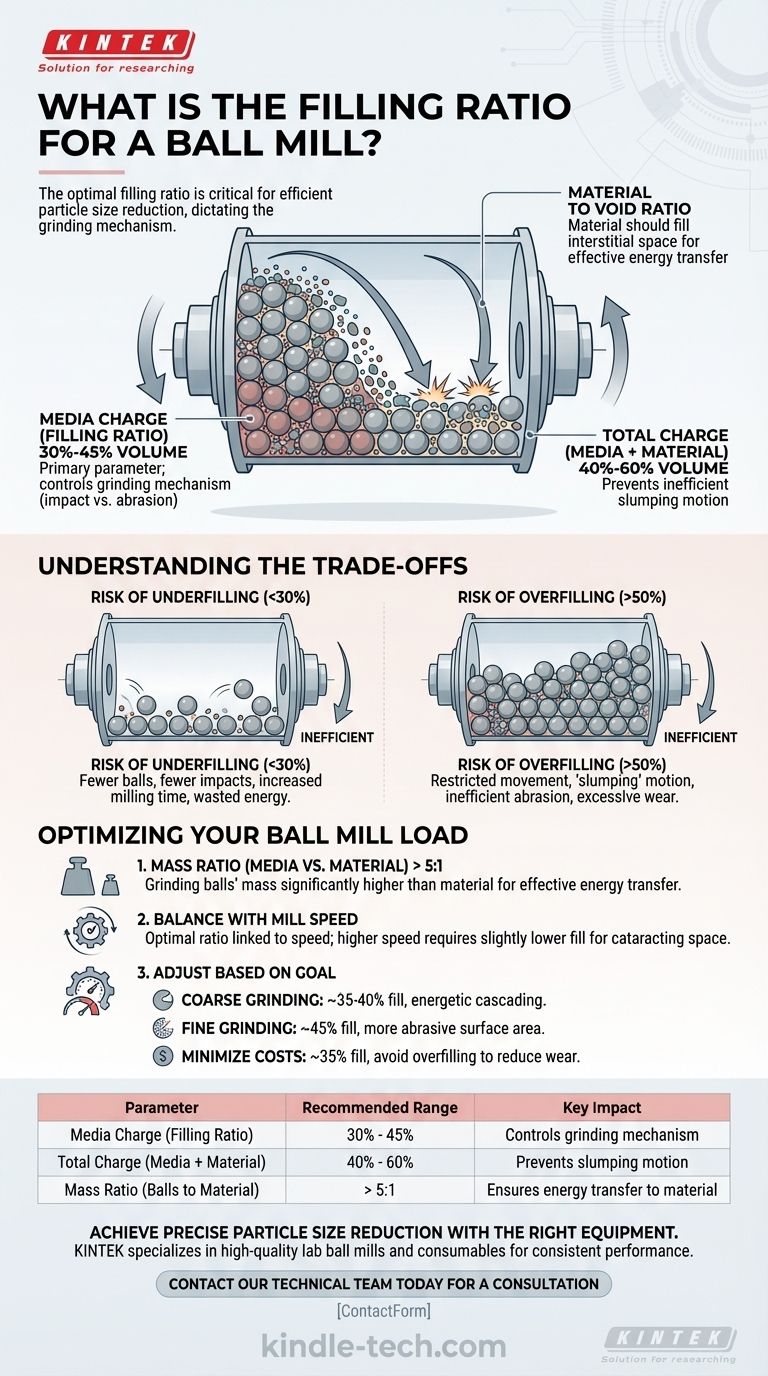
The optimal filling ratio for a ball mill typically refers to the volume occupied by the grinding media (the balls), which should be between 30% and 45% of the mill's internal volume. This media charge, combined with the material being ground, should result in a total charge volume between 40% and 60% of the mill for most applications.
The filling ratio is not a single fixed number but the most critical variable you can control. It directly dictates the grinding mechanism inside the mill, and finding the right balance between the media and the material is essential for achieving efficient particle size reduction.

What "Filling Ratio" Means and Why It Matters
The term "filling ratio" can be ambiguous, so it's vital to break it down into its core components. The efficiency of your entire process hinges on getting this balance right.
Defining the Core Components
The media charge, also known as the filling ratio, is the percentage of the mill's internal volume filled by the grinding media (e.g., steel or ceramic balls). This is the primary parameter.
The material charge is the substance you are grinding. It fills the void space between the grinding balls.
The total charge is the combined volume of the media and the material. The references indicate this total charge should ideally not exceed 80% and is often optimized between 40% and 60%.
The Grinding Mechanism
The filling ratio directly controls the motion of the balls inside the rotating drum. With the correct charge, the balls are lifted up the side of the shell and then cascade or cataract down, creating impacts that crush the material.
This cascading action is the heart of effective ball milling. The ratio of media-to-material determines the frequency and energy of these critical impacts.
Optimizing Your Ball Mill Load
Achieving the best performance requires balancing two key ratios: the volumetric fill and the mass ratio between the media and the material.
Media Charge Volume (The Filling Ratio)
The standard starting point for the media charge is 30% to 45% of the mill's volume.
Within this range, a lower fill (around 30%) allows for more energetic, higher-impact "cataracting" motion at higher speeds. A higher fill (around 45%) increases the number of grinding surfaces and favors abrasion, which can be useful for finer grinding.
Material to Void Ratio
The material being ground should fill the interstitial space, or voids, between the grinding balls. A proper material load ensures that energy is transferred from the balls to the material, not wasted on ball-on-ball or ball-on-liner collisions.
Mass Ratio (Media vs. Material)
As a guiding principle, the mass of the grinding balls should be significantly higher than the mass of the material. A common recommendation is a mass ratio of grinding balls to material greater than 5:1.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Deviating from the optimal range introduces significant inefficiencies and risks. Understanding these trade-offs is key to troubleshooting your process.
The Risk of Underfilling
If the media charge is too low (e.g., below 30%), there are fewer balls to perform the work. This results in fewer impact events per revolution, drastically increasing the required milling time and wasting energy.
The Risk of Overfilling
If the media charge is too high (e.g., above 50%), the movement of the balls becomes restricted. They can no longer cascade effectively. Instead, they tend to slide and roll over each other, a process known as "slumping."
This slumping motion leads to inefficient abrasive grinding rather than impact grinding, causing excessive wear on both the media and the mill liner without achieving effective particle size reduction.
The Balance with Mill Speed
The optimal filling ratio is directly linked to the mill's rotational speed. A mill running at a higher percentage of its "critical speed" (the speed at which media centrifuges against the liner) requires a slightly lower fill to allow the balls enough space to cataract properly.
How to Determine the Right Ratio for Your Process
Use the following guidelines as a starting point, but always be prepared to test and adjust based on your specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid, coarse grinding: Start with a media charge around 35-40% and ensure the mill speed is optimized to promote energetic cascading impacts.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine particle size: Consider a slightly higher media charge (around 45%) to maximize the surface area for abrasive grinding, but be prepared for longer milling times.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs and wear: Avoid overfilling at all costs. Start conservatively around 35% and ensure your material charge is sufficient to cushion the media.
Ultimately, the ideal filling ratio is the one that produces your desired particle size in the shortest time with the least amount of energy and wear.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Media Charge (Filling Ratio) | 30% - 45% of mill volume | Controls grinding mechanism (impact vs. abrasion) |
| Total Charge (Media + Material) | 40% - 60% of mill volume | Prevents inefficient slumping motion |
| Mass Ratio (Balls to Material) | > 5:1 | Ensures energy is transferred to the material |
Achieve precise particle size reduction and maximize your lab's productivity with the right equipment.
The optimal ball mill filling ratio is critical for your results, but it's only one part of the equation. Having a reliable mill that matches your specific application is just as important.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab ball mills and grinding consumables designed for consistent performance and durability. Whether you're in research, pharmaceuticals, or materials science, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to optimize your grinding process, save time, and reduce operational costs.
Ready to enhance your grinding efficiency? Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination



















