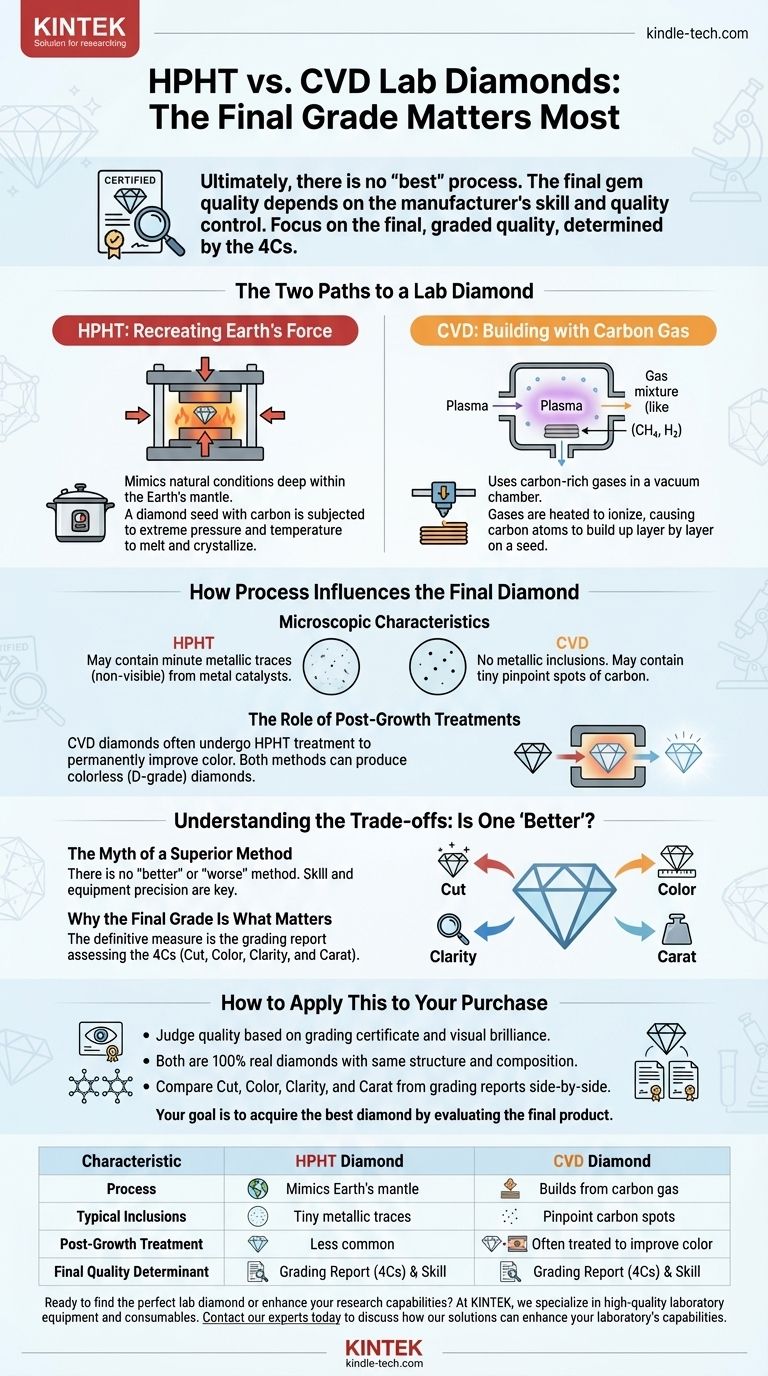
Ultimately, there is no "best" process for creating lab diamonds. The two primary methods, High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), both produce diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to those mined from the earth. The quality of the final gem depends on the specific manufacturer's skill and quality control, not on the inherent superiority of one method over the other.
The critical takeaway is to shift your focus from the diamond's creation method to its final, graded quality. An exceptional diamond is exceptional regardless of its origin story; its value is determined by the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat), not by whether it was made via HPHT or CVD.

The Two Paths to a Lab Diamond
To make an informed decision, you must first understand how each process works. Both begin with a "seed"—a microscopic slice of a pre-existing diamond—but from there, the paths diverge significantly.
HPHT: Recreating the Earth's Force
The High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) method is the original process for diamond creation, first developed in the 1950s. It directly mimics the natural conditions deep within the Earth's mantle that form diamonds.
In this process, a diamond seed is placed into a cell with pure, solid carbon. This cell is subjected to immense pressure and extreme temperatures, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a new, larger diamond.
Think of it as a highly advanced geological pressure cooker, replicating a process that takes nature billions of years in a matter of weeks.
CVD: Building with Carbon Gas
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a newer, more technologically nuanced method. Instead of pressure, it uses a specialized gas mixture in a vacuum chamber.
A diamond seed is placed in a sealed chamber which is then filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane). These gases are heated to extreme temperatures, causing them to ionize. The carbon atoms break away from the gas and "rain down" onto the diamond seed, building up layer by layer.
This method is often compared to 3D printing with individual atoms, slowly constructing a diamond crystal over several weeks.
How Process Influences the Final Diamond
While both methods produce real diamonds, their different approaches can sometimes leave behind subtle clues about their origin, which are only detectable with sophisticated gemological equipment.
Microscopic Characteristics
Because the HPHT process uses metal catalysts and high pressure, a finished stone may contain minuscule metallic traces. These are not visible to the naked eye and do not affect the diamond's beauty or durability.
CVD diamonds, grown in a gas environment, do not have metallic inclusions. Their growth patterns are different, and if inclusions are present, they are typically tiny pinpoint spots of carbon.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
It is common for CVD diamonds to undergo a secondary HPHT treatment after they are grown. This is not a repair or an alteration; it's a finishing step to permanently improve the diamond's color.
This demonstrates that the two processes are not mutually exclusive. The key is that both methods, with or without treatments, are capable of producing flawless, colorless (D-grade) diamonds.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Is One 'Better'?
The belief that one method is inherently superior is the most common misconception buyers face. The truth is far more practical.
The Myth of a Superior Method
There is no "better" or "worse" between HPHT and CVD. Both create high-quality, authentic diamonds. The skill of the laboratory technicians and the precision of their equipment are far more important factors in determining the final quality of a gem.
A poorly executed CVD process will yield a poor diamond, just as a poorly executed HPHT process will. A top-tier lab will produce exceptional diamonds using either method.
Why the Final Grade Is What Matters
The definitive measure of any diamond's quality is its grading report from a reputable gemological lab. This report objectively assesses the 4Cs.
A grading report tells you everything you need to know about the diamond's quality. Whether that D-color, VVS1-clarity diamond started as a piece of solid carbon or as a gas in a chamber is irrelevant to its beauty, brilliance, and value.
How to Apply This to Your Purchase
When selecting a lab diamond, let go of the process debate and focus entirely on the quality of the individual stone in front of you.
- If your primary focus is quality and value: Judge the diamond based on its grading certificate and its visual brilliance, not its growth method.
- If you are concerned about authenticity: Rest assured that both CVD and HPHT diamonds are 100% real diamonds, sharing the exact same crystal structure and chemical composition as their natural counterparts.
- If you are comparing two specific diamonds: Place their grading reports side-by-side and compare their Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat, choosing the one that best meets your standards and budget.
Your goal is to acquire the best possible diamond, and that is achieved by evaluating the final product, not by favoring its manufacturing journey.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | HPHT Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mimics Earth's mantle with high pressure & temperature | Builds diamond layer-by-layer from carbon gas |
| Typical Inclusions | May contain tiny metallic traces | May contain pinpoint carbon spots |
| Common Post-Growth Treatment | Less common | Often treated with HPHT to improve color |
| Final Quality Determinant | Grading Report (4Cs) & Manufacturer Skill | Grading Report (4Cs) & Manufacturer Skill |
Ready to find the perfect lab diamond for your needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether your lab is involved in advanced materials research, including diamond synthesis and analysis, we have the tools to support precision and excellence.
Let us help you achieve unparalleled results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- How is the pressure and temperature process used to make a synthetic diamond? Replicate Earth's Diamond Formation in a Lab
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury



















