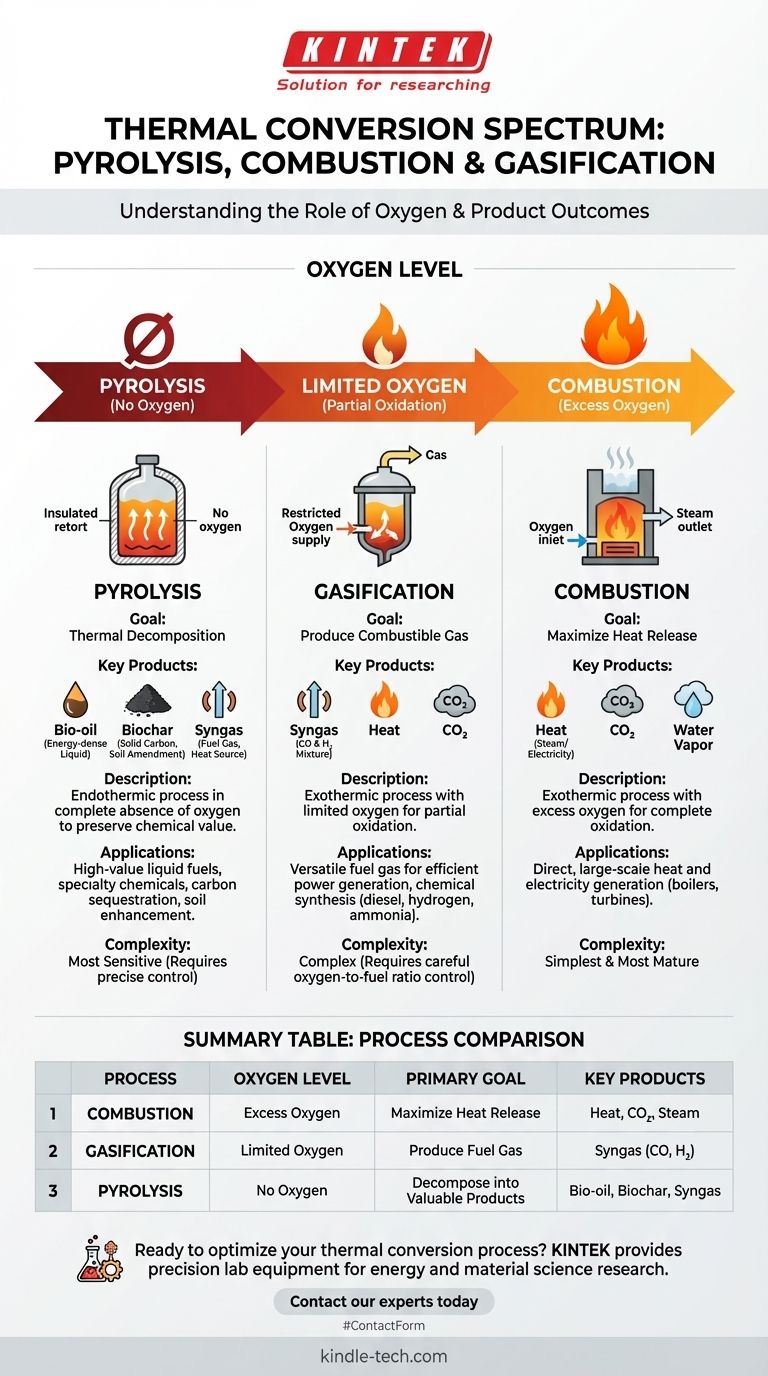
At their core, the difference between pyrolysis, combustion, and gasification is the amount of oxygen present during the thermal process. Combustion involves complete oxidation in the presence of excess oxygen to produce heat. Gasification uses a limited amount of oxygen for partial oxidation to create a combustible gas. Pyrolysis, in contrast, occurs in the complete absence of oxygen, using heat to decompose material into energy-dense oils, gases, and char.
While all three are thermal conversion technologies, the key is to see them not as isolated processes, but as points on a spectrum controlled by oxygen. The amount of oxygen you introduce directly determines whether your primary output is heat, fuel gas, or high-value chemical products.
The Role of Oxygen: A Spectrum of Conversion
Understanding these technologies is simplest when you view them as a continuum based on the oxygen-to-feedstock ratio. Each process has a distinct goal dictated by its unique chemical environment.
Combustion: Complete Oxidation for Maximum Heat
Combustion is the most familiar process, essentially the rapid burning of organic material. It operates with an abundance of oxygen.
The goal here is straightforward: maximize heat release. By providing more than enough oxygen, the fuel is fully oxidized, converting its chemical energy into thermal energy, carbon dioxide (CO₂), and water.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation for Fuel Gas
Gasification is the middle ground. It deliberately starves the reaction of the oxygen needed for complete combustion.
By using only a limited amount of oxygen, the organic material is only partially oxidized. This process generates a mixture of combustible gases known as synthesis gas, or syngas (primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen), along with some CO₂ and heat.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis sits at the zero-oxygen end of the spectrum. It is not a burning process but rather a thermal decomposition, akin to "cooking" the feedstock in a sealed, oxygen-free vessel.
Because there is no oxygen to react with, the material breaks down into smaller molecules. This process is endothermic, meaning it requires a consistent external heat source. It preserves the energy from the original feedstock in valuable new forms.
A Comparison of Outputs and Applications
The different chemical environments lead to vastly different products, each with its own set of applications. The choice of process depends entirely on the desired end product.
Combustion Products: Heat and Power
The primary output of combustion is a large amount of heat. This heat is most often used to boil water, create steam, and turn a turbine to generate electricity. It is the most direct route from solid fuel to power.
Gasification Products: Syngas as a Versatile Fuel
Gasification's main product, syngas, is highly flexible. It can be burned directly in a gas engine or turbine to produce electricity, often more efficiently than direct combustion.
Alternatively, syngas can serve as a chemical building block to synthesize liquid fuels (like diesel and gasoline), hydrogen, or valuable chemicals like methanol and ammonia.
Pyrolysis Products: Bio-oil and Biochar
Pyrolysis breaks down feedstock into three primary products:
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A dark, energy-dense liquid that can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used to produce specialty chemicals.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid that is an excellent soil amendment and a powerful tool for carbon sequestration.
- Syngas: A gaseous fraction that can be used to provide the heat needed to sustain the endothermic pyrolysis reaction itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right technology requires acknowledging the inherent trade-offs in complexity, efficiency, and feedstock handling.
Process Complexity and Control
Combustion is the simplest and most mature of the three technologies. Gasification is more complex, requiring careful control over the oxygen-to-fuel ratio to maximize syngas quality.
Pyrolysis is the most sensitive process. It demands a truly oxygen-free environment and precise temperature management to control the final product distribution (oil vs. char vs. gas).
Energy Balance
Combustion and gasification are exothermic—they release energy once initiated. This makes them self-sustaining as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.
Pyrolysis, being endothermic, requires a continuous input of energy to drive the decomposition. This energy is often supplied by burning a portion of the syngas produced, which impacts the overall net energy output of the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must be aligned with your strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is direct, large-scale heat or electricity generation: Combustion is the most established, cost-effective, and direct pathway.
- If your primary focus is producing a versatile fuel gas for efficient power or chemical synthesis: Gasification offers the necessary flexibility to convert solid feedstocks into a valuable gaseous intermediate.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value liquid fuels, chemicals, or carbon-sequestering soil products: Pyrolysis is the optimal choice, as it is designed to preserve chemical value in its material outputs.
Ultimately, mastering these technologies begins with understanding that oxygen is the fundamental control switch determining your final product.
Summary Table:
| Process | Oxygen Level | Primary Goal | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Excess Oxygen | Maximize Heat Release | Heat, CO₂, Steam |
| Gasification | Limited Oxygen | Produce Fuel Gas | Syngas (CO, H₂) |
| Pyrolysis | No Oxygen | Decompose into Valuable Products | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas |
Ready to optimize your thermal conversion process? Whether you're generating heat, producing syngas, or creating high-value bio-products, KINTEK's precision lab equipment is engineered to meet your specific needs. From reactors to gas analyzers, we provide reliable solutions for laboratories focused on energy and material science. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What is the temperature range for pyrolysis? Optimize for Biochar, Bio-oil, or Syngas



















