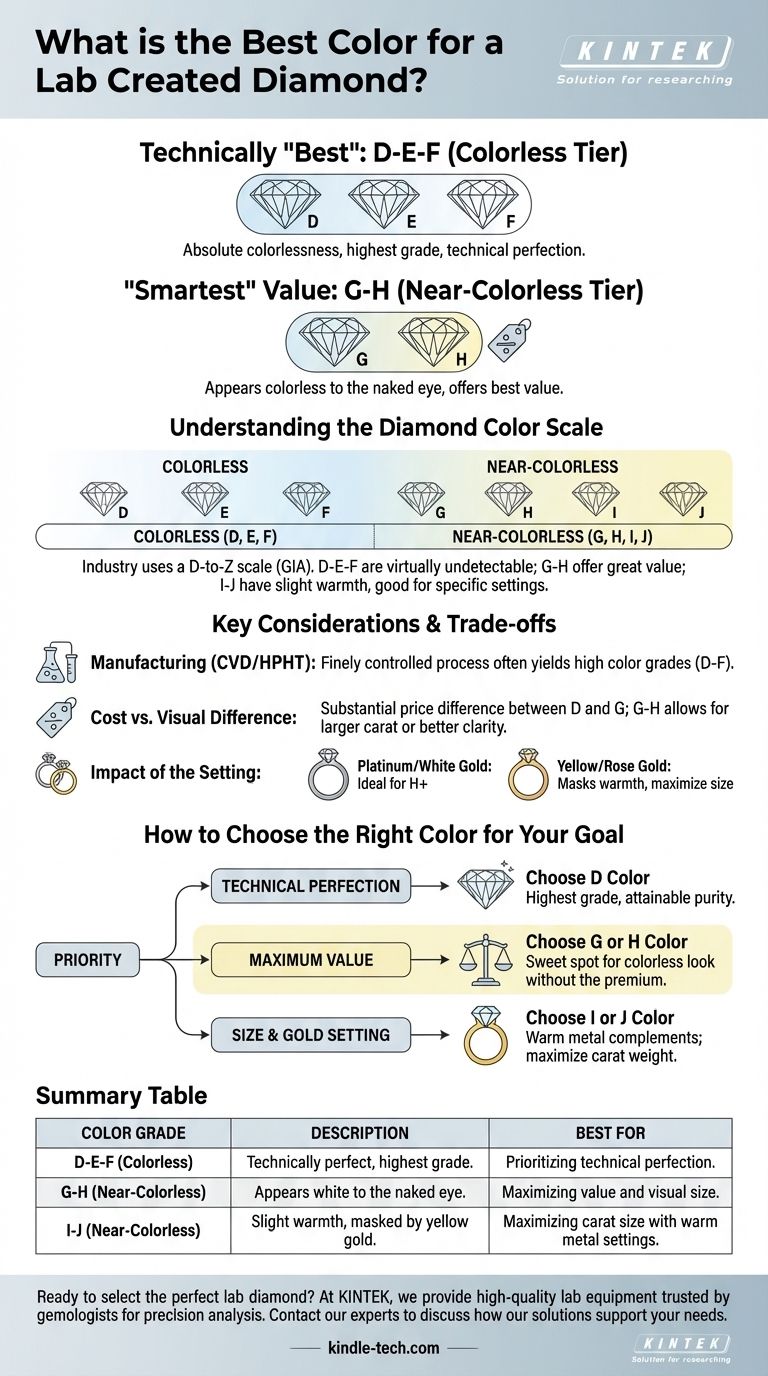
For a lab-created diamond, the technically "best" colors are in the D-E-F range. This tier is defined as truly colorless and represents the highest grade on the official diamond color scale. Because the creation process for lab diamonds can be finely controlled, achieving these top-tier colors is more common and accessible than with natural diamonds.
The core decision is not about finding the "best" color, but the "smartest" color for your goal. While D is technically the highest grade, a diamond in the G-H near-colorless range offers the best value, appearing colorless to the naked eye at a significantly lower cost.

Understanding the Diamond Color Scale
To choose wisely, you must first understand how diamonds are graded. The industry uses a D-to-Z scale established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), which applies equally to both natural and lab-grown diamonds.
The Colorless Tier (D, E, F)
A D color grade represents absolute colorlessness, the highest possible grade. It sets the standard for purity and is the rarest color grade in nature.
E and F colors are also colorless. Any distinction between D, E, and F is typically undetectable to an untrained eye and requires expert grading in a controlled environment.
Lab diamonds are frequently produced in this D-F range, offering access to technical perfection without the extreme premium of a mined D-color diamond.
The Near-Colorless Tier (G, H, I, J)
This is the most popular and value-oriented category for engagement rings and other fine jewelry.
Diamonds in the G and H range contain color traces that are so slight they are extremely difficult to see. To the naked eye, they appear just as white as colorless diamonds, especially once set in a piece of jewelry.
I and J colors have a slightly more noticeable warmth, but this can often be masked or complemented by the metal choice of the setting.
Key Considerations for Lab Diamonds
Lab diamonds possess the exact same chemical, physical, and optical properties as mined diamonds. However, the controlled environment in which they are grown presents unique considerations.
Manufacturing and Color
The two primary methods for creating lab diamonds are High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
CVD-grown diamonds are frequently colorless or near-colorless, making them a reliable source for high-color grades.
The Value Proposition
The primary advantage of a lab diamond is getting a visually superior stone for your budget. You can afford a higher color and clarity grade, or a larger carat size, than you could with a natural diamond at the same price point.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Making an informed decision means weighing technical perfection against practical beauty and cost.
Cost vs. Visual Difference
The price difference between a D-color and a G-color diamond of the same size and clarity can be substantial. For most buyers, this premium pays for a technical specification you cannot see.
Choosing a G or H color grade allows you to allocate more of your budget toward carat size or clarity, which have a much greater impact on the diamond's overall appearance.
The Impact of the Setting
The metal you choose for your ring or jewelry plays a significant role in how the diamond's color is perceived.
A diamond set in platinum or white gold will reveal its color more readily. For these settings, an H color or higher is ideal.
A diamond set in yellow or rose gold will naturally reflect the warm tones of the metal. In this context, even an I or J color diamond can appear perfectly white, making it an exceptionally smart buy.
Resale Value Is Not the Goal
It is critical to understand that lab-grown diamonds should not be considered a financial investment. While they are real diamonds, they do not hold or appreciate in value like their mined counterparts.
Their value is in the initial purchase, empowering you to own a beautiful, optically brilliant diamond that would otherwise be far more expensive.
How to Choose the Right Color for Your Goal
Your "best" choice depends entirely on your personal priority.
- If your primary focus is technical perfection: Choose a D color. It is the highest grade, and the lab-grown market makes this level of purity more attainable.
- If your primary focus is maximum value: Choose a G or H color. This is the sweet spot where the diamond appears perfectly colorless to the eye without the premium price of the D-F grades.
- If your primary focus is size and you're using a yellow gold setting: Choose an I or J color. The warm metal will make the diamond appear brilliantly white, allowing you to maximize the carat weight for your budget.
Ultimately, choosing a lab diamond empowers you to prioritize visible beauty over unseen rarity.
Summary Table:
| Color Grade | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| D-E-F (Colorless) | Technically perfect, highest grade. | Prioritizing technical perfection. |
| G-H (Near-Colorless) | Appears white to the naked eye. | Maximizing value and visual size. |
| I-J (Near-Colorless) | Slight warmth, masked by yellow gold. | Maximizing carat size with warm metal settings. |
Ready to select the perfect lab diamond for your needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. While we don't sell diamonds, our precision instruments are trusted by gemologists and researchers worldwide for accurate analysis. If your work involves material science or gemological analysis, contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable lab solutions can support your precision requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
















