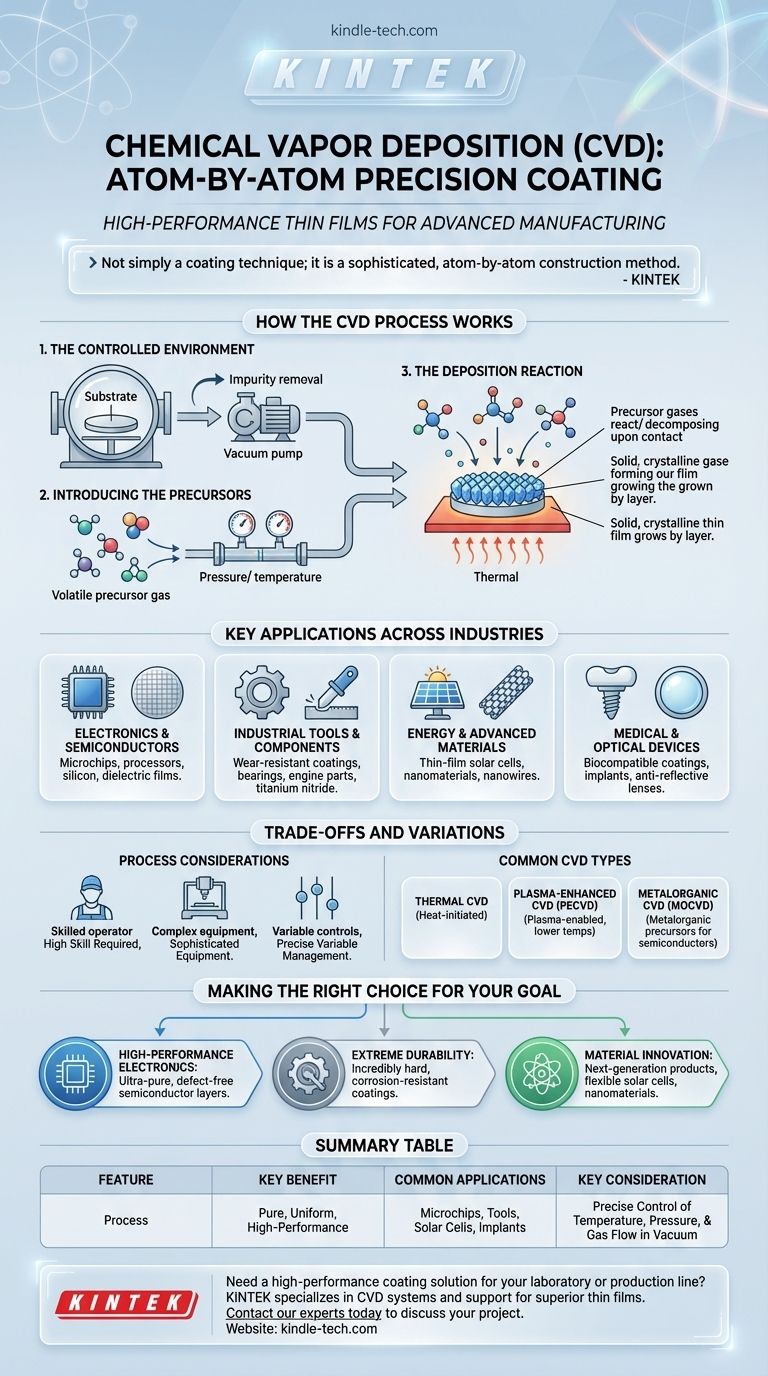
In essence, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a highly precise manufacturing process used to apply extremely thin, high-performance solid coatings onto a surface. In a controlled environment, a substrate (the object to be coated) is exposed to specific gaseous chemicals, known as precursors. These gases react and decompose on the substrate's surface, creating a solid, non-volatile thin film that bonds directly to it.
Chemical vapor deposition is not simply a coating technique; it is a sophisticated, atom-by-atom construction method. It allows for the creation of exceptionally pure and durable thin films that are fundamental to modern electronics, tools, and advanced materials.
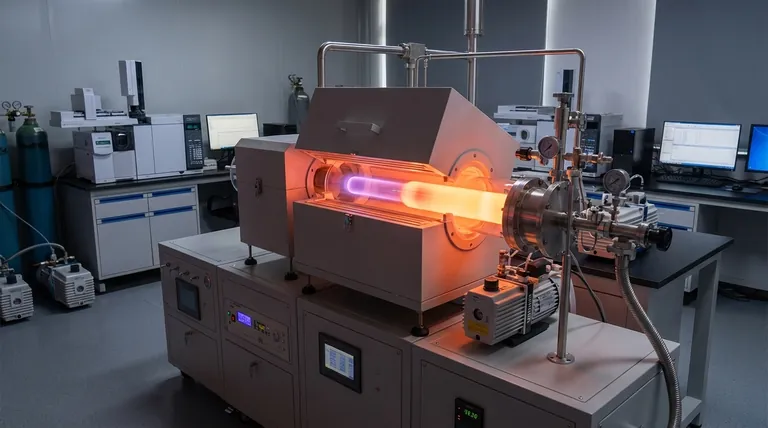

How the CVD Process Works
The core of CVD lies in transforming gaseous molecules into a solid layer through a controlled chemical reaction. The entire process takes place within a specialized reaction chamber under specific conditions.
The Controlled Environment
The object to be coated, or substrate, is placed inside a reaction chamber. This chamber is typically a vacuum environment to remove impurities that could interfere with the chemical reaction and the purity of the final film.
Introducing the Precursors
Volatile precursor gases, which contain the elements required for the final film, are introduced into the chamber. The flow, temperature, and pressure of these gases are meticulously controlled to manage the reaction.
The Deposition Reaction
When the precursor gases come into contact with the heated substrate, a chemical reaction is triggered. This reaction causes the precursors to decompose and deposit a solid material onto the substrate, building the desired thin film layer by layer.
Key Applications Across Industries
CVD is a foundational process used to create components that demand exceptional purity, durability, and specific electrical or physical properties. Its applications are widespread and critical.
Electronics and Semiconductors
This is one of the most significant uses of CVD. It is essential for depositing the thin films of silicon, dielectrics, and conductive materials required to manufacture microchips, processors, and other electronic components.
Industrial Tools and Components
CVD is used to apply hard, wear-resistant coatings onto cutting tools, bearings, and engine parts. These ceramic or metallic films, such as titanium nitride, dramatically increase durability and reduce corrosion.
Energy and Advanced Materials
The process is vital for producing thin-film solar cells by depositing photovoltaic materials onto a glass or metal substrate. It is also used to grow advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and nanowires for next-generation applications.
Medical and Optical Devices
Biocompatible coatings can be applied to medical implants using CVD to improve their integration with the body. It is also used to create anti-reflective coatings for lenses and other optical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While incredibly powerful, CVD is a complex and demanding process with several variations, each suited for different applications and materials.
Requirement for High Skill
Achieving a successful and consistent outcome with CVD requires a high level of expertise. Operators must precisely manage numerous variables, including temperature, pressure, gas composition, and flow rates.
Process Complexity
CVD systems involve sophisticated equipment, including vacuum pumps, heating systems, and gas handling controls. The complexity of the setup reflects the precision of the process itself.
The Many Types of CVD
There is no single CVD method. Different techniques are used depending on the material and desired outcome. Common variations include:
- Thermal CVD: Uses heat to initiate the reaction.
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Uses plasma to enable the reaction at lower temperatures.
- Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD): Uses metalorganic compounds as precursors, common in semiconductor manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the primary objective of the application is key to appreciating why CVD is often the chosen method.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: CVD is the definitive process for creating the ultra-pure, defect-free semiconducting layers that modern microchips depend on.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: CVD provides incredibly hard, corrosion-resistant coatings that significantly extend the operational life of industrial tools and mechanical parts.
- If your primary focus is material innovation: CVD is the fundamental technology used to construct next-generation products, from flexible solar cells to advanced nanomaterials.
Ultimately, chemical vapor deposition is a foundational technology that enables the creation of materials with precisely engineered properties, driving innovation across countless industries.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Gaseous precursors react on a heated substrate to form a solid thin film. |
| Key Benefit | Produces exceptionally pure, uniform, and high-performance coatings. |
| Common Applications | Microchips, wear-resistant tool coatings, solar cells, medical implants. |
| Key Consideration | Requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and gas flow in a vacuum chamber. |
Need a high-performance coating solution for your laboratory or production line?
Chemical vapor deposition is a sophisticated process that demands precision equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable CVD systems and support needed to achieve superior thin films for your research or manufacturing goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our CVD solutions can enhance your project's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















