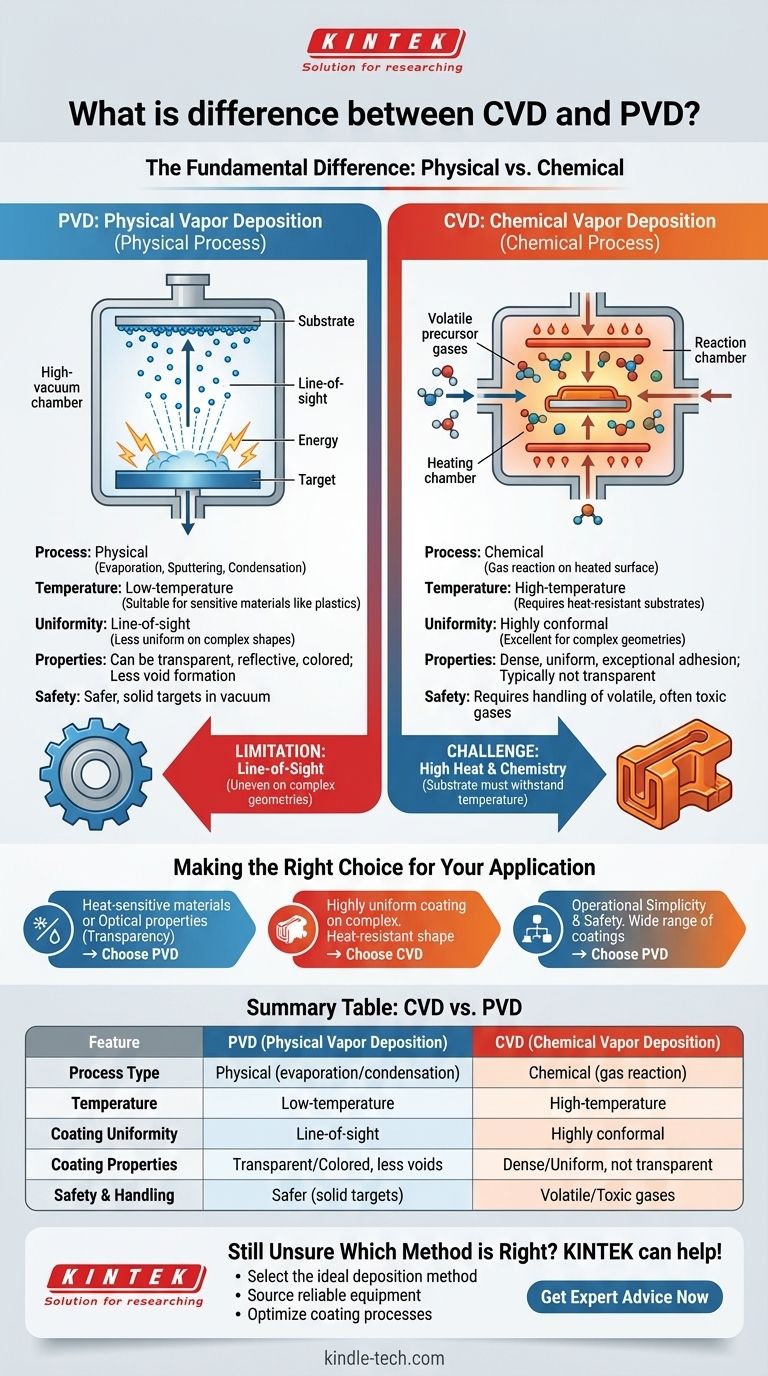
The fundamental difference between Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) lies in how the coating material reaches the target surface. PVD is a physical process, often involving the evaporation of a solid material in a vacuum, which then condenses onto the substrate. In contrast, CVD is a chemical process where precursor gases react on the substrate's surface to form the desired film.
While both CVD and PVD create thin-film coatings at the atomic level, the choice between them comes down to a simple trade-off. PVD's physical process is lower-temperature and more versatile for sensitive materials, while CVD's chemical process excels at creating highly uniform coatings on complex shapes, provided the substrate can withstand the heat.
The Core Process: Physical vs. Chemical
The names themselves reveal the primary distinction. One method relies on the physics of phase changes (solid to gas to solid), while the other relies on controlled chemical reactions.
How PVD Works (A Physical Process)
Physical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally a "line-of-sight" technique.
In a high-vacuum chamber, a solid source material (the "target") is bombarded with energy, causing it to vaporize or sublimate directly into a gas.
These gaseous atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum and condense onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin, solid film. Think of it as a highly controlled atomic spray-painting process.
How CVD Works (A Chemical Process)
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process of "building" a coating through surface chemistry.
Volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber containing the substrate, which is typically heated to high temperatures.
The heat energizes the gases, causing them to react or decompose on the substrate's surface, leaving behind a solid film of the desired material. This method "grows" the coating uniformly across all exposed surfaces.
Key Differentiating Factors
This core difference in process—physical versus chemical—leads to critical distinctions in application, temperature, and final coating properties.
Operating Temperature and Substrate Sensitivity
PVD is a low-temperature process. Because it doesn't rely on heat to drive a chemical reaction, it can be used to coat heat-sensitive materials like plastics or certain alloys without damaging them.
CVD typically requires very high temperatures (often several hundred degrees Celsius) to initiate and sustain the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate surface. This limits its use to materials that can withstand significant thermal stress.
Coating Properties and Adhesion
PVD coatings often exhibit less void formation and can be engineered for specific optical properties, including transparency, reflectivity, and color.
CVD coatings, because they are grown via a chemical reaction, are exceptionally conformal, meaning they can coat complex shapes and internal surfaces with excellent uniformity. However, they are typically not transparent.
Material Handling and Safety
PVD is a mechanically simpler and safer process. It involves a solid source material in a vacuum, eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals.
CVD relies on volatile, and often toxic or corrosive, precursor gases. This requires more complex equipment and stringent safety protocols for handling and disposal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the optimal choice is dictated entirely by the constraints of your project and the desired outcome.
The Limitation of PVD: Line-of-Sight
The primary drawback of PVD is its line-of-sight nature. Just like spray paint, it struggles to uniformly coat intricate geometries or the inside of deep holes. Areas not directly facing the source material will receive a much thinner coating, if any at all.
The Challenge of CVD: Heat and Chemistry
The high temperatures required for CVD can be its biggest limitation, immediately disqualifying any substrate that cannot withstand the heat without deforming or degrading. Furthermore, the compatibility between the precursor gases and the substrate material is critical to ensure proper film growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by your substrate material, the geometry of the part being coated, and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials or achieving specific optical properties (like transparency): PVD is the definitive choice due to its lower operating temperatures and material versatility.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform, dense coating on a complex shape that can withstand high heat: CVD is the ideal method, as its chemical reaction process ensures all surfaces are coated evenly.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity, safety, and a wide range of metal or ceramic coatings: PVD offers a more straightforward and less hazardous pathway to producing high-quality films.
Ultimately, understanding the core mechanism—physical condensation versus chemical growth—is the key to selecting the most effective deposition technology for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (evaporation/condensation) | Chemical (gas reaction) |
| Temperature | Low-temperature (suitable for heat-sensitive materials) | High-temperature (requires heat-resistant substrates) |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (less uniform on complex shapes) | Highly conformal (excellent for complex geometries) |
| Coating Properties | Can be transparent, reflective, or colored; less void formation | Dense and uniform; typically not transparent |
| Safety & Handling | Safer (solid targets, vacuum environment) | Requires handling of volatile, often toxic gases |
Still Unsure Which Deposition Method is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between CVD and PVD can be complex, but you don't have to navigate this decision alone. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance on thin-film deposition technologies.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal deposition method for your specific substrate and application requirements
- Source reliable CVD and PVD equipment that meets your research or production needs
- Optimize your coating processes for superior results and efficiency
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your project requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















