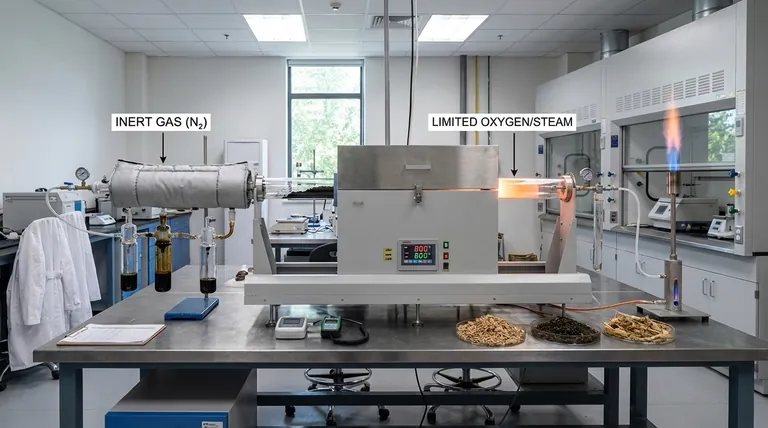
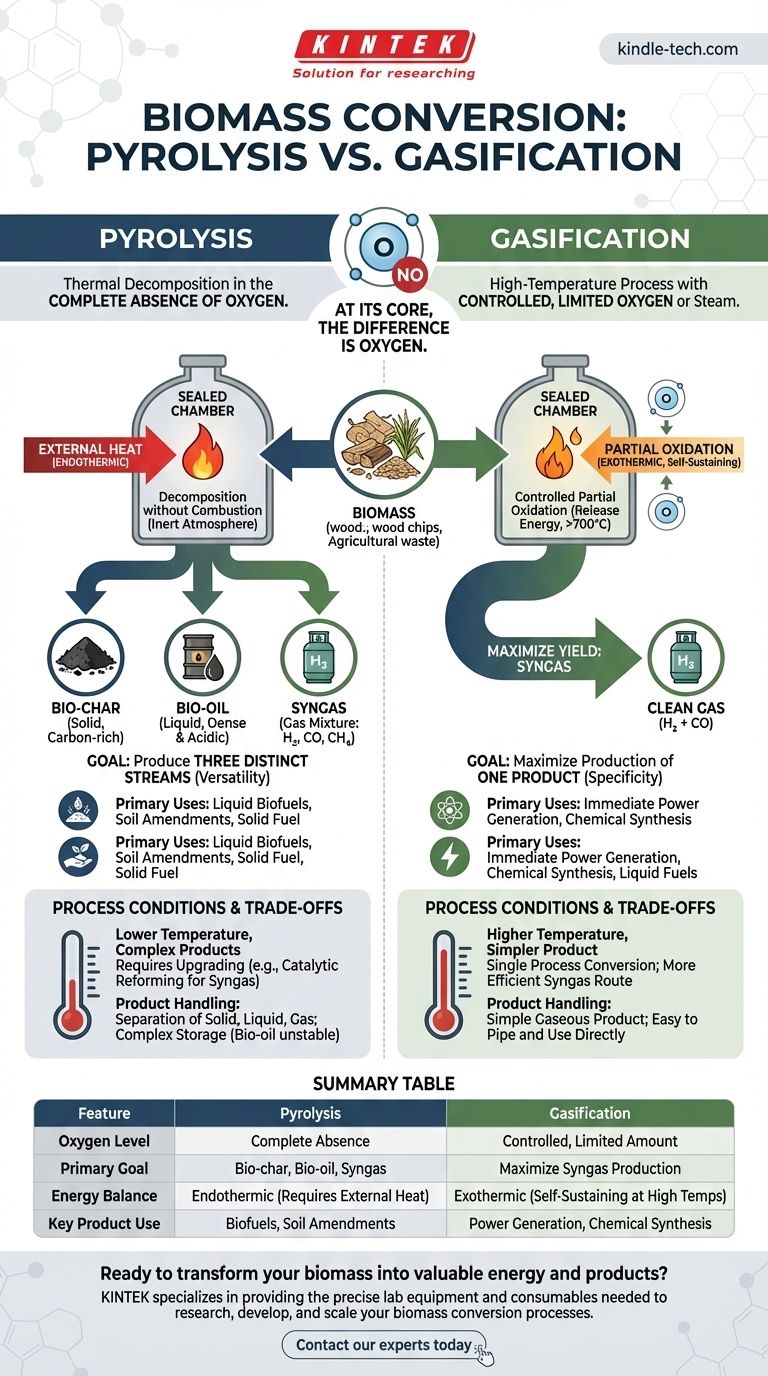
At its core, the difference is oxygen. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in the complete absence of oxygen, breaking it down into solid, liquid, and gaseous products. Gasification, conversely, is a high-temperature process that uses a controlled, limited amount of oxygen or steam to convert biomass almost entirely into a combustible gas called syngas.
The choice between pyrolysis and gasification is not about which is "better," but about what you want to create. Pyrolysis produces three distinct products—bio-char, bio-oil, and gas—while gasification is specifically engineered to maximize the yield of one product: syngas.

The Defining Factor: The Role of the Oxidizing Agent
The presence or absence of an oxidizing agent (like oxygen or steam) is the single most important variable that distinguishes these two processes. It fundamentally changes the chemistry, the energy balance, and the final output.
Pyrolysis: Decomposition in an Inert Atmosphere
Pyrolysis is essentially "cooking" biomass in a closed container without air. Because there is no oxygen, the material does not combust.
Instead, the heat breaks the complex hydrocarbon chains into a mix of smaller molecules. This process is primarily endothermic, meaning it requires a continuous external heat source to drive the reaction.
Gasification: Controlled Partial Oxidation
Gasification intentionally introduces a small amount of an oxidizing agent, but not enough for full combustion (burning).
This triggers a series of chemical reactions that convert the biomass into gas. This partial oxidation is exothermic, releasing energy that helps maintain the very high temperatures (>700°C) needed for the process, making it more self-sustaining than pyrolysis.
A Tale of Two Products: Versatility vs. Specificity
The different chemical environments of pyrolysis and gasification lead to vastly different product slates. This is the most critical practical distinction when choosing a technology.
The Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis breaks biomass down into three valuable, distinct streams:
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal. It can be used as a soil amendment or as a solid fuel.
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A dense, acidic liquid composed of tars, wood vinegar, and other organic compounds. It requires significant upgrading to be used as a transportation fuel.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄).
The Goal of Gasification
The primary objective of gasification is to maximize the production of one thing: syngas.
This mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide is a clean, flexible fuel. It can be burned directly in a gas engine to generate electricity or used as a chemical building block to synthesize liquid fuels and other high-value chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Conditions
While both processes can use similar feedstocks—such as wood chips, agricultural waste, or even municipal solid waste—their operating conditions and product complexities create important trade-offs.
Temperature and Process Complexity
Gasification requires significantly higher temperatures than pyrolysis to ensure the complete conversion of tars and hydrocarbons into a clean syngas.
The products of pyrolysis, particularly the bio-oil, are complex and often require an additional, energy-intensive step called catalytic reforming if the goal is to convert them into a clean syngas mixture. Gasification aims to achieve this conversion in a single process.
Product Handling and Upgrading
Gasification delivers a relatively simple gaseous product that is easy to pipe and use directly.
Pyrolysis, on the other hand, yields products in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) that must be separated and handled differently. The liquid bio-oil, in particular, can be corrosive and unstable, requiring specialized storage and significant downstream processing to become a usable fuel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision between pyrolysis and gasification should be driven entirely by your desired end product and application.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or solid soil amendments: Pyrolysis is the only choice, as it uniquely yields storable bio-oil and valuable bio-char.
- If your primary focus is generating a clean combustible gas for immediate power generation or chemical synthesis: Gasification is the more direct and efficient pathway to producing a high volume of quality syngas.
- If your primary focus is creating multiple, diverse product streams from a single feedstock: Pyrolysis offers unmatched flexibility with its simultaneous output of solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental difference between thermal decomposition and controlled oxidation is the key to unlocking the full potential of biomass as a sustainable resource.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | Complete absence | Controlled, limited amount |
| Primary Goal | Produce bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas | Maximize production of syngas |
| Energy Balance | Endothermic (requires external heat) | Exothermic (self-sustaining at high temps) |
| Key Product Use | Liquid biofuels, solid soil amendments | Immediate power generation, chemical synthesis |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable energy and products?
The choice between pyrolysis and gasification is critical for your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to research, develop, and scale your biomass conversion processes.
Whether you're focusing on versatile pyrolysis products or efficient gasification syngas, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for optimal results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific biomass conversion needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















