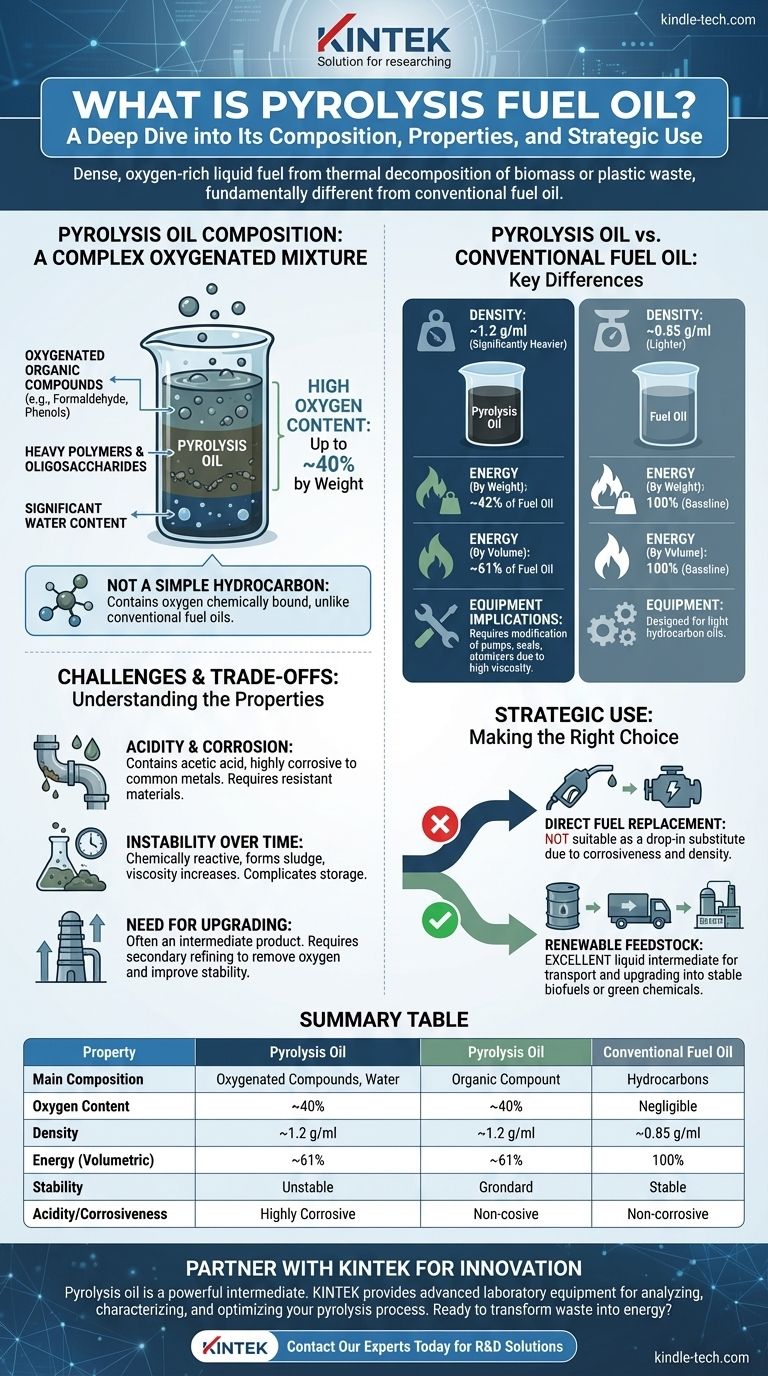
In short, pyrolysis oil is a dense, oxygen-rich liquid fuel produced from the thermal decomposition of organic materials like biomass or plastic waste. However, it is fundamentally different from conventional fuel oil. Its unique chemical composition gives it distinct properties that prevent it from being a simple "drop-in" replacement for traditional petroleum products.
The crucial takeaway is to understand that while it's called an "oil," pyrolysis oil is not a hydrocarbon. It is a complex mixture containing significant amounts of water and oxygen, which makes it denser, less energy-rich by weight, and more corrosive than conventional fuel oil.

What is Pyrolysis Oil Actually Made Of?
To understand the practical challenges of using pyrolysis oil, we must first look at its chemical makeup, which diverges significantly from the simple hydrocarbons found in fossil fuels.
A Complex Oxygenated Mixture
Pyrolysis oil is best described as a liquid emulsion or a complex mixture. It is composed of oxygenated organic compounds, heavy polymers, and a notable amount of water.
This mixture is the direct result of the rapid heating of biomass in an oxygen-free environment, which breaks down complex structures like cellulose and lignin into hundreds of smaller, oxygen-containing compounds.
The High Oxygen Content
The most defining characteristic of pyrolysis oil is its high oxygen content, which can be up to 40% by weight.
This oxygen is chemically bound within the fuel's molecules. In contrast, conventional fuel oils are almost entirely composed of carbon and hydrogen, with negligible oxygen.
A Soup of Diverse Chemicals
The oil is not a uniform substance but a blend of many different chemicals.
This includes low molecular weight compounds like formaldehyde and acetic acid, which contribute to its acidity, as well as high molecular weight substances like phenols and oligosaccharides.
How It Differs from Conventional Fuel Oil
The unique composition of pyrolysis oil leads to significant differences in its physical and energetic properties compared to the fuels it is meant to supplement or replace.
Physical Density
Pyrolysis oil is significantly denser than traditional fuels. Its density is around 1.2 g/ml, much higher than the approximate 0.85 g/ml for light fuel oil. This means a gallon of pyrolysis oil is substantially heavier than a gallon of diesel.
Energy Content by Weight vs. Volume
The high oxygen content creates a critical distinction in energy value. Oxygen adds weight but does not contribute to the energy released during combustion.
As a result, pyrolysis oil has only about 42% of the energy content of fuel oil on a weight basis. However, because it is so dense, it contains about 61% of the energy on a volumetric basis.
Implications for Equipment
These properties have direct consequences for engineering. Standard equipment like pumps, seals, and atomizers designed for light hydrocarbon oils will not function correctly with the heavier, more viscous pyrolysis oil without significant modification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a promising technology for waste-to-energy, raw pyrolysis oil presents several challenges that must be addressed before it can be widely used.
Acidity and Corrosion
The presence of acetic acid and other organic acids makes raw pyrolysis oil highly corrosive to common metals like carbon steel. This requires specialized, corrosion-resistant materials for storage tanks, pipes, and engine components.
Instability Over Time
Unlike stable petroleum fuels, pyrolysis oil is chemically reactive. Over time, its components can continue to react with each other, forming sludge and increasing in viscosity. This instability complicates long-term storage.
The Need for Upgrading
Due to these challenges, raw pyrolysis oil is often considered an intermediate product rather than a finished fuel. It typically requires a secondary refining process, known as "upgrading," to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve its stability for use in conventional engines or refineries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding pyrolysis oil's true nature is key to utilizing it effectively. It is less of a direct fuel and more of a renewable crude oil substitute.
- If your primary focus is direct fuel replacement: Raw pyrolysis oil is not a suitable drop-in substitute for diesel or heating oil due to its corrosiveness, high density, and incompatibility with standard equipment.
- If your primary focus is sourcing a renewable feedstock: It serves as an excellent liquid intermediate that can be transported and later upgraded into stable biofuels, green chemicals, or other advanced materials.
Ultimately, pyrolysis oil should be viewed as a valuable and transportable energy carrier that captures the chemical energy from waste biomass, setting the stage for further refinement.
Summary Table:
| Property | Pyrolysis Oil | Conventional Fuel Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Main Composition | Oxygenated organic compounds, water | Hydrocarbons (Carbon & Hydrogen) |
| Oxygen Content | Up to 40% by weight | Negligible |
| Density | ~1.2 g/ml | ~0.85 g/ml |
| Energy Content (Volumetric) | ~61% of fuel oil | 100% (Baseline) |
| Stability | Chemically unstable, viscosity increases over time | Stable for long-term storage |
| Acidity/Corrosiveness | Highly acidic and corrosive | Non-corrosive |
Ready to transform your biomass or plastic waste into valuable energy?
Pyrolysis oil is a powerful intermediate product, but handling its unique properties requires expertise and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing, testing, and developing pyrolysis processes. Whether you're in R&D or scaling up production, we provide the reliable tools you need to characterize your oil, optimize your process, and ensure quality control.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your renewable energy and waste valorization goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions






