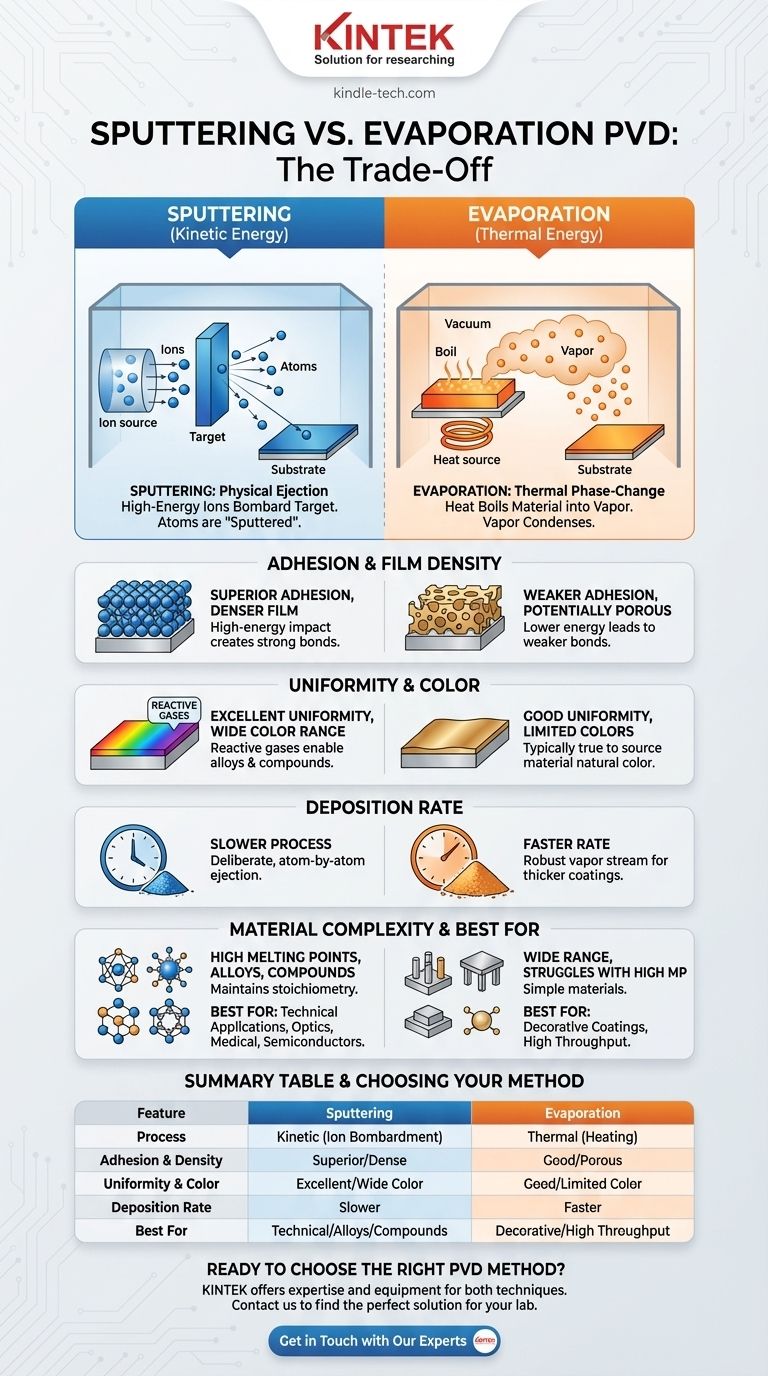
The fundamental difference between sputtering and evaporation is how they create a vapor to coat a substrate. Evaporation uses heat to boil a material into a gas, similar to how water creates steam. Sputtering uses a physical process where high-energy ions bombard a target material, knocking atoms loose like a cue ball breaking a rack of billiard balls.
The choice between sputtering and evaporation is a classic engineering trade-off. Evaporation is typically faster and simpler, while sputtering produces higher-quality, more durable, and more versatile thin films.

The Mechanism: Kinetic vs. Thermal Energy
The two Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods are distinguished by the energy source they use to liberate atoms from the source material. This core difference dictates the resulting film's properties.
Sputtering: A Physical Ejection Process
Sputtering takes place in a vacuum chamber filled with an inert gas, such as argon. A high voltage is applied, creating a plasma.
Positively charged ions from this plasma are accelerated and collide with the source material, called the target. The impact's kinetic energy is high enough to dislodge, or "sputter," atoms from the target. These ejected atoms travel through the chamber and condense on the substrate, forming a thin film.
Evaporation: A Thermal Phase-Change Process
Evaporation is a conceptually simpler process. Inside a high vacuum, the source material is heated until its vapor pressure becomes significant.
This is typically done using a resistive heat source (thermal evaporation) or a focused electron beam (e-beam evaporation). The material effectively boils, creating a vapor that travels in a straight line until it condenses on the cooler substrate surface.
Comparing the Resulting Film Characteristics
The way atoms arrive at the substrate—with high kinetic energy (sputtering) or lower thermal energy (evaporation)—has a profound impact on the final coating.
Adhesion and Film Density
Sputtered atoms arrive at the substrate with significantly higher energy. This allows them to physically impact and embed slightly into the surface, creating superior adhesion and forming a much denser, less porous film.
Evaporated atoms arrive with less energy, leading to weaker adhesion and a potentially more porous film structure.
Uniformity and Color
Sputtering naturally produces a more uniform coating with a realistic metal effect. It also offers far greater color versatility. By introducing reactive gases (like nitrogen or oxygen) during the process, it's possible to create compounds like nitrides and oxides, enabling a wide spectrum of colors.
Evaporation is typically limited to the true color of the source material, such as the natural color of aluminum. Achieving different colors often requires post-processing steps like painting.
Deposition Rate
Evaporation generally produces a more robust vapor stream, enabling higher deposition rates and shorter run times. This makes it efficient for applying thicker coatings.
Sputtering is a slower, more deliberate process, ejecting atoms one by one, which results in lower deposition rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior. The correct choice depends entirely on the application's requirements for quality, speed, and material complexity.
The Speed vs. Quality Dilemma
This is the central trade-off. Evaporation offers speed and high throughput, making it ideal for applications like decorative coatings on plastic where ultimate durability is not the primary concern.
Sputtering delivers higher-quality films. It is the preferred method for technical applications like semiconductor manufacturing, optical coatings, and medical implants, where adhesion, density, and durability are critical.
Material Compatibility and Complexity
While thermal evaporation works for a wide range of materials, it struggles with those that have very high melting points.
Sputtering excels at depositing refractory metals, alloys, and compounds. It maintains the stoichiometry (elemental ratio) of an alloy target, ensuring the resulting film has the same composition as the source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's priorities will dictate the best PVD method.
- If your primary focus is high-speed deposition for decorative or simple metallic finishes: Choose evaporation for its high throughput and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, durable films with excellent adhesion for technical applications: Choose sputtering for its superior film quality and performance.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys, compounds, or a wide range of colors: Choose reactive sputtering for its unmatched material versatility.
Ultimately, understanding the trade-off between evaporation's speed and sputtering's quality is the key to selecting the ideal process for your project.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sputtering | Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Kinetic energy from ion bombardment | Thermal energy from heating |
| Adhesion & Density | Superior, dense films | Good, potentially more porous |
| Uniformity & Color | Excellent, wide color range via reactive gases | Good, typically limited to metal's natural color |
| Deposition Rate | Slower | Faster |
| Best For | Technical applications, alloys, compounds | Decorative coatings, high throughput |
Ready to Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Lab?
Understanding the trade-offs between sputtering and evaporation is crucial for achieving optimal results in your thin-film applications. Whether you need the high-speed deposition of evaporation for decorative coatings or the superior film quality and material versatility of sputtering for technical applications, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including PVD systems, to meet the diverse needs of research and industrial laboratories. Our team can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your coating processes, improve film performance, and accelerate your research.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can bring value to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- How does chemical vapor deposition work for diamonds? Grow Lab-Created Diamonds Layer by Layer
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition



















