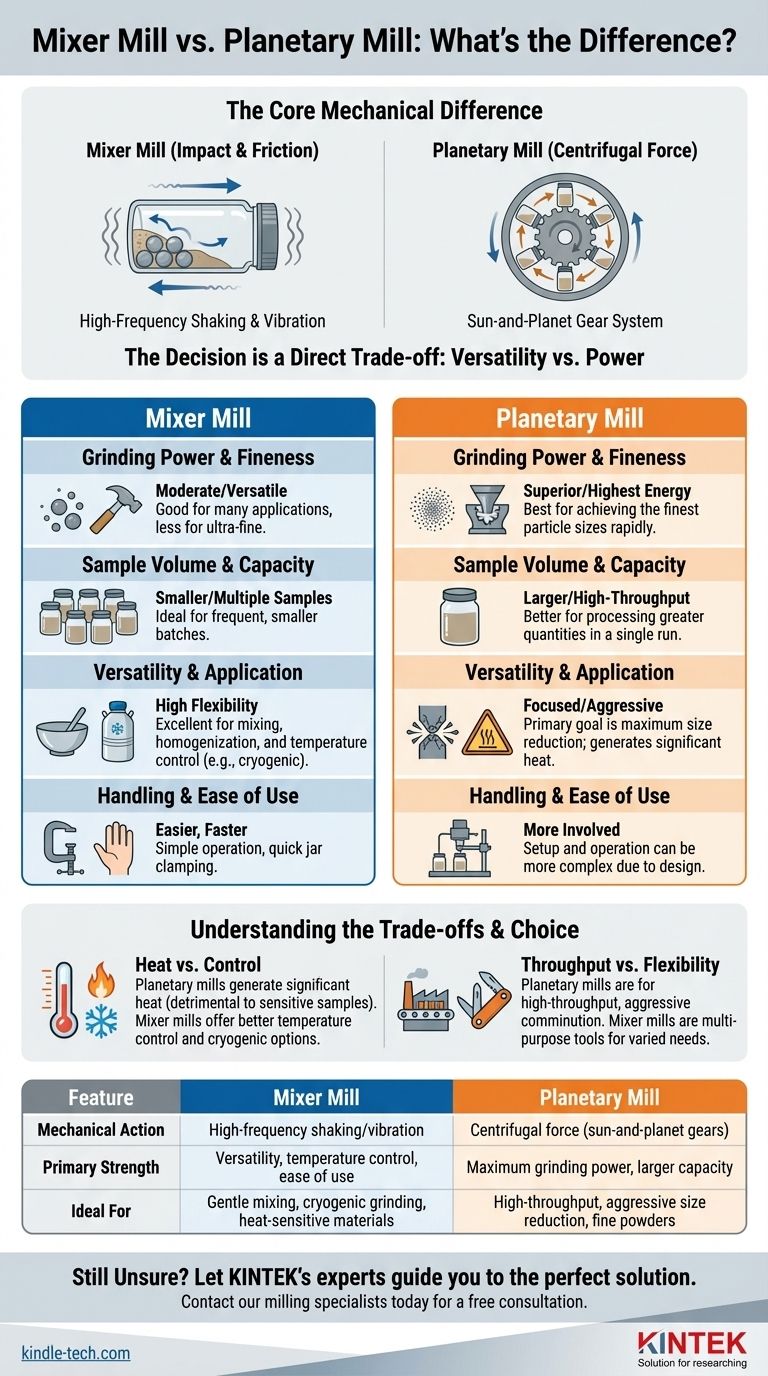
At a fundamental level, the difference between a mixer mill and a planetary mill lies in their mechanical action. A mixer mill utilizes high-frequency shaking and vibration to grind, while a planetary mill employs powerful centrifugal forces generated by a sun-and-planet gear system. This core distinction in operating principle leads to significant differences in power, capacity, and application suitability.
The decision between these two instruments is a direct trade-off. You must choose between the superior grinding power and larger capacity of a planetary mill versus the enhanced versatility, process control, and ease of use offered by a mixer mill.
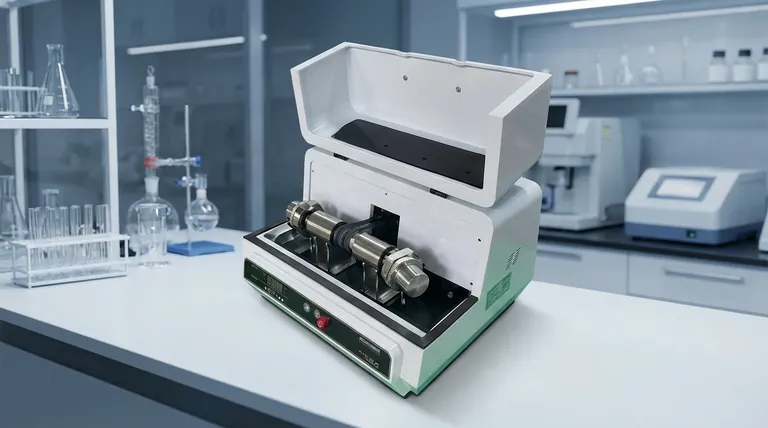

The Core Mechanical Difference
To understand which mill is right for you, it is essential to visualize how each one imparts energy to your sample.
How a Mixer Mill Works
A mixer mill grinds through impact and friction. The grinding jars, which contain the sample and grinding balls, are clamped into the machine and shaken in a high-frequency, typically horizontal, oscillating motion.
This rapid movement causes the grinding balls to collide with each other and the sample, effectively pulverizing the material. The action is similar to an extremely fast and powerful cocktail shaker.
How a Planetary Mill Works
A planetary mill generates much higher energy through centrifugal forces. The grinding jars are mounted on a large rotating disk (the "sun wheel") and simultaneously rotate on their own axis in the opposite direction (like "planets").
This compound motion creates extremely high acceleration on the grinding balls inside. The balls are thrown against the inner wall of the jar, crushing the sample with immense force.
Key Performance Characteristics Compared
The different operating principles result in distinct performance profiles.
Grinding Power and Final Fineness
Planetary mills offer significantly more power. The immense centrifugal forces achieve a higher energy input, allowing for more effective and faster size reduction. This makes them the superior choice for reaching the finest possible particle sizes.
Sample Volume and Capacity
Due to their design, planetary mills typically accommodate larger grinding jars and, therefore, larger sample volumes. They are better suited for processing greater quantities of material in a single run.
Versatility and Application
Mixer mills are generally more versatile. They excel not only at dry, wet, and even cryogenic grinding but are also highly effective for simple mixing and homogenization of powders without aggressive size reduction.
Handling and Ease of Use
For routine laboratory work, mixer mills often provide easier handling. Clamping the jars is typically faster, and the overall operation is more straightforward, making them efficient for frequent use with multiple small samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing one type of mill over the other involves accepting a clear set of compromises.
The Cost of Power: Heat Generation
The high energy input of a planetary mill inevitably generates significant heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive materials, potentially altering their chemical or physical properties.
The Benefit of Control: Temperature Management
A key advantage of many mixer mills is the ability to control the process temperature. Their design can more easily accommodate cooling systems or be used for cryogenic grinding with liquid nitrogen, which is critical for protecting delicate or biological samples.
Throughput vs. Flexibility
A planetary mill is a workhorse designed for high-throughput, aggressive comminution. Its goal is maximum size reduction as quickly as possible.
A mixer mill provides greater flexibility. It can perform gentle homogenization, high-impact grinding, or temperature-controlled processing, making it a multi-purpose tool for varied laboratory needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum size reduction and high throughput: A planetary mill is the superior choice for achieving the finest particle sizes with larger sample volumes.
- If your primary focus is versatility and process control: A mixer mill offers greater flexibility for diverse tasks, including the grinding of temperature-sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is ease of use for frequent, smaller samples: A mixer mill's simpler handling makes it a more efficient option for a busy laboratory environment.
Understanding this core distinction between raw power and controlled versatility is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mixer Mill | Planetary Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Action | High-frequency shaking/vibration | Centrifugal force (sun-and-planet gears) |
| Primary Strength | Versatility, temperature control, ease of use | Maximum grinding power, larger capacity |
| Ideal For | Gentle mixing, cryogenic grinding, heat-sensitive materials | High-throughput, aggressive size reduction, fine powders |
Still Unsure Which Mill is Right for Your Application?
Let KINTEK's experts guide you to the perfect solution. Selecting the right milling equipment is critical for achieving accurate and reproducible results. Our team specializes in matching your specific lab needs—whether for gentle homogenization, cryogenic grinding, or high-throughput pulverization—with the ideal equipment from our range of mixer mills and planetary mills.
We provide more than just equipment; we provide a partnership for your lab's success. By contacting us, you'll receive:
- Personalized Consultation: We analyze your sample type, desired fineness, and throughput requirements to recommend the optimal mill.
- Superior Process Control: Ensure the integrity of your temperature-sensitive materials with our advanced milling solutions.
- Enhanced Laboratory Efficiency: Streamline your sample preparation with reliable, easy-to-use equipment designed for busy lab environments.
Don't compromise on your results. Contact our milling specialists today for a free consultation and discover how KINTEK can optimize your sample preparation workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the average particle size of a ball mill? Master the Variables for Precise Grinding Results
- What is the procedure of a ball mill experiment? Master Particle Size Reduction for Your Lab
- What is the product size range of a ball mill? Achieve 40-300 Microns or Finer Grinding
- What is the working capacity of a ball mill? Optimize Volume, Speed, and Grinding Media for Maximum Output
- What is the ball mill used for in chemistry? Unlock Solvent-Free Synthesis & Nanomaterial Creation



















