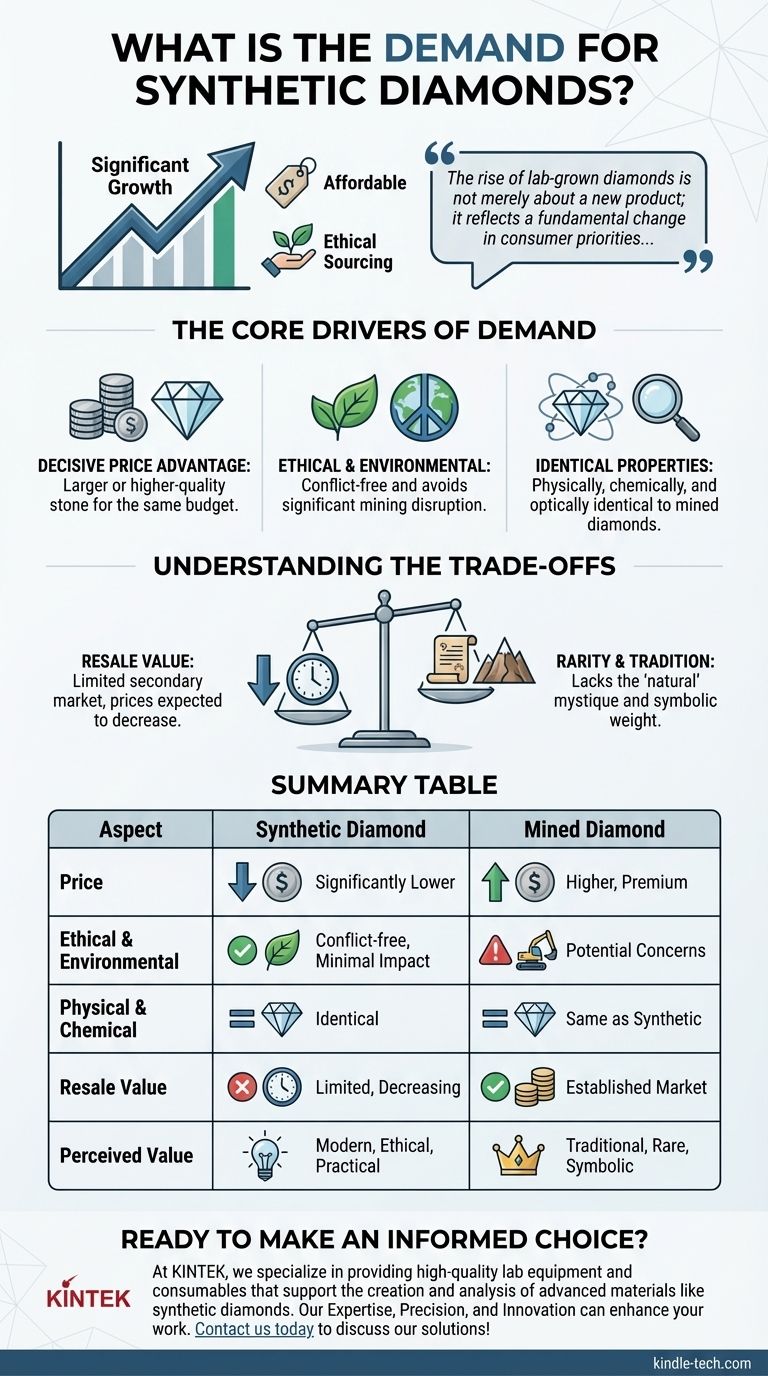
The demand for synthetic diamonds is experiencing significant growth. This increase is primarily fueled by consumers seeking more affordable and ethically sourced alternatives to traditional mined diamonds, marking a notable shift in the fine jewelry market.
The rise of lab-grown diamonds is not merely about a new product; it reflects a fundamental change in consumer priorities, where cost-effectiveness and ethical transparency are becoming as important as the tradition and perceived rarity of mined gems.

The Core Drivers of Synthetic Diamond Demand
The increasing demand is not a random trend but a response to several key factors that align with modern consumer values. Understanding these drivers is essential to grasping the current state of the jewelry market.
The Decisive Price Advantage
For many, the most compelling factor is price. A lab-grown diamond can be significantly less expensive than a natural diamond of the exact same size, cut, clarity, and color.
This price difference allows consumers to purchase a larger or higher-quality stone for the same budget, making them a highly practical choice for engagement rings and other fine jewelry.
The Ethical and Environmental Consideration
Modern consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social impact of their purchases. Lab-grown diamonds offer a clear answer to these concerns.
They are inherently conflict-free and avoid the significant environmental disruption associated with traditional diamond mining, appealing to buyers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Identical Physical and Chemical Properties
Crucially, synthetic diamonds are not "fake" diamonds. They are physically, chemically, and optically identical to mined diamonds.
They are made of the same material (crystallized carbon) and exhibit the same brilliance, fire, and hardness. This scientific reality has been a major factor in overcoming consumer hesitation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are clear, an objective analysis requires acknowledging the trade-offs and differing market perceptions that still exist.
The Question of Resale Value
The primary trade-off is long-term value. Mined diamonds have an established, albeit complex, secondary market that has existed for centuries.
Lab-grown diamonds currently have a very limited resale market. As production technology improves and supply increases, their prices are expected to continue to decrease, making them a poor choice for anyone viewing a diamond as a financial investment.
The "Rarity" and "Tradition" Factor
For some, the appeal of a natural diamond is its origin story—a unique gem formed deep within the Earth over billions of years. This perception of rarity and timelessness is a powerful emotional driver.
Because lab-grown diamonds can be created in a matter of weeks, they do not possess this same mystique. This distinction remains a key factor for those who value tradition and the symbolic weight of a natural gem.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a synthetic and a mined diamond depends entirely on your personal priorities. There is no single "better" option, only the right option for you.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget while ensuring ethical sourcing: A synthetic diamond offers a clear and compelling advantage.
- If your primary focus is long-term value retention and the tradition of a natural gem: A mined diamond with proper certification remains the conventional choice.
Ultimately, understanding these key differences empowers you to choose the diamond that truly aligns with your personal values and priorities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Synthetic Diamond | Mined Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Significantly lower for same quality | Higher, premium pricing |
| Ethical & Environmental Impact | Conflict-free, minimal environmental disruption | Potential ethical concerns, significant mining impact |
| Physical & Chemical Properties | Identical to mined diamonds | Same as synthetic |
| Resale Value | Limited, prices expected to decrease | Established secondary market |
| Perceived Value | Modern, ethical, practical | Traditional, rare, symbolic |
Ready to Make an Informed Choice?
Whether you're a jeweler, researcher, or enthusiast, understanding the nuances of synthetic diamonds is key. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support the creation and analysis of advanced materials like synthetic diamonds.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expertise: We serve laboratories and industries at the forefront of material science.
- Precision: Our equipment ensures accurate and reliable results for your research and production needs.
- Innovation: Stay ahead with tools designed for cutting-edge applications.
Let us help you achieve your goals. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your work in synthetic diamond technology and beyond!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses











