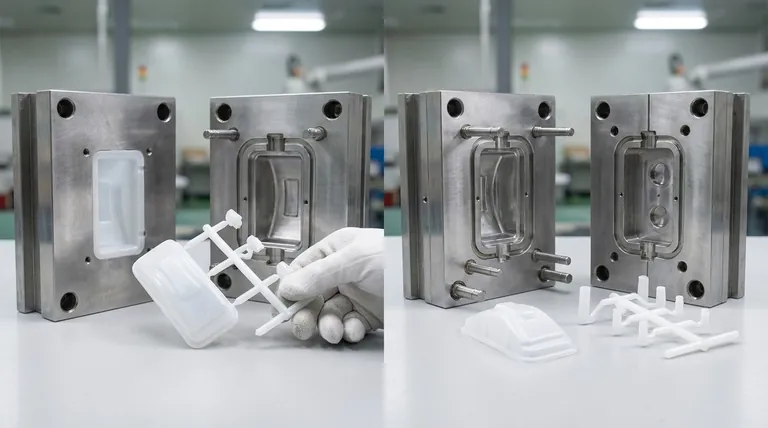
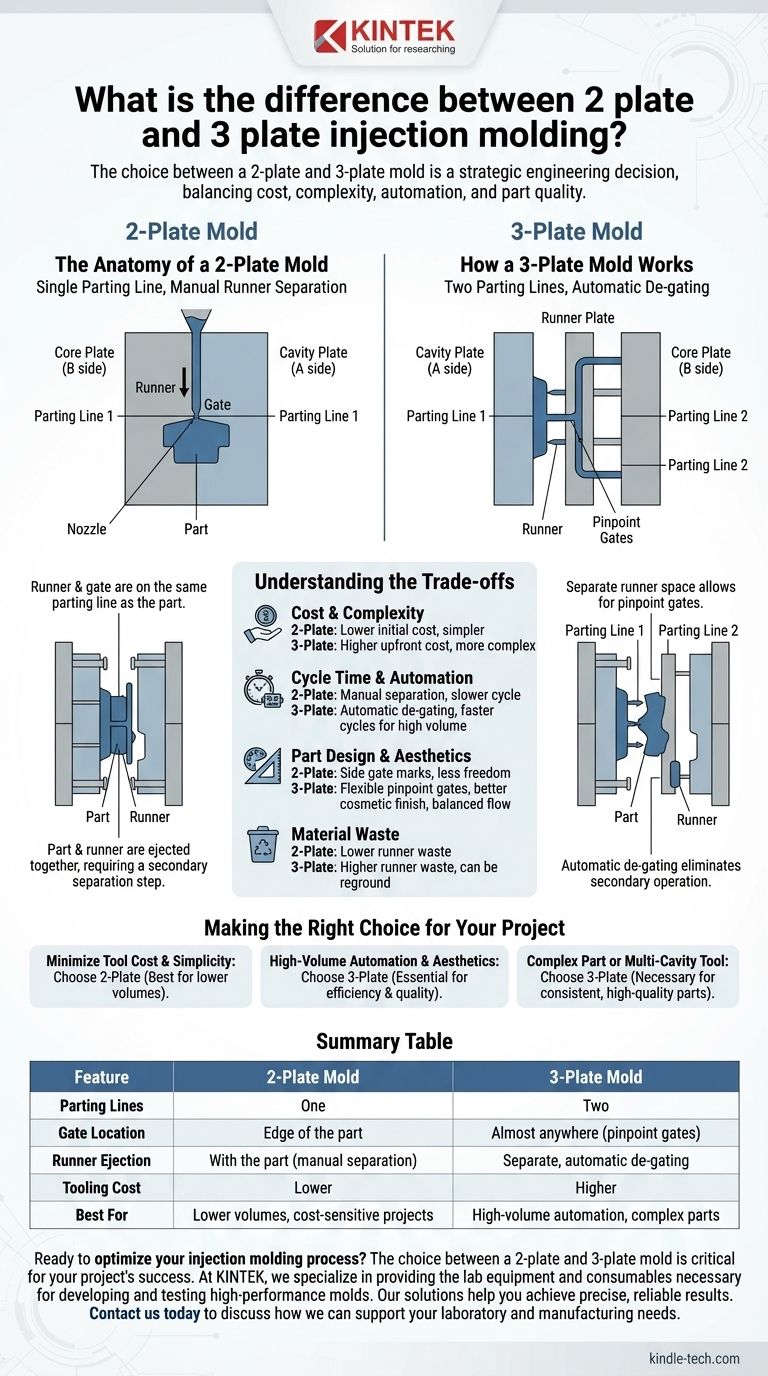
The fundamental difference between a 2-plate and 3-plate injection mold lies in their construction, which directly dictates how molten plastic is delivered to the part and how the waste material (the runner) is managed. A 2-plate mold has a single parting line and ejects the part and runner together, typically gating on the part's edge. A 3-plate mold uses two parting lines, allowing for more flexible gating locations and automatic separation of the runner from the part during ejection.
The choice between a 2-plate and 3-plate mold is a strategic engineering decision. It balances the simplicity and lower cost of a 2-plate design against the superior automation, design flexibility, and aesthetic finish offered by a more complex 3-plate tool.

The Anatomy of a 2-Plate Mold
A 2-plate mold is the most common and straightforward type of injection mold. Its design is based on two primary halves that come together.
A Single Parting Line
The entire mold splits open along a single plane, known as the parting line. This design consists of a cavity plate (the "A" side) and a core plate (the "B" side).
Runner and Gate System
In this design, the runner (the channel that carries plastic from the machine nozzle) and the gate (the opening into the part) are located on the same parting line as the part itself. This means the runner system is physically attached to the molded part upon ejection.
The Ejection Process
When the mold opens, the part and the attached runner are pushed out together by ejector pins. This requires a secondary operation—either manual or robotic—to separate the finished part from the runner scrap.
How a 3-Plate Mold Works
A 3-plate mold introduces a higher level of complexity to solve the limitations of the 2-plate design, particularly regarding gating and automation.
Two Parting Lines
As the name implies, this mold is constructed with three primary plates, creating two distinct parting lines. This design adds a "runner plate" between the top clamping plate and the cavity plate, creating a separate space just for the runner system.
Advanced Gating Flexibility
The key advantage of the second parting line is that it separates the runner from the part geometry. This allows the use of pinpoint gates, which can be placed almost anywhere on the surface of the part, not just on its edge. This is critical for achieving balanced plastic flow into complex shapes or multiple cavities.
Automatic De-gating
During the mold opening sequence, the first parting line opens to break the small pinpoint gates from the part. The second parting line then opens to eject the finished part, while the runner is ejected separately. This automatic de-gating eliminates the need for a secondary separation step, enabling faster and more automated production cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct mold type requires a clear understanding of the compromises between cost, performance, and design freedom.
Cost and Complexity
A 2-plate mold is simpler to design, manufacture, and maintain, resulting in a lower initial tooling cost. A 3-plate mold is significantly more complex, requires more precision machining, and has a higher upfront cost.
Cycle Time and Automation
For high-volume production, the 3-plate mold is often superior. Its automatic de-gating capability reduces cycle time and labor costs by eliminating the post-molding separation step.
Part Design and Aesthetics
3-plate molds offer far greater design freedom. Gating onto the center of a part provides a better cosmetic finish and can solve filling issues, whereas the side gates of a 2-plate mold will always leave a witness mark on the part's edge.
Material Waste
Because of their more intricate runner system, 3-plate molds often generate more plastic scrap per cycle. While this material can often be reground and reused, it is an important factor in material cost calculation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate mold is not about which is "better," but which is right for your specific application and goals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial tool cost and part simplicity: A 2-plate mold is the most direct and economical solution, especially for lower production volumes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume automation and optimal part aesthetics: A 3-plate mold's automatic de-gating and flexible pinpoint gate location are essential for efficiency and quality.
- If you are designing a complex part or a multi-cavity tool: The balanced filling and hidden gate marks provided by a 3-plate mold are often necessary to achieve consistent, high-quality parts.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the right tool that aligns perfectly with your part design, production volume, and budget.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 2-Plate Mold | 3-Plate Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Parting Lines | One | Two |
| Gate Location | Edge of the part | Almost anywhere (pinpoint gates) |
| Runner Ejection | With the part (manual separation) | Separate, automatic de-gating |
| Tooling Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best For | Lower volumes, cost-sensitive projects | High-volume automation, complex parts |
Ready to optimize your injection molding process? The choice between a 2-plate and 3-plate mold is critical for your project's success, impacting cost, efficiency, and part quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing high-performance molds. Our solutions help you achieve precise, reliable results. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs with the right equipment for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity

















