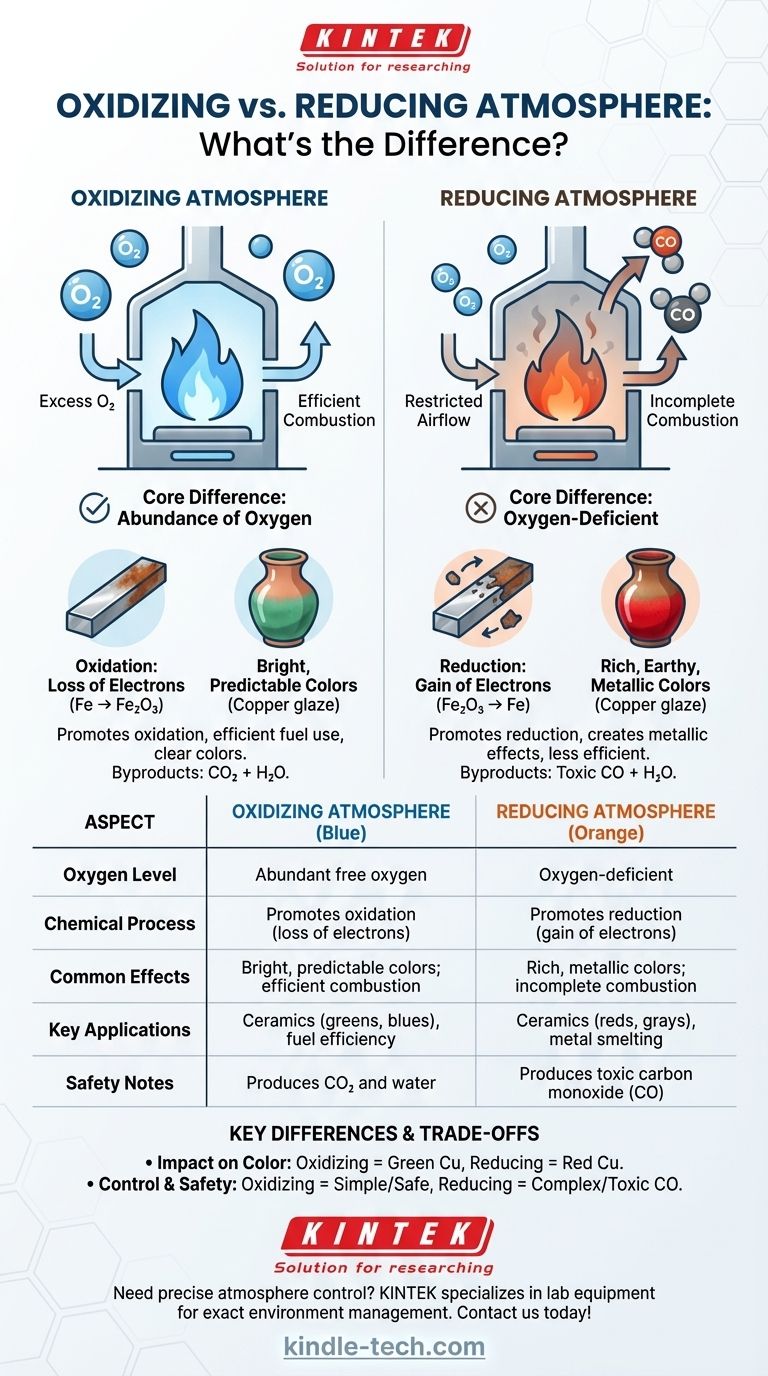
At its core, the difference between an oxidizing and a reducing atmosphere is the availability of oxygen. An oxidizing atmosphere has an abundance of free oxygen, which promotes chemical reactions like combustion and corrosion. A reducing atmosphere is oxygen-deficient and actively strips oxygen atoms from materials, reversing the process of oxidation.
The choice between an oxidizing or reducing atmosphere is a fundamental control mechanism in materials science and chemistry. It's not just about the environment; it's a tool used to deliberately change the chemical state and physical properties of a material.
What is an Oxidizing Atmosphere?
An oxidizing atmosphere is the "default" state we live in, defined by the presence of excess oxygen. In high-temperature applications like kilns or furnaces, it's maintained by ensuring a steady and ample supply of fresh air.
The Role of Excess Oxygen
The key characteristic is that there is more oxygen available than is required to completely combust any fuel present. This surplus oxygen is chemically active and ready to react with other materials.
The Chemical Process: Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction where a substance loses electrons. While other elements can cause this, in this context, it almost always involves a substance bonding with oxygen. This is the same fundamental process that causes iron to rust or a fire to burn cleanly.
Common Effects and Applications
In an oxidizing fire, fuel burns efficiently and completely, producing maximum heat with little to no soot. In ceramics, it yields clear, bright, and often predictable colors from glazes and clay bodies (e.g., iron producing tans and reds, copper producing greens and blues).
What is a Reducing Atmosphere?
A reducing atmosphere is an oxygen-starved environment. It is deliberately created in a kiln or furnace by restricting the air intake or introducing more fuel than the available air can burn.
The Role of Unburnt Fuel
With insufficient oxygen for complete combustion, the unburnt fuel releases compounds like carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen. These compounds are chemically unstable and aggressively seek out oxygen atoms to bond with.
The Chemical Process: Reduction
Reduction is the opposite of oxidation; it is a chemical reaction where a substance gains electrons. In this environment, the carbon monoxide actively "steals" oxygen atoms from metallic oxides within the clay or glazes, reducing them back to a more metallic state.
Common Effects and Applications
A reducing fire is often cooler and smokier, a sign of incomplete combustion. It is essential for processes like smelting metal from ore. In ceramics, it creates rich, complex, and often unpredictable earthy and metallic colors (e.g., iron producing deep blues and grays, copper producing vibrant reds).
Understanding the Key Differences and Trade-offs
The decision to use one atmosphere over the other is driven entirely by the desired outcome, but it comes with significant trade-offs.
Impact on Color and Material Properties
This is the most visible difference. A glaze containing copper oxide will turn green in an oxidizing atmosphere. The same glaze, when fired in a reducing atmosphere, will have its oxygen stripped away, reducing the copper to its metallic form and creating a brilliant red.
Control and Efficiency
Achieving an oxidizing atmosphere is simple: provide plenty of air. Creating a reducing atmosphere requires active management, such as closing a damper to starve the fire of oxygen. This makes the process less fuel-efficient, as you are not extracting all the potential energy from your fuel.
Safety and Byproducts
Oxidizing fires primarily produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water. Reducing fires, due to incomplete combustion, produce significant amounts of carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas. Proper ventilation is absolutely critical when creating a reducing atmosphere.
How to Choose the Right Atmosphere
Your choice depends entirely on your material and your goal. The atmosphere is not a background condition; it is an active ingredient in the chemical process.
- If your primary focus is bright, stable colors and fuel efficiency: Use an oxidizing atmosphere by ensuring constant, ample airflow to your kiln or furnace.
- If your primary focus is rich, earthy, or metallic effects in ceramics: Use a reducing atmosphere by carefully restricting airflow at specific temperatures to force the chemical reduction of metallic oxides.
- If your primary focus is smelting ore or preventing surface scale on steel: Use a strongly reducing atmosphere to strip oxygen from the ore or prevent it from forming on the metal's surface.
Mastering the interplay between oxygen and heat gives you precise control over your material's final form and function.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Oxidizing Atmosphere | Reducing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | Abundant free oxygen | Oxygen-deficient |
| Chemical Process | Promotes oxidation (loss of electrons) | Promotes reduction (gain of electrons) |
| Common Effects | Bright, predictable colors; efficient combustion | Rich, metallic colors; incomplete combustion |
| Key Applications | Ceramics (greens, blues), fuel efficiency | Ceramics (reds, grays), metal smelting |
| Safety Notes | Produces CO₂ and water | Produces toxic carbon monoxide (CO) |
Need precise atmosphere control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering furnaces and kilns that provide exact control over oxidizing or reducing environments. Whether you're developing new materials, testing ceramics, or conducting high-temperature experiments, our solutions ensure accurate, repeatable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















