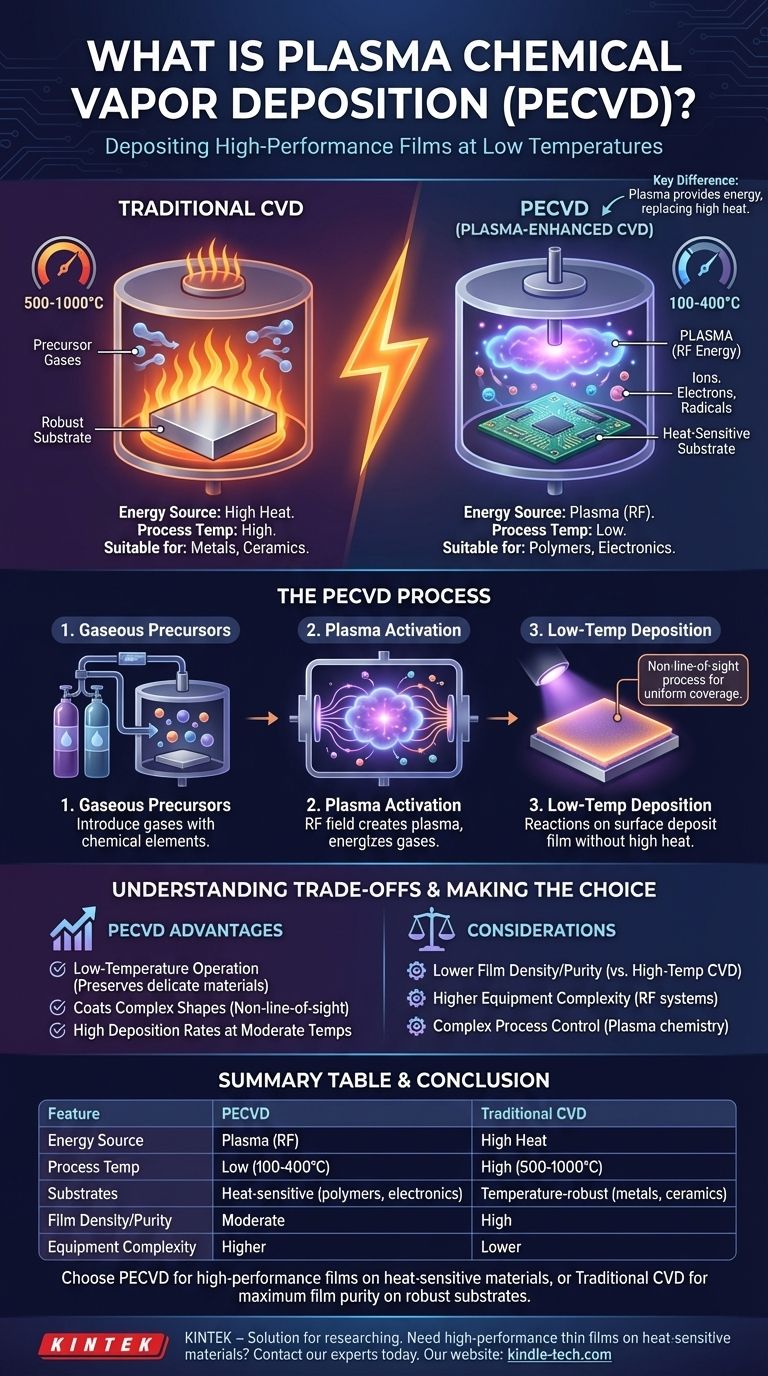
At its core, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process for depositing thin, high-performance films onto a surface. It builds upon the principles of standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) but adds a crucial element: plasma. This plasma energizes the precursor gases, allowing the chemical reactions needed for deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures than traditional methods.
The essential difference between PECVD and conventional CVD is the energy source. While standard CVD relies on high heat to drive chemical reactions, PECVD uses an electric field to create a low-temperature plasma that provides the necessary energy, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials.

The Foundation: Standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
To understand PECVD, we must first understand the process it enhances. Standard CVD is a powerful and versatile coating technology.
The Core Principle: Gaseous Precursors
The process begins by placing a part, or substrate, inside a reaction chamber. Precursor gases containing the chemical elements of the desired coating are then introduced.
The Role of Energy: Thermal Activation
In traditional CVD, this chamber is heated to extremely high temperatures. This thermal energy breaks down the precursor gases and drives a chemical reaction on the substrate's surface, depositing a solid, thin film atom by atom.
The Outcome: A High-Quality Film
Because the coating is built from a gas phase, CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. This allows it to create highly uniform and pure coatings that can completely cover complex shapes and precision surfaces. The resulting films are durable and can be engineered for properties like corrosion or abrasion resistance.
The Innovation: Adding Plasma
PECVD fundamentally alters how energy is supplied to the system, which unlocks new capabilities.
What Is Plasma?
Often called the "fourth state of matter," plasma is an ionized gas. By applying a strong electric field (typically a radio frequency or RF field) to the low-pressure gas in the chamber, its atoms are broken apart into a mix of ions, electrons, and highly reactive neutral species called radicals.
How Plasma Replaces Heat
These energetic electrons and radicals in the plasma are what drive the chemical reactions. They collide with the precursor gas molecules, breaking them down into the building blocks needed for deposition.
This process provides the activation energy for the reaction without requiring high temperatures. The bulk temperature of the substrate can remain hundreds of degrees cooler than in a traditional CVD process.
The Advantage of Lower Temperatures
This low-temperature operation is the primary reason for using PECVD. It allows for the deposition of high-quality films on materials that would be damaged or destroyed by the intense heat of conventional CVD, such as plastics, polymers, and complex integrated circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal replacement for all CVD processes. The choice involves clear trade-offs.
Film Quality and Density
Because PECVD operates at lower temperatures, the deposited atoms have less thermal energy to arrange themselves into a perfect crystal structure. This can result in films that have a lower density or incorporate more impurities (like hydrogen from the precursor gases) compared to films grown with high-temperature CVD.
Equipment Complexity
A PECVD system requires additional hardware to generate and control the plasma, including RF power supplies and impedance matching networks. This increases the complexity and potential cost of the equipment compared to a simpler thermal CVD reactor.
Process Control
Managing plasma chemistry is inherently more complex than managing a purely thermal process. The final film properties are highly sensitive to parameters like RF power, pressure, and gas flow rates, requiring precise control to ensure consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between traditional CVD and PECVD depends entirely on your substrate and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and density on a temperature-robust substrate: Traditional high-temperature CVD is often the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing a high-performance film onto a heat-sensitive material like a polymer or an assembled electronic device: PECVD is the necessary and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving high deposition rates at moderate temperatures: PECVD provides a valuable balance between processing speed and thermal budget.
Understanding the fundamental difference between thermal energy and plasma energy is the key to selecting the correct deposition technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD | Traditional CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Plasma (RF) | High Heat |
| Process Temperature | Low (100-400°C) | High (500-1000°C) |
| Suitable Substrates | Heat-sensitive (polymers, electronics) | Temperature-robust (metals, ceramics) |
| Film Density/Purity | Moderate | High |
| Equipment Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Need to deposit high-performance thin films on heat-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PECVD systems, to help you achieve precise, low-temperature coatings for polymers, electronics, and other delicate substrates. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research or production process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- What is MPCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Synthesis



















