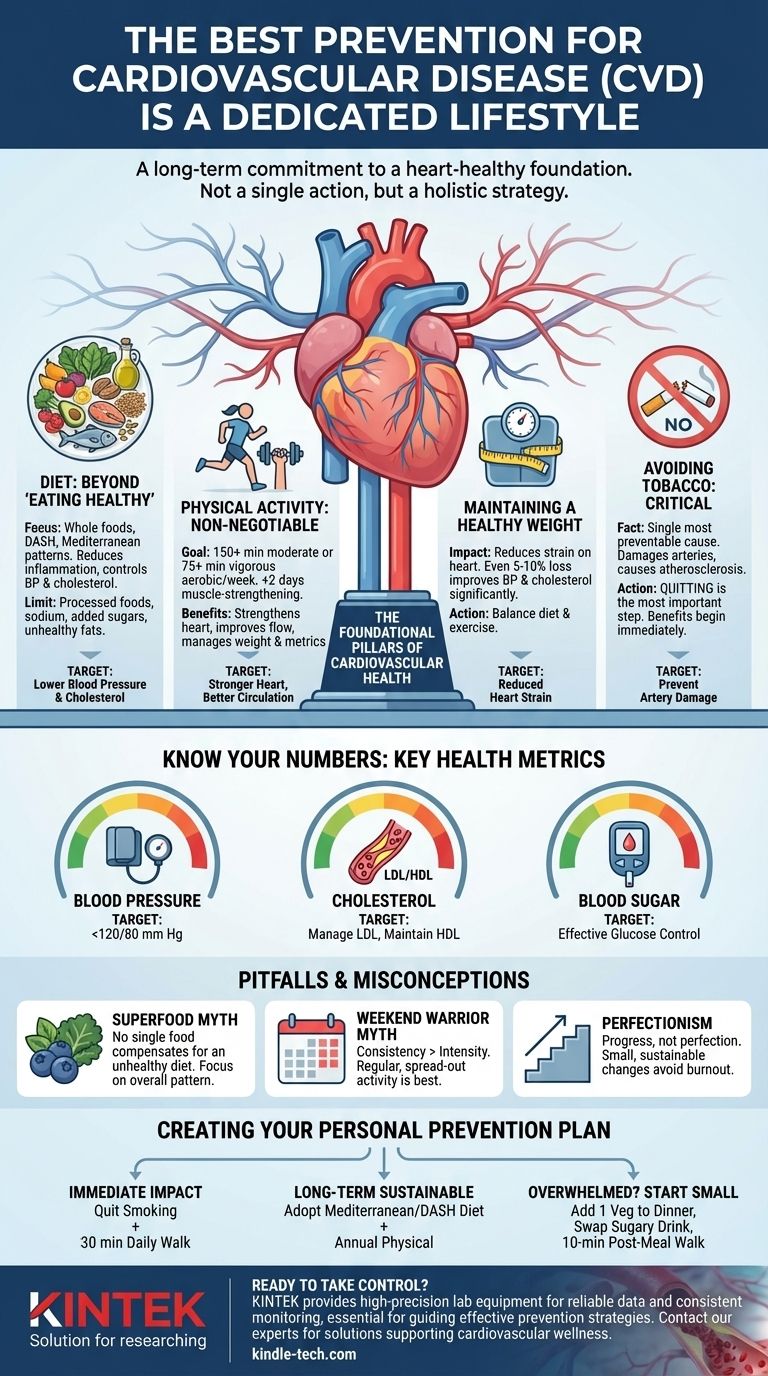
The single best prevention for cardiovascular disease (CVD) is not one action, but a dedicated, long-term commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle. This strategy is built on a foundation of a balanced diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco. These controllable factors have a more profound impact on your long-term cardiovascular health than any single supplement or medication.
Preventing cardiovascular disease is not about pursuing perfection or a single "magic bullet." It is about consistently managing a small set of key lifestyle factors and health metrics that collectively protect your heart and blood vessels over your lifetime.

The Foundational Pillars of Cardiovascular Health
The most effective prevention strategy is a holistic one. It involves consciously managing the daily choices that have the greatest impact on your heart, arteries, and overall circulatory system.
The Role of Diet: More Than Just 'Eating Healthy'
Your dietary pattern is a powerful tool for CVD prevention. The goal is to choose foods that reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and control cholesterol.
Focus on whole foods and well-researched eating patterns like the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) or Mediterranean diet. These prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (like fish and poultry), and healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and avocados.
Simultaneously, it's critical to limit intake of processed foods, sodium, added sugars, and unhealthy fats (saturated and trans fats). These contribute to high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and systemic inflammation—all direct risk factors for CVD.
Physical Activity: The Non-Negotiable Component
Regular exercise strengthens your heart muscle, improves blood flow, and helps manage weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol. It is a cornerstone of prevention.
The general recommendation is at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity (like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling) or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week.
In addition, incorporating muscle-strengthening activities at least two days a week helps improve overall metabolic health, further reducing your cardiovascular risk.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, forces your heart to work harder and is a major risk factor for high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes.
Weight management is a direct result of balancing diet and physical activity. Even a modest weight loss of 5% to 10% of your body weight can produce significant improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
The Critical Importance of Not Smoking
There is no ambiguity on this point: smoking is one of the most significant and preventable causes of CVD. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lining of your arteries, leading to atherosclerosis (the buildup of fatty plaque), which narrows the arteries and can cause heart attacks and strokes.
Quitting smoking is the single most important lifestyle change you can make for your heart health. The benefits begin almost immediately.
Know Your Numbers: The Key Health Metrics to Monitor
Lifestyle changes are the "how," but health metrics are the "what." Knowing and managing these numbers with your healthcare provider is essential for understanding your personal risk profile.
Blood Pressure: The 'Silent Killer'
High blood pressure (hypertension) often has no symptoms but dramatically increases your risk of heart attack and stroke. A healthy blood pressure is typically considered to be below 120/80 mm Hg.
Cholesterol: Understanding 'Good' vs. 'Bad'
Your body needs cholesterol, but an imbalance can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries. The key is to manage LDL ('bad') cholesterol, which deposits plaque, and maintain healthy levels of HDL ('good') cholesterol, which helps remove it.
Blood Sugar: Managing Glycemic Control
Chronically high blood sugar levels, even in a pre-diabetic state, can damage blood vessels and nerves that control your heart. Regular monitoring helps ensure your body is processing glucose effectively, reducing a key stressor on your cardiovascular system.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Common Misconceptions
Building a heart-healthy lifestyle requires navigating a great deal of information. Being aware of common pitfalls is critical for long-term success.
The Myth of the 'Superfood'
No single food, like blueberries or kale, can compensate for an otherwise unhealthy diet. The benefit comes from the overall dietary pattern, not from one isolated ingredient. Focus on the whole picture rather than searching for a single miracle food.
'Weekend Warrior' vs. Consistent Activity
While any activity is better than none, sporadic, intense bursts of exercise can put undue strain on the body. The greatest benefits for heart health come from regular, consistent activity spread throughout the week. Consistency is more important than intensity.
Perfection Is the Enemy of Progress
Attempting a drastic, perfect overhaul of your lifestyle overnight often leads to burnout and failure. It is far more effective to make small, sustainable changes that you can build upon over time. Progress, not perfection, is the goal.
Creating Your Personal Prevention Plan
Your ideal strategy depends on your current habits, health status, and priorities. Use the following to guide your first steps.
- If your primary focus is immediate action with the highest impact: The most powerful combination is to quit smoking and begin a consistent walking routine of 30 minutes per day.
- If your primary focus is long-term, sustainable health: Adopt a Mediterranean or DASH-style eating pattern and schedule an annual physical to track your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
- If you feel overwhelmed and don't know where to start: Choose one small, manageable change. Commit to adding a vegetable to every dinner, swapping one sugary drink for water each day, or taking a 10-minute walk after a meal.
Ultimately, preventing cardiovascular disease is an act of empowerment, and your daily choices are the most powerful tools you have.
Summary Table:
| Prevention Pillar | Key Action | Target Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Adopt a Mediterranean or DASH diet | Lower blood pressure & cholesterol |
| Physical Activity | 150+ mins moderate exercise per week | Strengthen heart muscle, improve circulation |
| Weight Management | Achieve & maintain a healthy BMI | Reduce strain on heart & blood vessels |
| Tobacco Avoidance | Quit smoking entirely | Prevent artery damage & plaque buildup |
| Health Monitoring | Regular checks of BP, cholesterol, blood sugar | Early detection & management of risk factors |
Ready to take control of your heart health?
At KINTEK, we understand that managing your cardiovascular risk requires reliable data and consistent monitoring. Our high-precision laboratory equipment, including analyzers for blood chemistry and metabolic studies, provides the accurate results healthcare professionals and research facilities need to guide effective prevention strategies.
Whether you are a clinical lab supporting patient care or a research institution studying cardiovascular disease, KINTEK's reliable consumables and equipment are essential for generating the trusted data that informs lifelong heart-healthy plans.
Contact our experts today to learn how our solutions can support your mission to promote cardiovascular wellness.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using the Pechini sol-gel method? Boost Perovskite Quality with Molecular-Level Precision
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis plant? Turn Waste into Profit with Advanced Recycling
- What are the properties of the graphite? Unlock High-Temperature Strength & Conductivity
- What is the principle of magnetron sputtering technique? Achieve Superior Thin-Film Deposition
- Can FTIR determine purity? Uncover Contaminants with Chemical Fingerprinting
- What are the benefits of vacuum pyrolysis? Maximize Your Bio-Oil Yield and Quality
- How does heat treating affect the strength of a metal? A Guide to Tailoring Metal Properties
- What are the benefits of setting an ultra-low temperature freezer to -70C instead of -80C? Save 30-40% on Energy Costs






