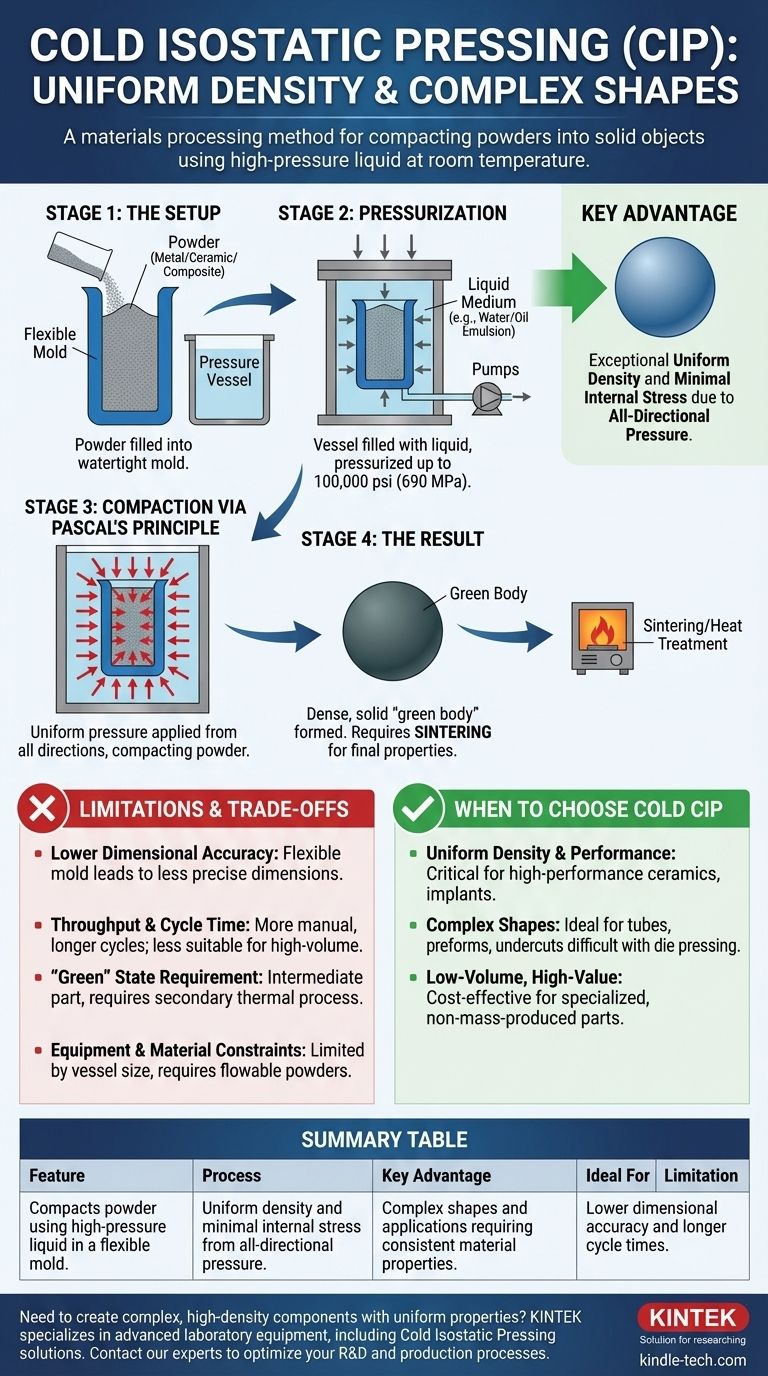
At its core, Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a materials processing method that compacts powders into a solid object using high-pressure liquid at or near room temperature. The powder is sealed in a flexible mold, which is then submerged in a fluid-filled pressure chamber. By applying intense, uniform pressure from all directions, the powder is compacted into a dense, solid shape known as a "green body" that is ready for further processing.
While many methods compact powders by pressing from one or two directions, Cold CIP’s defining advantage is its use of a liquid medium to apply equal pressure on all surfaces simultaneously. This creates components with exceptionally uniform density and minimal internal stress, which is critical for high-performance applications.

How the Cold CIP Process Works
The elegance of Cold CIP lies in its direct application of a fundamental law of physics to achieve a superior material outcome. The process can be broken down into a few key stages.
The Setup: Powder and Mold
The process begins with the raw material in powder form—typically metal, ceramic, or a composite. This powder is carefully filled into a flexible, watertight mold, often made from an elastomer like polyurethane or rubber, which defines the initial shape of the part.
The Pressurization Stage
The sealed mold is placed inside a robust pressure vessel. The vessel is then filled with a liquid medium, commonly a water-and-oil emulsion, which completely surrounds the mold. This liquid is then pressurized by pumps, with pressures reaching as high as 100,000 psi (approximately 690 MPa).
Compaction via Pascal's Principle
This stage is a direct application of Pascal's principle, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the container. The liquid transmits this immense pressure evenly onto every surface of the flexible mold, compressing the powder inside uniformly from all directions.
The Result: The "Green" Body
This all-around pressure forces the powder particles into tight mechanical contact, significantly increasing the material's density and forming a solid object. This resulting part is called a green body. It has sufficient strength to be handled but is still in a fragile state and requires a subsequent thermal process, like sintering, to fuse the particles and achieve its final mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No manufacturing process is without its compromises. Acknowledging the limitations of Cold CIP is essential for making an informed decision.
Lower Dimensional Accuracy
Because the compaction relies on a flexible mold, the final dimensions of the green body are less precise than those achieved with rigid steel dies used in uniaxial pressing. For components requiring tight tolerances, post-process machining is often necessary.
Throughput and Cycle Time
The process of loading the mold, sealing the vessel, pressurizing, depressurizing, and unloading is inherently more manual and time-consuming than automated pressing methods. This makes Cold CIP less suitable for very high-volume production of simple parts.
The "Green" State Requirement
It is critical to remember that Cold CIP produces an intermediate part. The green body has no true metallurgical bonds. The necessity of a secondary sintering or heat treatment step adds time, cost, and complexity to the overall manufacturing workflow.
Equipment and Material Constraints
The size of a component is ultimately limited by the capacity of the pressure vessel. Furthermore, the process is most effective with powders that have good flowability and compaction characteristics.
When to Choose Cold Isostatic Pressing
Deciding if Cold CIP is the right choice depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for density, shape, and volume.
- If your primary focus is uniform density and performance: Cold CIP is an excellent choice for creating components where consistent material properties are critical, such as in high-performance ceramics, refractory nozzles, or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes: The flexible mold allows for geometries that are difficult or impossible with traditional die compaction, making it ideal for parts like tubes, complex preforms, or components with undercuts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: You should likely consider other methods like die compaction, as CIP's longer cycle times can make it less cost-effective for simple, mass-produced parts.
By understanding its unique ability to create highly uniform green bodies, you can leverage Cold CIP to produce superior components that other methods simply cannot achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Compacts powder using high-pressure liquid in a flexible mold. |
| Key Advantage | Uniform density and minimal internal stress from all-directional pressure. |
| Ideal For | Complex shapes (tubes, preforms) and applications requiring consistent material properties. |
| Limitation | Lower dimensional accuracy and longer cycle times compared to die pressing. |
Need to create complex, high-density components with uniform properties?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment, including solutions for powder processing like Cold Isostatic Pressing. Our expertise can help you achieve superior material performance for your most demanding applications in ceramics, metals, and composites.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can optimize your R&D and production processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a cold isostatic press (CIP) required after Li/Li3PS4-LiI/Li battery assembly? Optimize Your Solid-State Interface
- What is the function of a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) in the fabrication of pouch-type all-solid-state batteries?
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts
- What are the different types of cold isostatic pressing? Wet-Bag vs. Dry-Bag for Your Production Needs
- What are the disadvantages of cold isostatic pressing? Key Limitations in Dimensional Accuracy & Speed
- What is the pressure for isostatic pressing? Unlock the Key to Uniform Material Densification
- What is the purpose of stainless steel cans in the HIP treatment? Achieve Full Densification of AlFeTiCrZnCu Alloys
- What is the role of a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) in C-PSC lamination? Enhance Solar Efficiency Without Heat



















