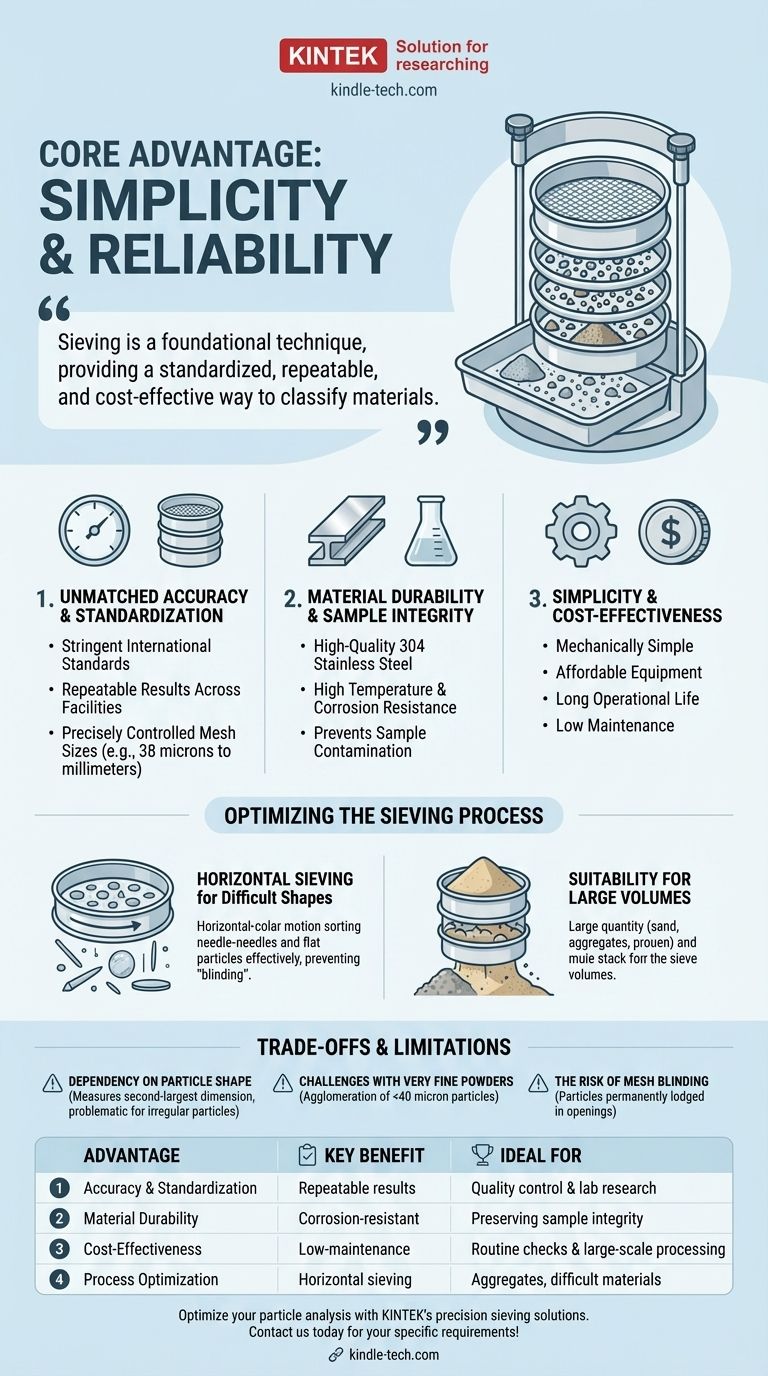
At its core, the primary advantage of sieving is its simplicity and reliability. This technique offers a straightforward, cost-effective, and highly accurate method for separating and classifying particles based on their size. Its main benefits arise from the use of durable, standardized equipment that ensures repeatable and trustworthy results, making it a cornerstone of quality control and material analysis across many industries.
Sieving is not merely a method for separation; it is a foundational technique for particle size analysis. Its true advantage lies in providing a standardized, repeatable, and cost-effective way to classify materials, ensuring they meet precise quality and performance specifications.
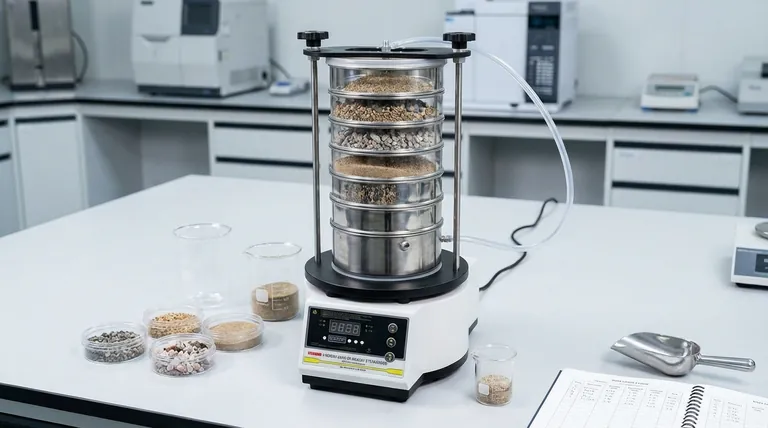

Why Sieving Remains a Foundational Technique
Sieving has endured as a primary method for particle analysis because it excels in several key areas. The technique's value is rooted in the quality and design of the tools themselves.
Unmatched Accuracy and Standardization
The most significant advantage is the ability to achieve accurate and repeatable results. Sieves are manufactured to meet stringent international standards.
This standardization ensures that a test performed in one facility can be reliably replicated in another. Mesh sizes are precisely controlled, ranging from several millimeters down to just 38 microns, allowing for highly specific classification.
Material Durability and Sample Integrity
Modern lab sieves are typically constructed from high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel. This choice is deliberate.
Stainless steel provides high temperature and corrosion resistance, preventing the sieve itself from contaminating the sample. This chemical stability ensures the material being tested is not altered during analysis, preserving the integrity of the results.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to more advanced particle analysis methods like laser diffraction, sieving is mechanically simple and far more affordable.
The equipment is durable and has a long operational life, requiring minimal maintenance beyond proper cleaning. This accessibility makes it the go-to method for routine quality control and large-scale material processing.
Optimizing the Sieving Process
The effectiveness of sieving can be enhanced by choosing the right method for the specific material being analyzed. The physical motion of the sieve shaker has a direct impact on the outcome.
Handling Difficult Particle Shapes
For materials containing needle-shaped, flat, or long particles, horizontal sieving is highly advantageous.
A simple vertical tapping motion can cause these particles to turn sideways and block the mesh openings, a problem known as "blinding." The horizontal, circular motion keeps these particles flat, allowing them to be sorted more effectively and preventing the sieve from quickly becoming blocked.
Suitability for Large Sample Volumes
The same horizontal sieving motion is ideal for analyzing large quantities of material. It is frequently used for bulk materials like construction aggregates, sand, and other industrial minerals.
This capability allows sieving to scale from small laboratory samples to large-scale industrial quality assurance, demonstrating its versatility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Dependency on Particle Shape
Sieving fundamentally measures the second-largest dimension of a particle, as this determines if it can pass through the mesh.
For highly irregular or elongated particles, this can be misleading. A long, thin fiber might pass through a mesh that would block a spherical particle of the same mass, leading to an inaccurate size distribution profile.
Challenges with Very Fine Powders
Sieving particles smaller than approximately 40 microns becomes progressively more difficult.
Very fine powders are prone to forming agglomerates (clumps) due to electrostatic forces or moisture. This prevents individual particles from passing through the mesh, requiring specialized techniques or alternative analysis methods to overcome.
The Risk of Mesh Blinding
Even with the correct technique, mesh blinding can occur when particles become permanently lodged in the sieve openings. This reduces the effective sieving area, skews results, and requires pausing the process for intensive cleaning or sieve replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To apply sieving effectively, align your technique with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Sieving provides an essential, standardized check to ensure incoming materials like aggregates, grains, or powders meet size specifications.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research: The high accuracy and repeatability of certified analyzing sieves are critical for characterizing new materials and developing consistent processes.
- If your primary focus is processing large, irregular materials: Consider specialized techniques like horizontal sieving to prevent mesh blockage and ensure efficient, accurate separation.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently leverage sieving as a powerful and reliable tool for material classification and process control.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy & Standardization | Repeatable results per international standards | Quality control & lab research |
| Material Durability | Stainless steel construction, corrosion-resistant | Preserving sample integrity |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Affordable, low-maintenance equipment | Routine checks & large-scale processing |
| Process Optimization | Horizontal sieving for irregular particles | Aggregates, minerals, difficult materials |
Optimize your particle analysis with KINTEK's precision sieving solutions. Whether you're in quality control, research, or large-scale material processing, our durable, standardized lab sieves deliver the accuracy and reliability you need. Contact us today to find the perfect sieving equipment for your laboratory's specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















