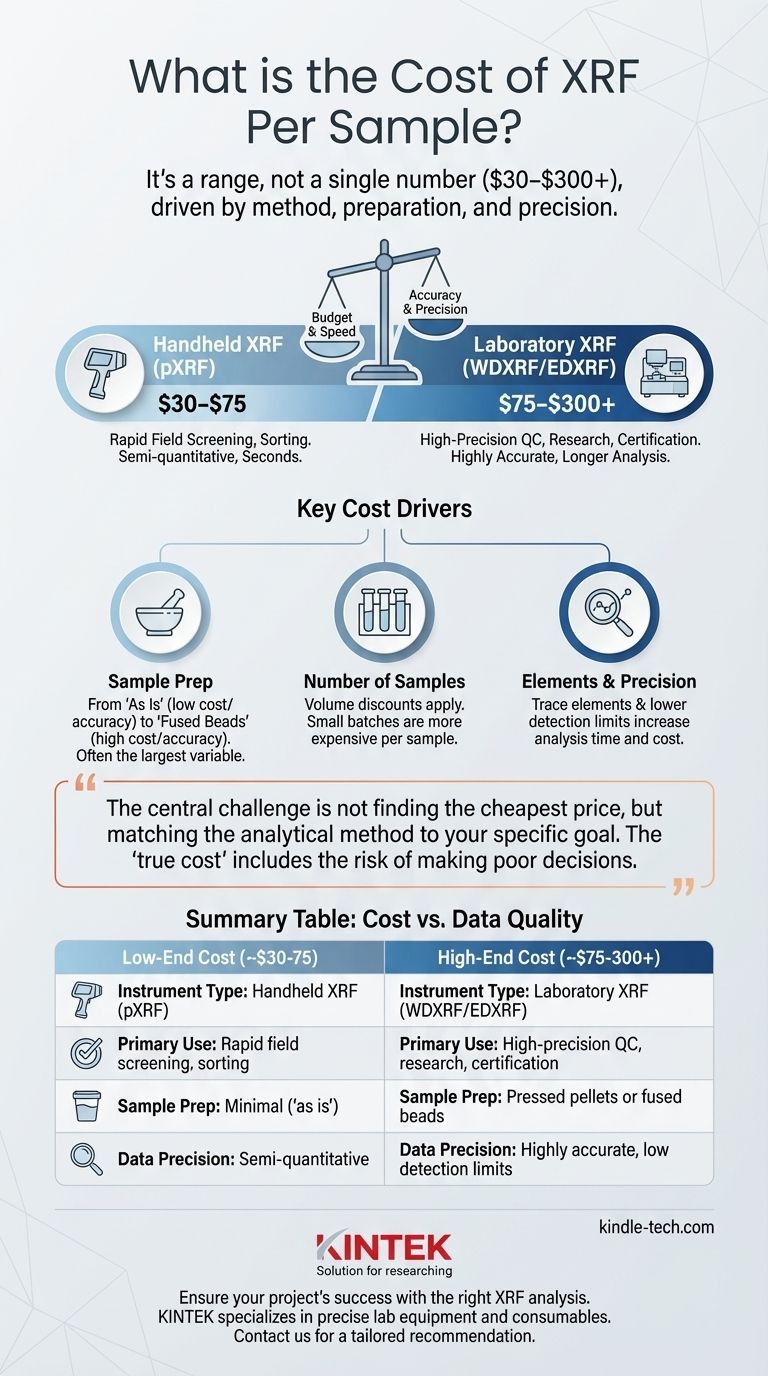
The cost of X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis is not a single number, but a range that typically falls between $30 and $300 per sample. This variation is driven by the type of XRF instrument used (handheld vs. laboratory), the complexity of sample preparation required, and the desired level of data precision. A quick, field-based screening will be at the lower end, while a high-precision, certified analysis will be at the upper end.
The central challenge is not finding the cheapest price, but matching the analytical method to your specific goal. The "true cost" of an XRF analysis includes the risk of making poor decisions based on data that isn't fit for your purpose.

The Two Worlds of XRF: Handheld vs. Laboratory
The most significant factor determining cost is the choice between a portable, field-based unit and a high-power laboratory instrument. They serve fundamentally different purposes.
Handheld XRF (pXRF): The "Point-and-Shoot" Approach
A portable XRF (pXRF) analyzer is designed for speed and convenience, providing semi-quantitative results in seconds. It is ideal for rapid screening, sorting, and preliminary assessments in the field.
The cost for pXRF analysis typically ranges from $30 to $75 per sample. This is excellent for identifying major elemental differences but lacks the precision needed for certification or trace element analysis.
Laboratory XRF (WDXRF/EDXRF): The High-Precision Standard
Laboratory-based systems, such as Wavelength Dispersive (WDXRF) or high-end Energy Dispersive (EDXRF) spectrometers, are large, powerful, and highly accurate. They are the gold standard for quantitative analysis required for quality control, research, and regulatory compliance.
The cost for laboratory XRF analysis usually ranges from $75 to over $300 per sample. The higher price reflects more extensive sample preparation, longer analysis times, and superior accuracy and detection limits.
Key Factors That Determine Your Final Cost
Beyond the instrument type, several other variables will influence the quote you receive from an analytical lab.
Sample Preparation
This is often the largest variable. The way a sample is prepared directly impacts the quality of the data and the cost.
- No Preparation: Analyzing a sample "as is" with a pXRF is the cheapest but least accurate method due to surface effects and heterogeneity.
- Pressed Pellets: Grinding the sample into a fine powder and pressing it into a pellet is a common lab technique. This costs more but significantly improves accuracy.
- Fused Beads: The most expensive and accurate method involves melting the sample with a flux to create a perfectly homogeneous glass disc. This eliminates mineralogical and particle size effects, providing the highest quality data.
Number of Samples
Standard volume discounts apply. Analyzing 500 samples will have a much lower per-sample cost than analyzing only 5. Labs often have a minimum charge to cover their setup and calibration time, which makes very small batches expensive on a per-sample basis.
Elements of Interest & Precision
A standard analysis for a suite of common elements is more affordable than a custom analysis looking for specific trace elements at very low detection limits. Requiring the instrument to count for longer to achieve higher precision will also increase the cost.
Data Reporting and Interpretation
Receiving a raw data spreadsheet is the most basic and cheapest option. A full report that includes quality control summaries, data interpretation, and professional sign-off by a chemist or geologist will add to the final cost but provides far more value and context.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Data Quality
Choosing an XRF provider is a balancing act between budget and confidence in the results.
The Pitfall of the Cheapest Option
Opting for a low-cost, low-quality analysis for a critical application can be a costly mistake. If you make an incorrect engineering, environmental, or manufacturing decision, the cost of remediation or failure will dwarf the initial savings on analysis.
When "Good Enough" is the Right Choice
For many applications, high precision is overkill. If you are simply sorting scrap metal into broad categories (e.g., stainless steel vs. aluminum), a fast and affordable pXRF scan is the perfect tool for the job. The key is to define how good your data needs to be before you request a quote.
The Hidden Cost of Bad Sampling
Remember that even a perfect, high-cost analysis is worthless if the sample sent to the lab is not representative of the material you are investigating. The cost and effort of developing a proper sampling protocol are critical to the overall success of your project.
How to Get an Accurate Quote for Your Project
To ensure you are paying for the right level of analysis, you must first define your objective. When contacting a lab, be prepared to answer what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening or initial fieldwork: A handheld pXRF analysis will provide the best value and fastest turnaround.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy quantitative results for certification or research: You need lab-based XRF, likely with fused bead sample preparation for the highest data quality.
- If your primary focus is a large-scale project (e.g., mine exploration): Consider a tiered approach—screen thousands of samples with pXRF and confirm a select percentage with high-quality lab XRF.
Ultimately, understanding your analytical goal is the first and most important step in determining the true cost of your XRF analysis.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Low-End Cost (~$30-75) | High-End Cost (~$75-300+) |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument Type | Handheld XRF (pXRF) | Laboratory XRF (WDXRF/EDXRF) |
| Primary Use | Rapid field screening, sorting | High-precision QC, research, certification |
| Sample Prep | Minimal ('as is') | Pressed pellets or fused beads |
| Data Precision | Semi-quantitative | Highly accurate, low detection limits |
Ensure your project's success with the right XRF analysis.
KINTEK specializes in providing precise lab equipment and consumables for accurate material analysis. Whether you need robust handheld units for field screening or high-performance laboratory systems for certification, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to balance cost and data quality.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a tailored recommendation that fits your budget and accuracy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Temperature Measurement Double-Sided Coated Germanium Ge Lens
People Also Ask
- What is the use of C type power press? Versatile Metal Forming for Punching, Stamping, and Bending
- What are KBr pellets used for? A Key to Accurate FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
- What products can be made on a hydraulic press? From Metal Parts to Lab Samples
- What is the difference between hydraulic and mechanical press machine? Choose the Right Press for Your Application
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to CSP for transparent ceramics? Achieve High-Density Densification
- How does the pressing machine work? A Guide to Force, Heat, and Control
- How do you prepare samples for IR spectroscopy? A Step-by-Step Guide for Solids, Liquids, and Gases
- What materials are used in press forming? Choosing the Right Metal for Your Stamped Parts










