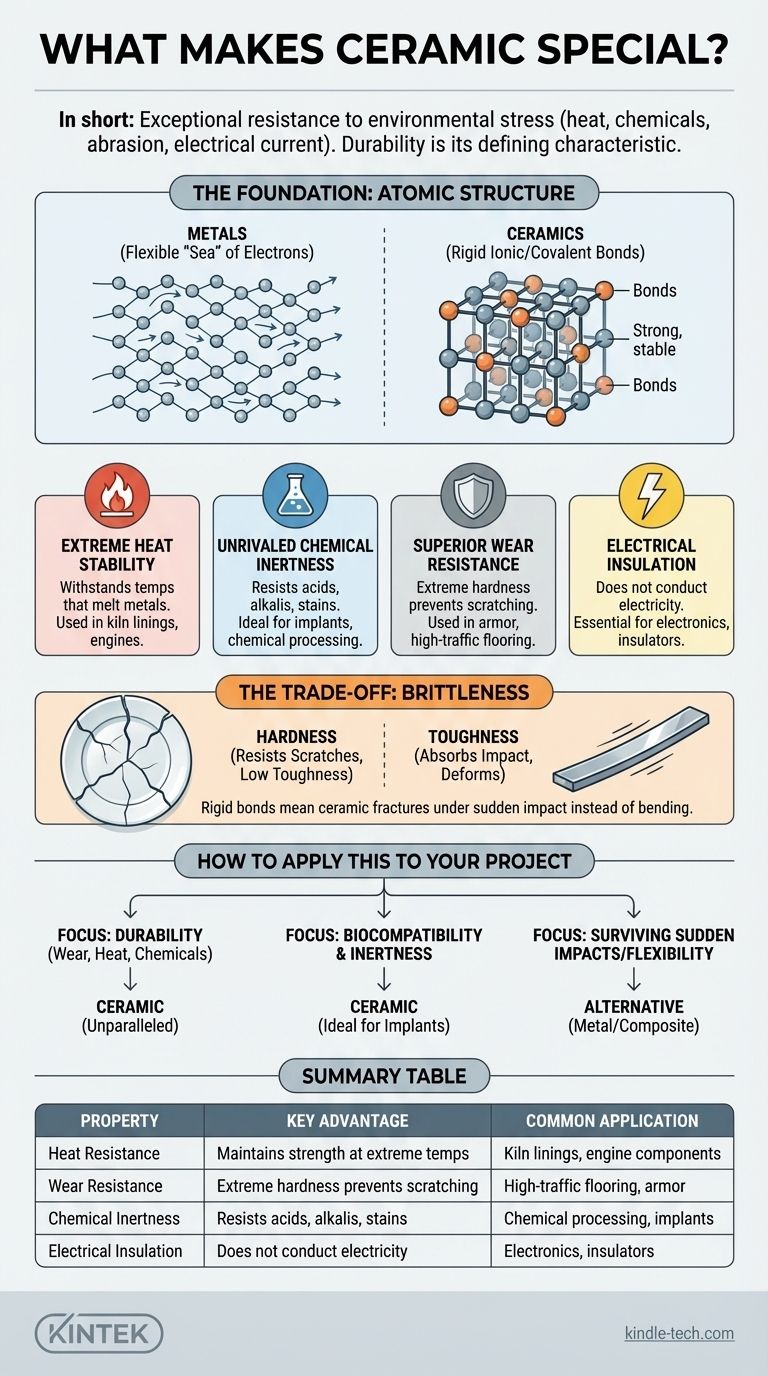
In short, what makes ceramic special is its exceptional resistance to nearly every form of environmental stress. It withstands extreme heat, chemical corrosion, physical abrasion, and electrical current to a degree that most other materials, particularly metals and plastics, cannot. This durability is the defining characteristic that drives its use in a vast range of demanding applications.
The unique power of ceramic comes from its incredibly strong and rigid atomic bonds. This internal structure is the source of its legendary hardness and stability, but it is also the reason for its primary weakness: brittleness.

The Foundation of Ceramic's Strength: Atomic Structure
The properties of any material are a direct result of how its atoms are held together. Unlike metals, which have a flexible "sea" of shared electrons, ceramics are defined by very strong, localized bonds.
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
Most advanced ceramics are formed by either ionic bonds (electrons are transferred between atoms) or covalent bonds (electrons are shared in a fixed position).
These bonds are extremely powerful and lock the atoms into a rigid, stable crystal lattice. This structure is difficult to disrupt, which is the fundamental reason for ceramic's signature properties.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
The strong atomic bonds resist being displaced. This makes the material's surface incredibly difficult to scratch or wear down.
This is why sintered ceramics are used for high-traffic flooring, countertops, and even the armor on military vehicles. They can withstand significant abrasion without degrading.
High-Temperature Stability
Heat is a form of energy that makes atoms vibrate. In ceramics, the powerful bonds require a massive amount of thermal energy to be weakened or broken.
As a result, ceramics can maintain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause metals to melt and plastics to vaporize. This makes them essential for things like kiln linings, engine components, and heat shields on spacecraft.
Unrivaled Chemical Resistance
The stable, tightly-bonded atomic structure leaves very few "opportunities" for foreign chemicals to react with it.
This makes ceramics highly resistant to acids, alkalis, stains, and environmental factors like UV rays and acid rain. They are essentially inert, which is why they are used in chemical processing equipment and for durable outdoor cladding.
Understanding the Trade-off: The Brittleness Factor
No material is perfect, and the very source of ceramic's strength is also the source of its primary limitation. The rigidity that makes it so durable also makes it brittle.
Hardness vs. Toughness
Hardness is the resistance to surface scratching and indentation. Toughness is the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. Ceramics are extremely hard, but they have low toughness.
Because the atomic bonds are so rigid, they cannot stretch or deform to absorb the energy of a sudden, sharp impact. Instead of bending, the material fractures.
Susceptibility to Sudden Impact
While a ceramic plate can withstand the heat of an oven and the scratching of a knife, it will shatter if dropped on a hard floor.
This trade-off is the central challenge in ceramic engineering. For applications where impact is a risk, the material must be designed or reinforced in a way that protects it from sudden shocks.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding this core trade-off is key to using ceramic effectively. Your decision should be based on the primary stress your component will face.
- If your primary focus is durability against wear, heat, or chemicals: Ceramic is an unparalleled choice for creating surfaces and components that must last in hostile environments.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and inertness: The chemical stability of ceramics makes them ideal for medical implants like dental crowns and hip replacements.
- If your primary focus is surviving sudden impacts or requiring flexibility: You must either design to mitigate shock or consider a tougher material like a metal alloy or composite.
Choosing the right material is about matching its inherent properties to the demands of the task.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Advantage | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Maintains strength at extreme temperatures | Kiln linings, engine components |
| Wear Resistance | Extreme hardness prevents scratching & abrasion | High-traffic flooring, armor |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, alkalis, and stains | Chemical processing, medical implants |
| Electrical Insulation | Does not conduct electricity | Electronics, insulators |
Need a material that can withstand extreme environments? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components designed for superior heat resistance, chemical inertness, and long-term durability. Let our experts help you select the perfect material for your demanding application. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity zirconia grinding balls recommended for LATP ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and High Conductivity.
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What is the purpose of using high-hardness zirconia grinding balls? Ensure Purity & Power in Electrolyte Milling
- Why are zirconia grinding balls recommended for sulfide solid electrolytes? Essential Tips for High Purity Milling
- What are the technical advantages of using zirconia (ZrO2) grinding balls? Enhancing Silicon Composite Anode Performance



















