In essence, sputter coating is a high-tech manufacturing process that embeds microscopic layers of metal onto glass or a window film. This process, conducted in a vacuum chamber, allows for the precise application of materials like silver, gold, or titanium to create a surface that is exceptional at selectively filtering sunlight. The result is a high-performance product that can reject heat and UV radiation without significantly compromising visible light or clarity.
The core problem with traditional window treatments is the trade-off between performance and aesthetics; you either get dark, tinted glass or insufficient solar control. Sputter coating solves this by creating an optically clear, atomically bonded layer that offers superior heat rejection and durability.

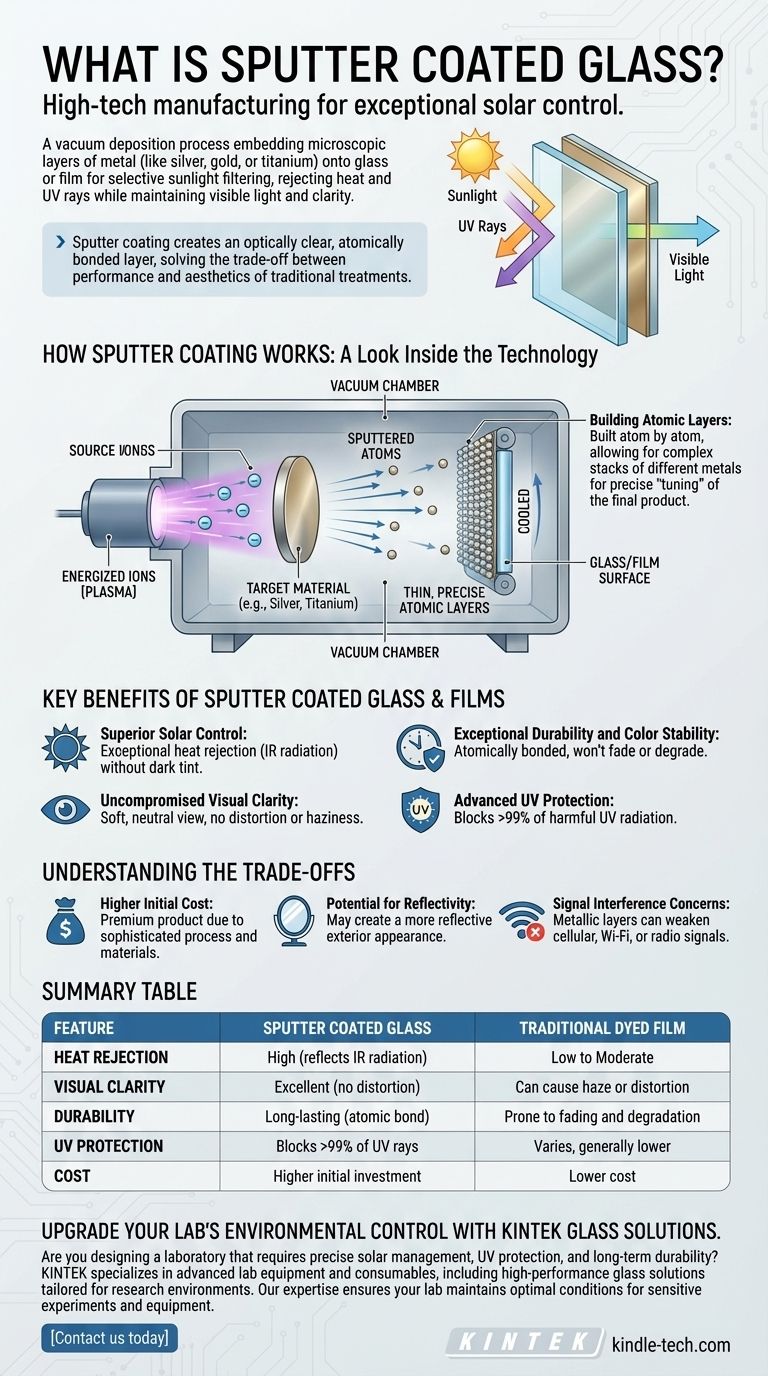
How Sputter Coating Works: A Look Inside the Technology
Sputter coating, also known as vacuum deposition, is a sophisticated process that manipulates materials at an atomic level. Understanding how it works reveals why it is so effective.
The Vacuum Deposition Process
The process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. A target material, typically a high-value metal like silver or titanium, is bombarded by energized ions (a plasma).
This high-energy impact "sputters" or knocks individual atoms off the target material. These atoms then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the cooler surface of the glass or film, forming a thin, uniform layer.
Building Atomic Layers
Because the coating is built atom by atom, the process is incredibly precise. Manufacturers can create a complex stack of different metal layers, each just a few atoms thick.
This precision is key to "tuning" the final product. Different metals and layer thicknesses can be combined to achieve specific goals, such as maximizing heat rejection while allowing a certain amount of visible light to pass through.
Key Benefits of Sputter Coated Glass & Films
The atomic-level precision of sputter coating delivers tangible performance benefits that older technologies like dyed films cannot match.
Superior Solar Control
The primary benefit is exceptional heat rejection. The specific metal layers (often silver) are chosen for their ability to reflect infrared (IR) radiation, which is the primary component of solar heat. This keeps interiors cooler without a heavy, dark tint.
Uncompromised Visual Clarity
Because the metallic layers are microscopically thin and perfectly uniform, they do not cause the optical distortion or haziness associated with lower-quality films. This provides a soft, neutral view from the inside, preserving the visual connection to the outdoors.
Exceptional Durability and Color Stability
The coating is atomically bonded to the glass or film substrate. Unlike dyes, which can fade and change color over time due to sun exposure, sputtered metals are completely stable. The color and performance will not degrade, ensuring a long service life.
Advanced UV Protection
Sputter coated products are highly effective at blocking over 99% of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This protects occupants from harmful rays and dramatically slows the fading of furniture, flooring, and artwork.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While sputter coating offers premium performance, it is essential to be aware of its specific characteristics and limitations.
Higher Initial Cost
The sophisticated machinery and valuable metals used in the vacuum deposition process make sputter coated glass and films more expensive than traditional dyed or simple vapor-deposited metallic films. It is a premium product with a corresponding price point.
Potential for Reflectivity
The metal layers that reject heat can also create a more reflective or mirror-like appearance from the exterior, especially during the daytime. While the reference material describes this as "subtle," the level of reflectivity varies and may not suit all aesthetic preferences.
Signal Interference Concerns
A well-known trade-off for any window film that uses metal layers is the potential for signal interference. The metallic particles can sometimes weaken cellular, Wi-Fi, or radio signals passing through the glass. This is a critical factor to consider, especially in modern, connected buildings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you choose a sputter coated product depends entirely on your project's specific needs, balancing budget, performance requirements, and application type.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance for new construction: Opt for integrated sputter coated glass (a "hard coat"), where the coating is sealed inside a multi-pane insulated glass unit (IGU).
- If your primary focus is upgrading existing windows with high performance: A high-quality sputter coated film is the ideal retrofit solution, offering many of the same benefits as integrated glass.
- If your primary focus is budget and basic glare reduction: A simpler dyed film may be sufficient, but you will be trading away the superior heat rejection and color stability of sputter coating.
- If your primary focus is avoiding any signal interference: You should investigate high-performance ceramic films, which offer excellent heat rejection without using metals.
Ultimately, choosing the right glass or window film is about making an informed decision based on a clear understanding of the underlying technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sputter Coated Glass | Traditional Dyed Film |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Rejection | High (reflects IR radiation) | Low to Moderate |
| Visual Clarity | Excellent (no distortion) | Can cause haze or distortion |
| Durability | Long-lasting (atomic bond) | Prone to fading and degradation |
| UV Protection | Blocks >99% of UV rays | Varies, generally lower |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost |
Upgrade Your Lab's Environmental Control with KINTEK Glass Solutions
Are you designing a laboratory that requires precise solar management, UV protection, and long-term durability? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including high-performance glass solutions tailored for research environments. Our expertise ensures your lab maintains optimal conditions for sensitive experiments and equipment.
Contact us today to discuss how our sputter coated glass products can enhance your lab's efficiency and protection!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
- CF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window Window Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
People Also Ask
- What are the five methods used to sterilize materials in a laboratory? A Guide to Matching Method to Material
- How does a rotary vacuum evaporator work? A Guide to Gentle, Efficient Solvent Removal
- Is pyrolysis for converting biomass to more useful liquid? Unlock Bio-Oil, Biochar & Syngas
- What are the three types of annealing? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Treatment
- What is a heat treatment furnace? Achieve Precise Metallurgical Transformations
- How do you ensure the safe operation of equipment and machinery? A Proactive Guide to Risk Management
- Why sputter coating is used for specimen preparation? Prevent Charging for Clear SEM Imaging
- How do metal oxides like Cerium Oxide (CeO2) or Zinc Oxide (ZnO) function in solar thermochemical cycles?








