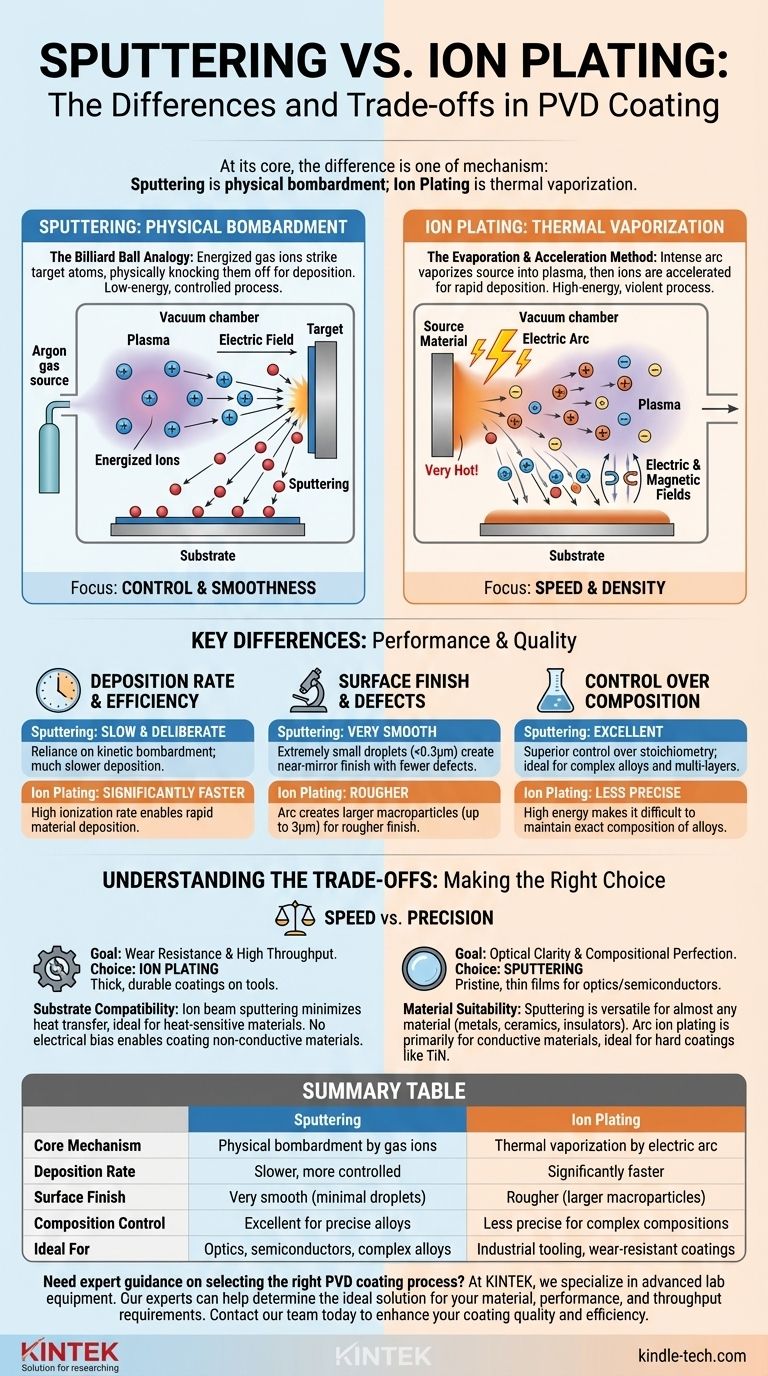
At its core, the difference is one of mechanism: sputtering is a physical bombardment process, while ion plating is a thermal vaporization process. Sputtering uses energized gas ions to physically knock atoms off a target material, which then deposit onto a substrate. In contrast, ion plating typically uses an intense electric arc to vaporize the source material into a plasma of ions that are then accelerated toward the substrate.
Choosing between sputtering and ion plating is a classic engineering trade-off between coating quality and deposition speed. Sputtering offers superior control, smoothness, and compositional accuracy at the cost of speed, while ion plating provides rapid, dense coatings but generally with a rougher surface finish.

Understanding the Core Mechanisms
To select the right process, it's critical to understand how each one works. Though both are forms of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), their methods for generating vapor are fundamentally different and lead to distinct outcomes.
How Sputtering Works: A Billiard Ball Analogy
Sputtering operates by creating a plasma, typically from an inert gas like argon. An electric field accelerates these gas ions, causing them to collide with a solid source material called the target.
Think of this as a molecular-scale game of pool. The argon ion is the cue ball, striking the rack of target atoms. This impact has enough energy to physically eject, or "sutter," atoms from the target surface.
These ejected atoms then travel through the vacuum chamber and condense on your substrate, forming a thin, highly uniform film.
How Ion Plating Works: The Evaporation and Acceleration Method
Arc-based ion plating uses a high-current, low-voltage electric arc that moves across the surface of the source material.
This arc creates an incredibly hot, localized spot that vaporizes the material directly into a plasma. This process results in a very high percentage of ionization compared to sputtering.
These newly created metal ions are then guided by electric and magnetic fields and accelerated toward the substrate with significant energy, resulting in an exceptionally dense and well-adhered coating.
Key Differences in Performance and Quality
The differences in mechanism directly translate to tangible differences in the final coating. Understanding these is key to matching the process to the application.
Deposition Rate and Efficiency
Ion plating is significantly faster. Its high ionization rate allows for much more material to be deposited in a shorter amount of time, making it ideal for high-throughput industrial applications.
Sputtering is a much slower, more deliberate process. This lower deposition rate is a direct result of its reliance on the less efficient kinetic bombardment mechanism.
Surface Finish and Defects
Sputtering produces a much smoother surface. The process generates extremely small particles (droplets up to 0.3µm), resulting in a near-mirror finish with fewer defects. This is critical for optical coatings and applications requiring low friction or high corrosion resistance.
Ion plating creates larger macroparticles (droplets up to 3µm) as part of the arc vaporization process. These droplets result in a rougher surface finish compared to sputtered coatings.
Control Over Composition
Sputtering offers superior control over stoichiometry. The slow, steady nature of the process makes it perfect for depositing complex alloys or multi-layered structures where maintaining a precise chemical ratio is non-negotiable.
Ion plating is less precise for complex compositions. The violent, high-energy nature of the arc makes it more difficult to maintain the exact composition of an alloy target in the final film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally better; they are simply suited for different goals. The choice involves balancing speed, quality, and material compatibility.
The Speed vs. Precision Dilemma
This is the central trade-off. If your goal is to quickly apply a thick, durable, wear-resistant coating onto a tool, ion plating is the clear choice.
If your goal is a pristine, thin, and compositionally perfect film for an optical lens or semiconductor component, the control offered by sputtering is required.
Substrate Compatibility
Some advanced sputtering techniques, like ion beam sputtering, operate without a plasma between the target and the substrate. This minimizes heat transfer and makes it ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials.
Because there is no electrical bias between the target and substrate, these sputtering methods can also effectively coat both electrically conductive and non-conductive materials.
Material and Application Suitability
Sputtering is exceptionally versatile and can be used to deposit nearly any material, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and insulators (using a variant called RF sputtering).
Arc ion plating is primarily used for electrically conductive materials that can sustain an arc, making it a mainstay for hard coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) on cutting tools and industrial components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To make a definitive decision, align the process capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is surface smoothness and optical clarity: Sputtering is the superior choice due to its minimal droplet size and high-quality finish.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and high throughput: Arc ion plating delivers durable, dense coatings at much faster rates, ideal for industrial tooling.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys or precise stoichiometry: Sputtering provides the slow, controlled deposition necessary to maintain exact compositional accuracy.
- If you are coating a heat-sensitive or non-conductive material: Specific variants of sputtering offer clear advantages by minimizing plasma interaction and substrate heating.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the deposition technique that aligns perfectly with your material, performance, and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sputtering | Ion Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical bombardment by gas ions | Thermal vaporization by electric arc |
| Deposition Rate | Slower, more controlled | Significantly faster |
| Surface Finish | Very smooth (minimal droplets) | Rougher (larger macroparticles) |
| Composition Control | Excellent for precise alloys | Less precise for complex compositions |
| Ideal For | Optics, semiconductors, complex alloys | Industrial tooling, wear-resistant coatings |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right PVD coating process for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including PVD coating systems. Our experts can help you determine whether sputtering or ion plating is the ideal solution for your specific material, performance, and throughput requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your coating quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















