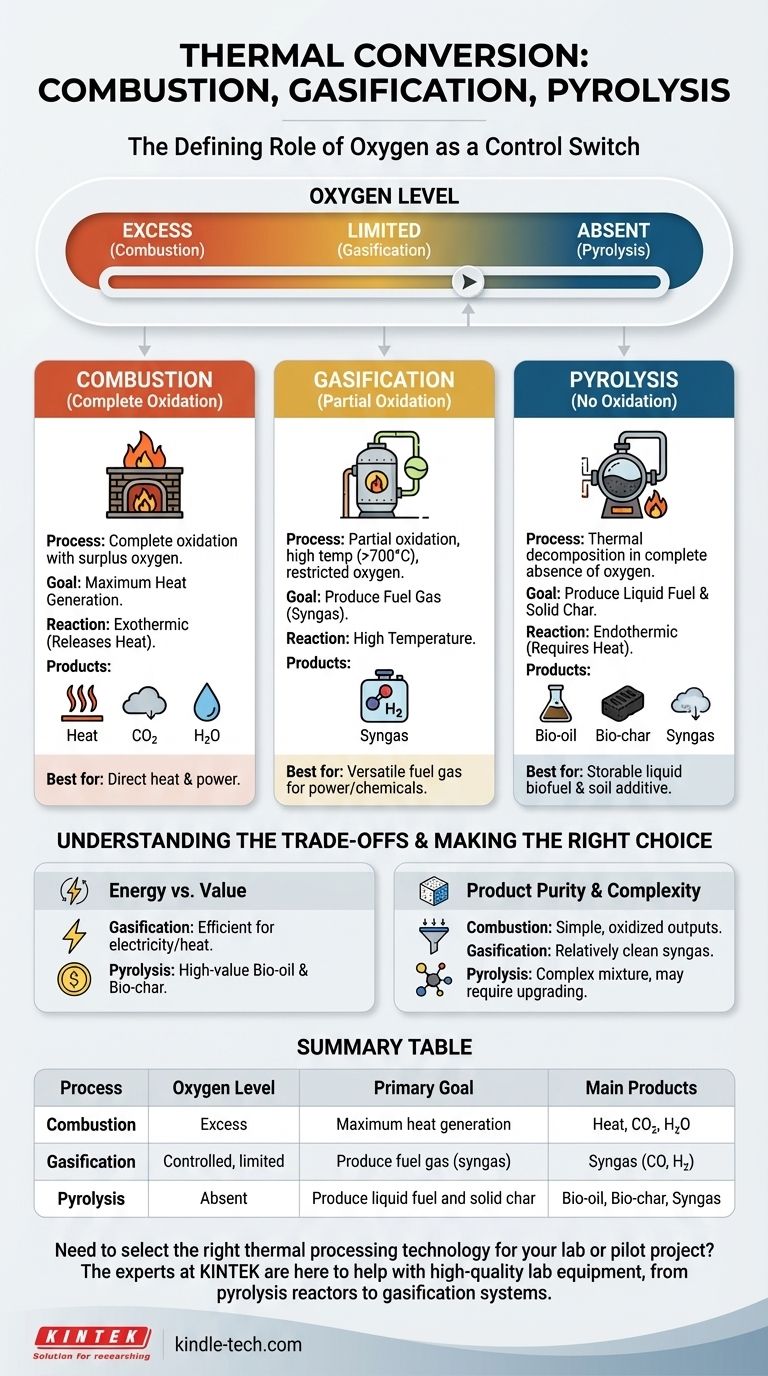
At their core, the fundamental difference between combustion, pyrolysis, and gasification is the amount of oxygen present during the process. Combustion involves the complete oxidation of a material with an excess of oxygen, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in the complete absence of oxygen, and gasification is a partial oxidation that occurs in a controlled, oxygen-starved environment.
The level of oxygen acts as a control switch, determining whether you completely burn a material for heat (combustion), partially break it down into a fuel gas (gasification), or thermally deconstruct it into liquid fuel and solid char (pyrolysis).

The Defining Factor: The Role of Oxygen
The presence and quantity of an oxidizing agent, typically oxygen from the air, dictates the chemical pathways, the final products, and the primary application of each thermal conversion technology.
Combustion (Complete Oxidation)
Combustion is the most familiar process, commonly known as burning. It is an exothermic reaction that occurs with a surplus of oxygen.
The goal of combustion is to achieve complete oxidation, releasing the maximum amount of a material's stored chemical energy as heat.
Its primary products are heat, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O). It is the simplest method for direct heat and power generation.
Gasification (Partial Oxidation)
Gasification takes place at high temperatures (typically above 700°C) with a restricted, insufficient supply of oxygen. It is not complete combustion.
The process is designed to convert organic material into a combustible gas mixture known as synthesis gas, or syngas.
This syngas is primarily composed of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2), which can be burned to generate electricity or used as a feedstock for producing liquid fuels and chemicals.
Pyrolysis (No Oxidation)
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the complete absence of oxygen. The material is simply heated, causing its complex molecules to break down into smaller ones.
Because there is no oxidation, pyrolysis is primarily an endothermic process, meaning it requires a consistent external heat source.
This process uniquely produces three distinct products: a liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), a solid carbon-rich residue called bio-char, and a smaller amount of non-condensable gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a technology depends entirely on the desired end product, as each process comes with distinct advantages and complexities.
Energy Efficiency vs. Product Value
Gasification is generally considered more efficient than pyrolysis for the direct production of electricity and heat from the resulting syngas.
However, the high-value products of pyrolysis—bio-oil for transportation fuel and bio-char for soil amendment—offer different economic and environmental pathways that direct energy generation does not.
Product Purity and Complexity
Combustion produces simple, fully oxidized outputs. Gasification produces a relatively clean syngas mixture suitable for engines or turbines.
Pyrolysis, on the other hand, can produce a complex mixture of hydrocarbon compounds in its gas and oil streams. These often require an additional processing step, like catalytic reforming, to be upgraded into cleaner, more uniform fuels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal technology is defined by your objective, not by the inherent superiority of one process over another.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat and electricity generation: Combustion is the most direct and established technology.
- If your primary focus is creating a versatile fuel gas (syngas) for power or chemical synthesis: Gasification provides the ideal feedstock for these applications.
- If your primary focus is producing storable liquid biofuel and a solid bio-char soil additive: Pyrolysis is the only process specifically designed to yield these outputs.
Ultimately, understanding the role of oxygen empowers you to select the precise thermal process that transforms your feedstock into your desired product.
Summary Table:
| Process | Oxygen Level | Primary Goal | Main Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Excess | Maximum heat generation | Heat, CO₂, H₂O |
| Gasification | Controlled, limited | Produce fuel gas (syngas) | Syngas (CO, H₂) |
| Pyrolysis | Absent | Produce liquid fuel and solid char | Bio-oil, Bio-char, Syngas |
Need to select the right thermal processing technology for your lab or pilot project? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal conversion research needs, from pyrolysis reactors to gasification systems. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















