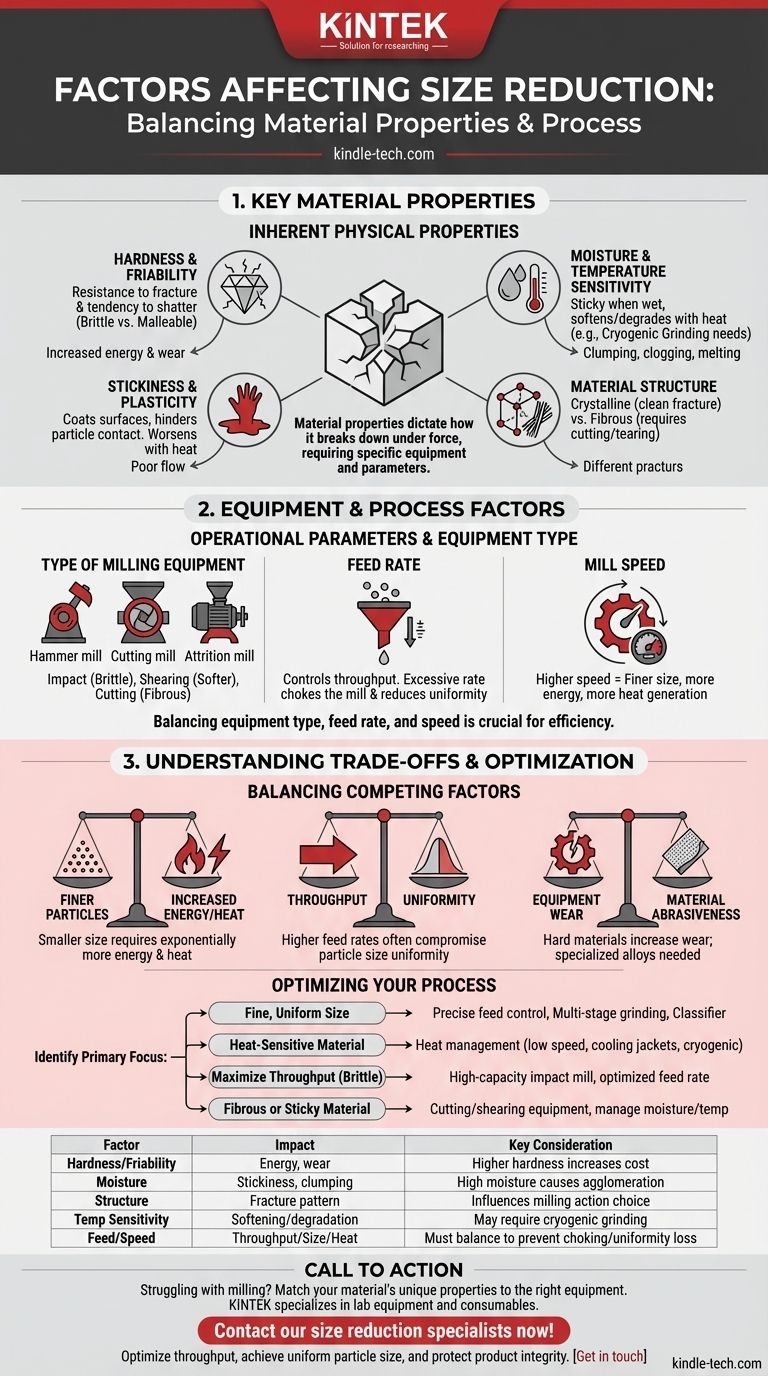
The primary factors affecting size reduction are the inherent physical properties of the material itself. While the machinery used is important, characteristics like hardness, stickiness, and moisture content fundamentally dictate how a material will break down when subjected to force.
The efficiency and outcome of any size reduction process are determined by a balance between the external forces applied by the equipment and the material's internal resistance to fracture, which is governed by its physical and chemical properties.
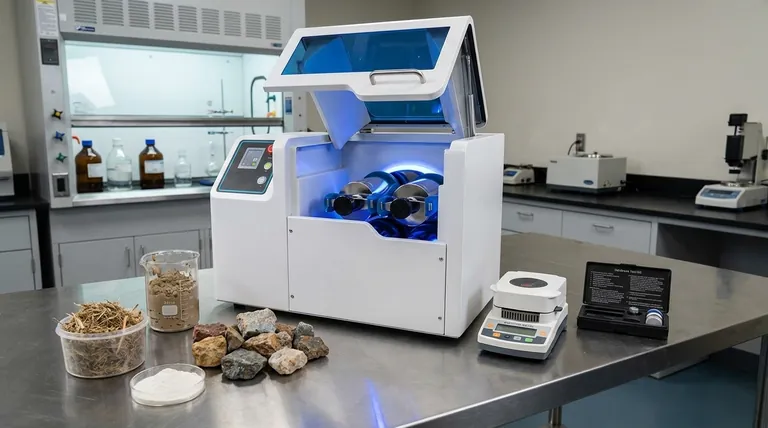

Key Material Properties Influencing Size Reduction
The characteristics of the substance being milled are the most significant variables. Understanding them allows for the selection of the right equipment and process parameters.
Hardness and Friability
Hardness is a measure of a material's resistance to localized deformation. Harder materials require significantly more energy to fracture, leading to higher operational costs and increased wear on milling equipment.
Friability is the tendency of a substance to break into smaller pieces. A highly friable (brittle) material shatters easily upon impact, while a less friable (malleable or ductile) material may deform without breaking.
Moisture Content
The amount of moisture in a material is a critical factor. Even small variations can dramatically change a material's behavior during milling.
As noted in the provided reference, moisture influences properties like hardness and stickiness. High moisture can cause particles to clump together (agglomeration), clogging screens and coating the inside of the mill, which severely reduces efficiency.
Stickiness and Plasticity
Sticky, gummy, or oily materials are notoriously difficult to mill. They tend to coat the grinding surfaces and screens, preventing effective particle contact and flow.
This property is often linked to moisture and temperature. A material that is brittle at room temperature may become plastic and sticky if it heats up during the milling process.
Material Structure
The internal structure of a material dictates how it will fracture.
Crystalline materials have defined cleavage planes and tend to fracture cleanly into smaller, similarly shaped particles. Fibrous materials, like wood or plant matter, are tougher and are more effectively reduced by cutting or tearing actions rather than impact.
Temperature Sensitivity
Significant heat is generated during size reduction. For heat-sensitive materials, this can be a major problem, causing them to melt, soften, or degrade chemically.
This softening can lead to the plasticity issues mentioned above, completely halting the milling process. In such cases, specialized techniques like cryogenic grinding, which uses liquid nitrogen to make the material brittle, are often necessary.
Equipment and Process Factors
While material properties are paramount, the operational parameters of the milling equipment also play a crucial role.
Type of Milling Equipment
Different mills apply force in different ways. Impact mills (like a hammer mill) are effective for brittle materials, while attrition mills (which use shearing force) or cutting mills are better for softer or fibrous materials.
Feed Rate
The rate at which material is introduced into the mill must be carefully controlled. An excessively high feed rate can "choke" the mill, overwhelming its capacity and leading to poor performance and potential blockages.
Mill Speed
For equipment like hammer or pin mills, the rotational speed is a key variable. Higher speeds impart more energy, generally resulting in a finer particle size. However, higher speeds also generate more heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a size reduction process is rarely about maximizing a single variable. It involves balancing competing factors to achieve the desired outcome.
Finer Particles vs. Increased Energy and Heat
Achieving a smaller particle size requires more energy input. This exponential increase in energy not only raises costs but also generates more heat, which can damage the product or the equipment.
Throughput vs. Particle Size Uniformity
Pushing for a higher feed rate (throughput) can often compromise the quality of the final product. A faster process may result in a wider particle size distribution and less uniformity.
Equipment Wear vs. Material Abrasiveness
Processing hard or abrasive materials will inevitably cause wear and tear on the milling components. This increases maintenance costs and downtime. Choosing machinery built with hardened or specialized alloys is a trade-off between upfront investment and long-term operational cost.
Optimizing Your Size Reduction Process
To control the outcome, you must align the material properties with the correct equipment and operating parameters.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine, uniform particle size: Prioritize precise control over feed rate and consider multi-stage grinding or using a classifier to separate particles.
- If your primary focus is processing a heat-sensitive material: Your main concern is heat management, which means using lower mill speeds, cooling jackets, or cryogenic grinding.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput on a brittle material: Select a high-capacity impact mill and carefully optimize the feed rate to prevent choking while running at efficient speeds.
- If your primary focus is reducing a fibrous or sticky material: Avoid impact mills and instead choose equipment that uses a cutting, shearing, or tearing action, and carefully manage moisture and temperature.
Ultimately, mastering size reduction comes from understanding that you are managing the material's inherent properties, not just operating a machine.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Size Reduction | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Friability | Determines energy required; brittle materials shatter easily. | Higher hardness increases wear and energy costs. |
| Moisture Content | Affects stickiness and clumping; high moisture reduces efficiency. | Can cause agglomeration and clogging. |
| Material Structure | Dictates fracture pattern; fibrous vs. crystalline materials behave differently. | Influences choice of milling action (impact, cutting, shearing). |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Heat can soften or degrade materials; may require cryogenic grinding. | Critical for heat-sensitive substances. |
| Feed Rate & Mill Speed | Controls throughput and particle size; high speeds generate more heat. | Must be balanced to prevent choking and ensure uniformity. |
Struggling with inefficient milling or inconsistent particle sizes? The challenge often lies in matching your material's unique properties to the right equipment and process parameters. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the expertise and machinery to optimize your size reduction for any material—whether it's heat-sensitive, fibrous, abrasive, or sticky.
Let our experts help you select the perfect mill and configure the ideal parameters to maximize throughput, achieve uniform particle size, and protect your product integrity. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and see the difference the right partnership can make.
Get in touch with our size reduction specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-energy planetary ball mill preferred over traditional casting for nanocrystalline HEAs?
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- How does a planetary high-energy ball mill contribute to the top-down preparation of layered materials? Optimize Yield
- What is the function of a high-energy planetary ball mill in zirconium-doped CaO synthesis? Optimize Material Stability
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?



















