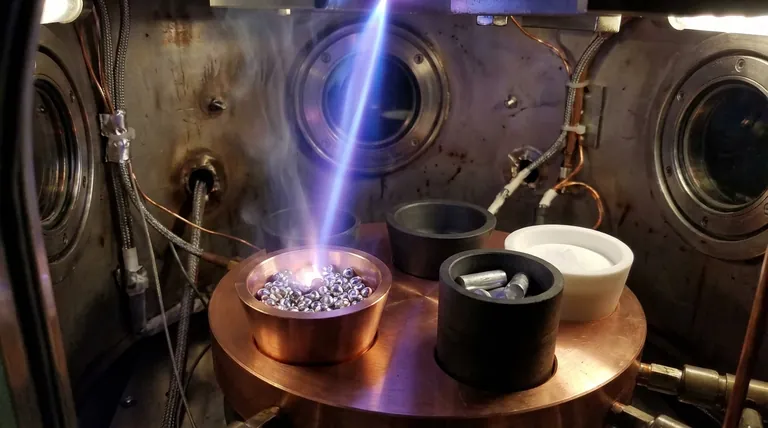
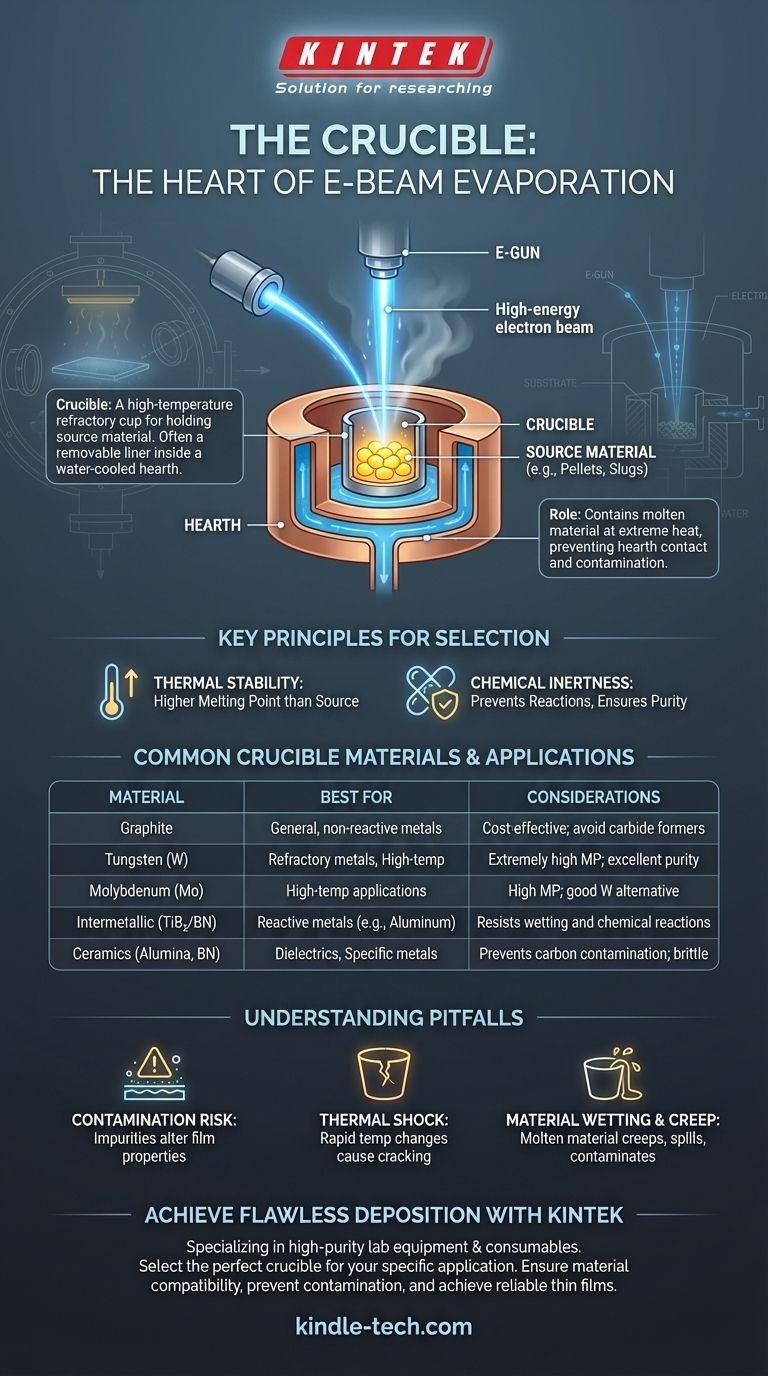
In electron-beam evaporation, the container that holds the source material is called a crucible. This component is a high-temperature, refractory cup that contains the material—often in pellet, slug, or powder form—that will be heated and vaporized by the electron beam.
The crucible is far more than a simple container; it is a critical process component whose material composition must be carefully chosen to ensure the purity and quality of the final deposited thin film. An incompatible crucible can contaminate the entire process.

The Role of the Crucible in E-Beam Evaporation
To understand the importance of the crucible, we must first place it within the context of the e-beam system. It is a central element in the successful vaporization of the source material.
A Critical Component in a Larger System
The crucible is typically a removable insert, often called a crucible liner, that sits inside a water-cooled copper structure known as a hearth. The hearth draws away immense amounts of heat, preventing the e-gun assembly from melting.
The electron beam is magnetically guided to strike the material inside the crucible. This focused energy melts and then evaporates the source material, creating a vapor cloud that travels upward to coat the substrate.
Why It's Necessary
The crucible's primary function is to contain the molten source material at extremely high temperatures. This prevents the valuable source material from alloying with or damaging the copper hearth.
Without a crucible, the molten source would directly contact the water-cooled hearth, leading to poor thermal transfer, potential contamination, and damage to the e-gun assembly.
Choosing the Right Crucible Material
The selection of a crucible is one of the most important decisions in designing an e-beam evaporation process. The choice is governed by two fundamental principles: thermal stability and chemical inertness.
The Principle of Compatibility
The core rule is that the crucible must have a significantly higher melting point than the source material it holds. It must also be chemically inert with respect to the molten source material to prevent reactions that could introduce impurities into the vapor stream.
Common Crucible Materials
Different materials are chosen based on the source material being evaporated.
- Graphite: A common and cost-effective choice for many metals that do not form carbides. It offers good thermal conductivity.
- Tungsten (W): Ideal for very high-temperature evaporations due to its extremely high melting point (3422 °C). It is often used for depositing other refractory metals.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Similar to tungsten but with a lower melting point (2623 °C). It is another excellent choice for high-temperature applications.
- Intermetallic (e.g., Titanium Diboride/Boron Nitride): These composite ceramics are excellent for evaporating reactive metals like Aluminum. They resist "wetting," where the molten metal creeps up and over the crucible walls.
- Ceramics (e.g., Alumina, Boron Nitride): Often used for evaporating dielectric materials or specific metals where carbon contamination from graphite is a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
A poor crucible choice can be the hidden cause of failed deposition runs, poor film quality, and inconsistent results. Understanding the potential failures is key to avoiding them.
Contamination Risk
This is the most significant pitfall. If the crucible material reacts with the molten source, atoms from the crucible itself can co-evaporate and become incorporated into your thin film as impurities, altering its electrical or optical properties.
Thermal Shock and Cracking
Many crucible materials, especially ceramics, are brittle. Rapid heating or cooling can cause them to crack, which can terminate the deposition process and potentially damage the system.
Material Wetting and Creep
Some molten materials have a tendency to "wet" the crucible surface. This can cause the material to creep up the crucible walls and spill over, contaminating the hearth and wasting valuable source material. This is a common problem when evaporating aluminum from an improper crucible.
How to Select the Correct Crucible
Your selection should be guided by the material you are depositing and your desired film properties. Always consult a compatibility chart from a reputable supplier.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Choose a crucible material that is exceptionally inert with your source, such as tungsten for refractory metals or a specific ceramic for dielectrics.
- If your primary focus is evaporating reactive metals like Aluminum: Use a specialized intermetallic or ceramic crucible (like TiB₂/BN) designed specifically to prevent wetting and chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, non-reactive metals: High-purity graphite is often a reliable and cost-effective starting point.
Choosing the right crucible is a foundational step that directly governs the success and quality of your thin-film deposition.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | General-purpose, non-reactive metals | Cost-effective; avoid with carbide-forming materials. |
| Tungsten (W) | Refractory metals, high-temperature applications | Extremely high melting point; excellent for high purity. |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | High-temperature applications | High melting point; good alternative to tungsten. |
| Intermetallic (e.g., TiB₂/BN) | Reactive metals like Aluminum | Resists wetting and chemical reactions. |
| Ceramics (e.g., Alumina) | Dielectrics, specific metals | Prevents carbon contamination; can be brittle. |
Achieve Flawless Thin-Film Deposition with KINTEK
Selecting the right crucible is critical to the success of your e-beam evaporation process. The wrong choice can lead to contaminated films, inconsistent results, and costly downtime.
KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables. We provide the expertise and crucible solutions—from graphite and tungsten to specialized ceramics—that laboratories need to ensure material compatibility, prevent contamination, and achieve reliable, high-quality thin films.
Let our experts help you select the perfect crucible for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your e-beam evaporation requirements and ensure the purity and performance of your depositions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- What is electron beam coating? A Guide to High-Performance PVD Thin Films
- How thick is the sputter coating for SEM? Achieve Optimal Imaging & Analysis
- What is sputter coating used for? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Electronics, Optics, and Tools
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials



















