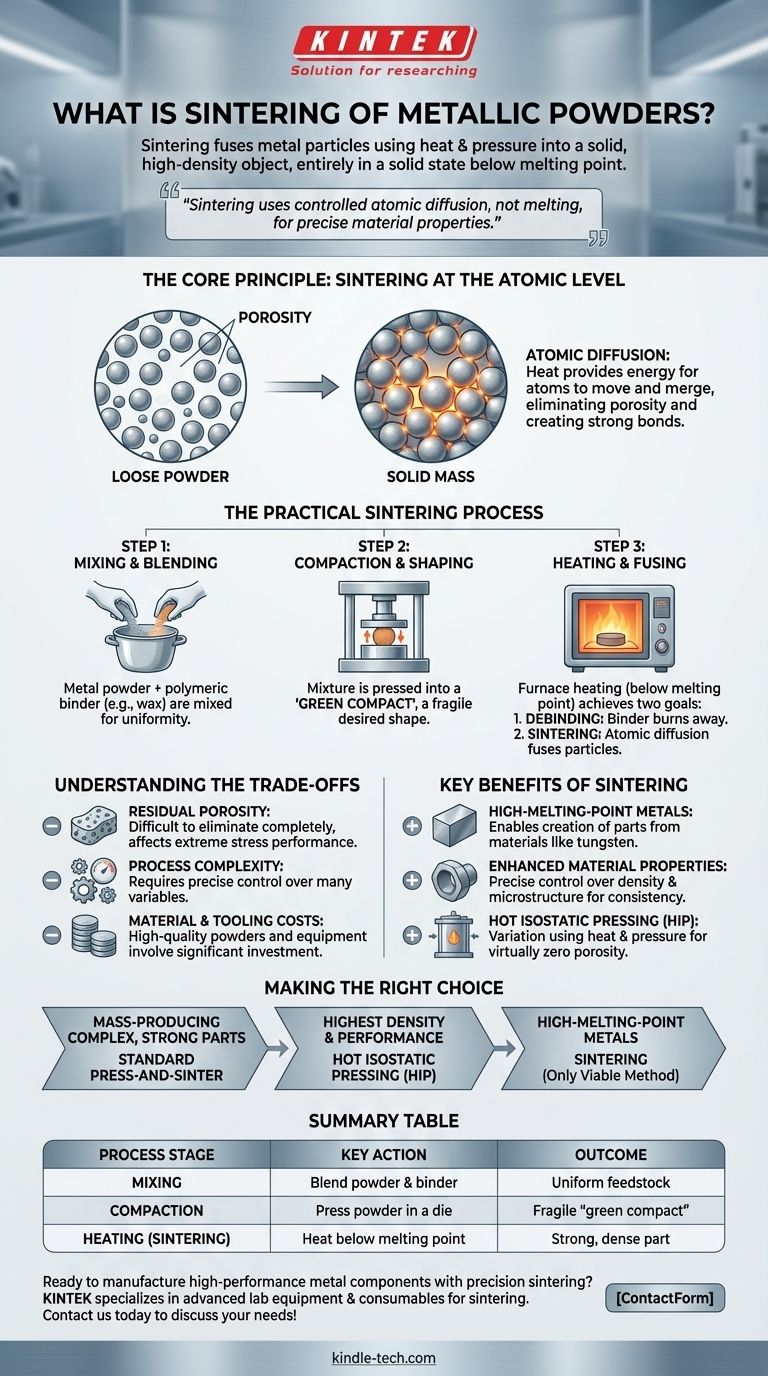
In essence, sintering of metallic powders is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to fuse metal particles into a solid, high-density object. Unlike casting or welding, this transformation occurs entirely in a solid state, well below the metal's melting point. This technique bonds the individual particles together, dramatically increasing the material's strength and structural integrity.
Sintering is not about melting metal; it's about using controlled atomic diffusion to achieve a strong, dense final product. This fundamental difference gives manufacturers precise control over material properties, enabling the creation of components with superior consistency and performance from a wide range of metals.

The Core Principle: Sintering at the Atomic Level
To understand sintering, you must first understand the fundamental mechanism that makes it possible. The process mirrors natural geological phenomena but accelerates it in a controlled industrial environment.
From Loose Powder to Solid Mass
The starting point is a collection of fine metal particles, such as aluminum, bronze, or stainless steel. In this state, the material has very low density and no structural integrity. The goal is to eliminate the empty space, or porosity, between these particles.
The Role of Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by applying heat, which provides the energy for atoms at the surfaces of the metal particles to move and migrate. This atomic diffusion causes the boundaries between individual particles to blur and eventually merge, creating strong inter-atomic bonds. The particles fuse together, forming a dense, solid piece in a process analogous to how mineral deposits form high-density ore over geological time.
The Practical Sintering Process
While atomic diffusion is the underlying science, the industrial application involves a precise, multi-step method to create a finished component.
Step 1: Mixing and Blending
The process begins by mixing the primary metal powder with other elements or a temporary polymeric binder, like paraffin wax. The mixing can be done through dry, semi-dry, or wet processes depending on the specific material requirements. This binder helps the powder hold its shape during the next stage.
Step 2: Compaction and Shaping
The prepared metal powder mixture is then poured into a die and compacted under high pressure. This can be done through methods like pressing or injection molding. The result is a fragile, preliminary part often called a "green compact" which has the desired shape but lacks strength.
Step 3: Heating and Fusing
The green compact is placed in a specialized furnace, often a vacuum or graphite furnace. It is heated in a carefully controlled atmosphere to a temperature below the metal's melting point. This stage achieves two goals:
- Debinding: The binder is cleanly burned away.
- Sintering: The high temperature activates atomic diffusion, fusing the metal particles and densifying the part into its final, solid form.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its inherent limitations is key to using it effectively.
Residual Porosity
Although sintering dramatically reduces porosity, it can be difficult to eliminate it completely, especially in standard press-and-sinter operations. This residual microporosity can be a factor in applications requiring absolute peak performance under extreme stress.
Process Complexity
The multi-step nature of the process—mixing, pressing, debinding, and sintering—requires precise control over many variables. Any inconsistency in powder quality, pressure, or furnace temperature can affect the final product's quality and consistency.
Material and Tooling Costs
High-quality metal powders can be more expensive than their bulk raw material counterparts. Additionally, the high-pressure dies and specialized furnaces represent a significant capital investment, which is typically justified by high-volume production runs.
Key Benefits of Sintering
The complexities of the process are often outweighed by its unique advantages, particularly for specific manufacturing challenges.
Working with High-Melting-Point Metals
Sintering is one of the most effective ways to create components from metals with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten. Melting and casting these materials is often impractical or impossible.
Enhanced Material Properties
The process allows for precise control over the final product's density and microstructure. This results in components with high strength, excellent structural integrity, and highly consistent properties from one part to the next.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
A key variation is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), where high temperature and immense gas pressure are applied simultaneously from all directions. This method excels at forcing plastic deformation and diffusion, resulting in products with virtually zero porosity and maximum density.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing approach depends entirely on your project's specific needs.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex but strong metal parts: Standard press-and-sinter provides an excellent balance of cost, speed, and consistent properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and mechanical performance: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior method, as it virtually eliminates porosity.
- If your primary focus is working with materials that are difficult to melt, like tungsten or molybdenum: Sintering is one of the few viable manufacturing methods to create solid components from these metals.
Ultimately, understanding sintering empowers you to create high-performance components that would be impossible to achieve through traditional melting methods.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing | Blend metal powder with binder | Creates uniform feedstock for shaping |
| Compaction | Press powder in a die | Forms a fragile 'green compact' in the desired shape |
| Heating (Sintering) | Heat in a controlled furnace below melting point | Binds particles via atomic diffusion, creating a strong, dense part |
Ready to manufacture high-performance metal components with precision sintering? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for sintering processes, including furnaces and material solutions. Whether you're working with high-melting-point metals like tungsten or need to achieve maximum density with Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), our expertise ensures superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials



















