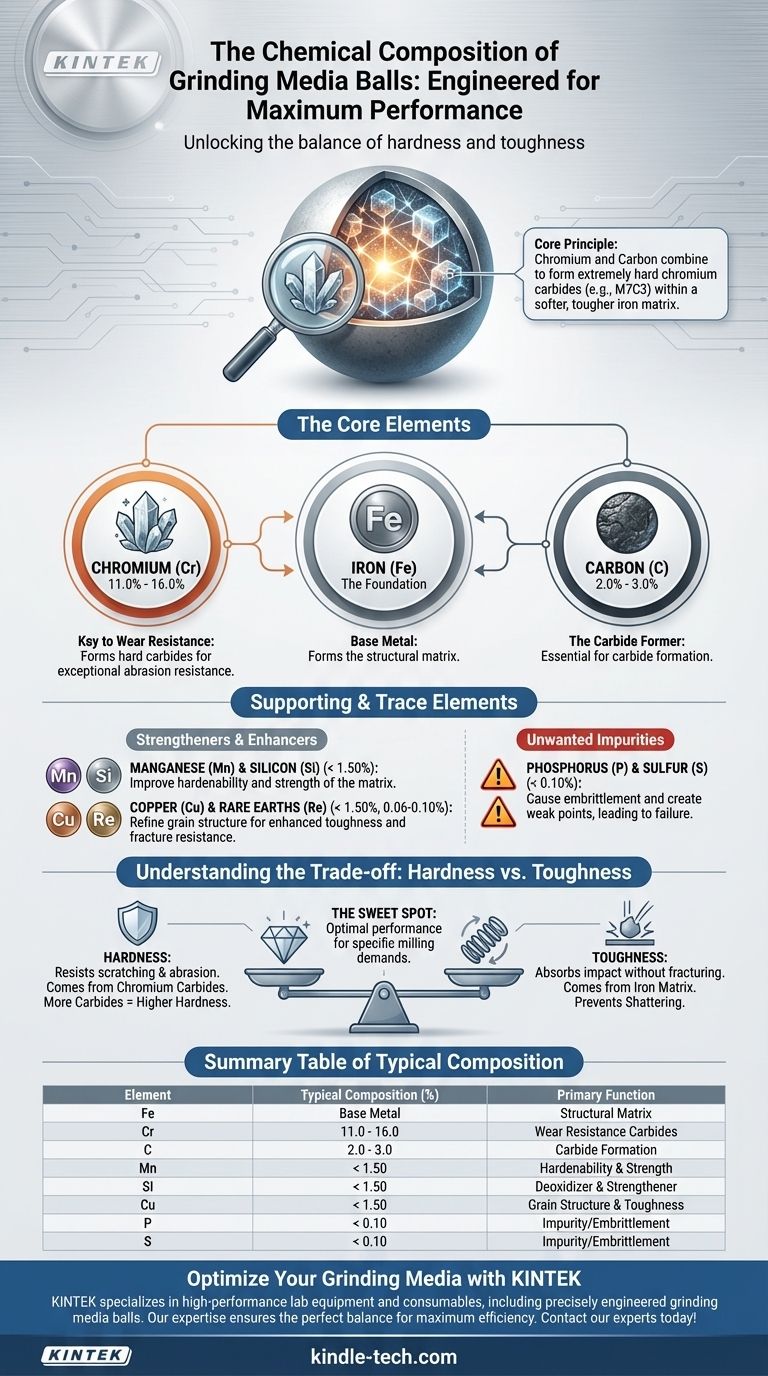
The chemical composition of grinding media is precisely engineered to maximize hardness and wear resistance while maintaining toughness. A common, high-performance formulation is high-chromium cast iron, which is predominantly Iron (Fe) alloyed with significant amounts of Chromium (Cr) and Carbon (C). It also contains smaller, controlled quantities of elements like Manganese (Mn), Silicon (Si), and trace additives to refine its properties.
The core principle is straightforward: Chromium and Carbon combine to form extremely hard carbide microstructures within a softer, tougher iron matrix. This composition creates a grinding ball that can effectively crush materials without shattering or wearing away too quickly.
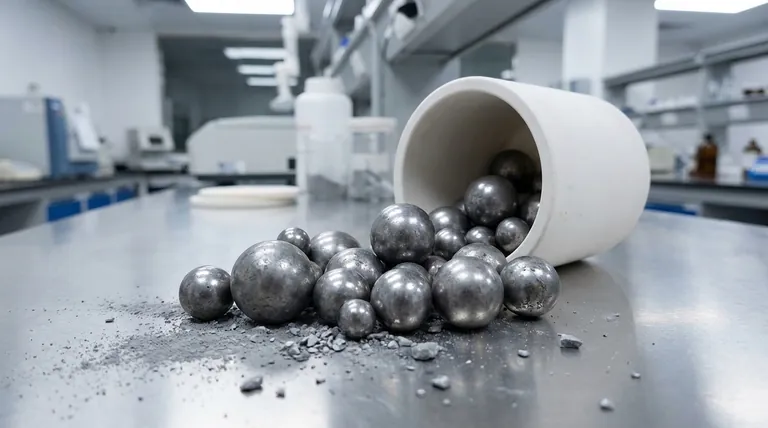

The Core Elements of High-Performance Grinding Media
To understand the performance of a grinding ball, we must first understand the specific function of each component in the alloy. The balance between these elements is critical.
Iron (Fe): The Foundation
Iron serves as the base metal, forming the bulk of the alloy. It creates the structural matrix that holds the all-important hard carbide particles in place.
Chromium (Cr): The Key to Wear Resistance
Chromium is the most critical alloying element, typically present in concentrations of 11.0% to 16.0%. Its primary role is to combine with carbon during the cooling and heat treatment process.
This reaction forms incredibly hard chromium carbides (e.g., M7C3) throughout the iron matrix. These carbides are what provide the exceptional resistance to abrasion required for grinding ore, cement, and other hard materials.
Carbon (C): The Carbide Former
Carbon, typically present from 2.0% to 3.0%, is the essential partner to chromium. Without sufficient carbon, the hard chromium carbides cannot form.
The amount of carbon is carefully controlled. Too little carbon results in a softer ball that wears quickly, while too much can create an excess of carbides, making the ball brittle and prone to fracture under impact.
The Role of Supporting and Trace Elements
While Iron, Chromium, and Carbon are the primary actors, other elements are added in smaller amounts to refine the final properties of the grinding media.
Manganese (Mn) and Silicon (Si): The Strengtheners
Both Manganese (less than 1.50%) and Silicon (less than 1.50%) contribute to the hardenability and strength of the iron matrix itself. They also act as deoxidizers during the casting process, helping to remove impurities.
Copper (Cu) and Rare Earths (Re): Performance Enhancers
Specialized elements like Copper (less than 1.50%) and rare earth metals like Rhenium (0.06-0.10%) are often added as micro-alloying agents. Their purpose is to refine the grain structure of the metal, which improves the overall toughness and fracture resistance of the ball.
Phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S): The Unwanted Impurities
These elements are considered impurities and are kept to a minimum (less than 0.1%). Both Phosphorus and Sulfur can cause embrittlement, creating weak points within the metal that can lead to catastrophic failure during operation.
Understanding the Trade-off: Hardness vs. Toughness
The chemical composition of a grinding ball is a masterclass in managing a fundamental engineering compromise: the balance between hardness and toughness.
Hardness is the ability to resist scratching and abrasion. This property comes from the chromium carbides. More carbides mean a harder, more wear-resistant ball.
Toughness is the ability to absorb impact and energy without fracturing. This property comes from the iron matrix. A ball that is too hard becomes brittle and will shatter in a grinding mill.
The specified chemical percentages represent a carefully calculated sweet spot. The goal is to produce a ball with maximum wear resistance that can still withstand the immense, repeated impacts inside a mill.
Matching Composition to Your Goal
Selecting the right grinding media composition is directly tied to the specific demands of your milling operation.
- If your primary focus is grinding highly abrasive material: A composition at the higher end of the chromium and carbon range is ideal to maximize the formation of wear-resistant carbides.
- If your primary focus is high-impact grinding (e.g., SAG mills): The composition may be adjusted with micro-alloying elements to enhance the toughness of the matrix, preventing ball breakage even if it means a slight reduction in absolute hardness.
Ultimately, understanding the role of each chemical element empowers you to select the most efficient and cost-effective grinding media for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Element | Typical Composition (%) | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Base Metal | Forms the structural matrix |
| Chromium (Cr) | 11.0 - 16.0 | Forms hard carbides for wear resistance |
| Carbon (C) | 2.0 - 3.0 | Essential for carbide formation |
| Manganese (Mn) | < 1.50 | Improves hardenability and strength |
| Silicon (Si) | < 1.50 | Acts as deoxidizer and strengthens matrix |
| Copper (Cu) | < 1.50 | Refines grain structure for toughness |
| Phosphorus (P) | < 0.10 | Impurity, causes embrittlement |
| Sulfur (S) | < 0.10 | Impurity, causes embrittlement |
Need grinding media optimized for your specific milling application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precisely engineered grinding media balls. Our expertise ensures you get the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your grinding processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill? Mastering SiC/Al Composite Mixing for Homogeneity
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill in MAX phase powder preparation? Unlock High-Purity Atomic Homogeneity
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the solid-state synthesis of NASICON-type solid electrolytes? Unlock Purity
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of (Cu–10Zn)-Al2O3 nanocomposites? High-Energy Alloying
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill in ODS steel prep? Achieving Nanoscale Mechanical Alloying












