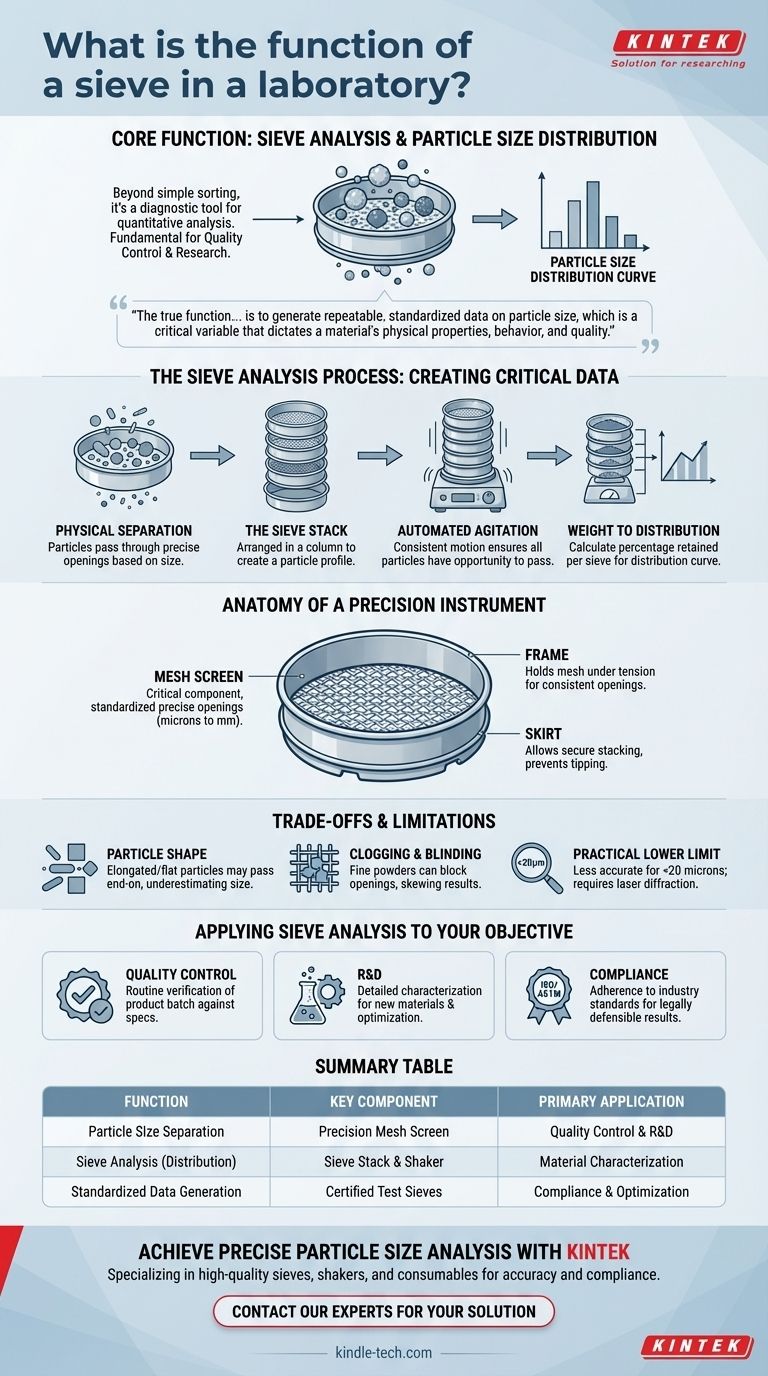
At its core, a laboratory sieve is a precision instrument designed for the physical separation of particles based on their size. Its primary function is not just to sort materials, but to perform a sieve analysis: a quantitative procedure that determines the particle size distribution within a given sample. This analysis is fundamental to quality control and research in countless industries.
The true function of a lab sieve goes beyond simple sorting. It is a diagnostic tool used to generate repeatable, standardized data on particle size, which is a critical variable that dictates a material's physical properties, behavior, and quality.

How a Sieve Analysis Provides Critical Data
Understanding the process of a sieve analysis reveals why it is an indispensable quality control method. The procedure is designed for accuracy and repeatability.
The Fundamental Principle: Physical Separation
The concept is straightforward. A sample is placed on a mesh screen with openings of a precise, uniform size. When agitated, particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained on top.
The Sieve Stack: Creating a Particle Profile
For a detailed analysis, sieves are not used individually. Instead, a sieve stack is created by arranging several sieves in a column, with the largest mesh openings at the top and progressively smaller ones toward the bottom. A solid collection pan sits at the very bottom.
The Role of Agitation
The stack is placed in a mechanical shaker. This device imparts a consistent vibration or tapping motion, ensuring particles have every opportunity to pass through the apertures they can fit. This automated agitation removes operator variability and ensures the results are repeatable.
From Weight to Distribution
After shaking is complete, the material retained on each individual sieve is weighed. By dividing the weight on each sieve by the total sample weight, you can calculate the percentage of particles that fall within each size range. This data creates a particle size distribution curve, a powerful fingerprint of the material.
The Anatomy of a Precision Instrument
A laboratory test sieve is not just a kitchen strainer; it is a highly engineered and standardized tool built for accuracy.
The Mesh: The Heart of the Sieve
The most critical component is the mesh screen. It is typically made of stainless steel woven wire with extremely precise and consistent openings. These aperture sizes are standardized and can range from several millimeters down to just a few microns (a human hair is about 70 microns).
The Frame and Skirt: Ensuring Consistency
The mesh is held under tension in a rigid, circular frame, ensuring the openings do not change during use. An interlocking skirt on the bottom of the frame allows multiple sieves to be stacked securely, preventing tipping and sample loss during agitation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is a mechanical process with inherent limitations that are important to acknowledge.
Particle Shape and Orientation
Sieving assumes particles are roughly spherical. Elongated or flat particles may pass through an aperture end-on or diagonally, leading to an underestimation of their true size.
Clogging and Blinding with Fine Powders
Very fine particles, especially those with electrostatic properties, can clog the mesh openings—a phenomenon known as blinding. This prevents other particles from passing through and skews the final results. Specialized electromagnetic shakers are often used to mitigate this for very fine powders.
The Practical Lower Limit
Mechanical sieving becomes impractical and less accurate for particles smaller than about 20 microns. For nano-sized materials, other methods like laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering are required.
Applying Sieve Analysis to Your Objective
How you use a sieve depends entirely on your goal. The objective dictates the method and the required level of precision.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Use a standardized set of sieves and a fixed shaking time to quickly verify that a product batch falls within an established size specification.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Employ a wider range of sieve sizes in your stack to generate a detailed particle size distribution curve for characterizing new materials or optimizing a formulation.
- If your primary focus is compliance with industry standards: You must use certified test sieves that conform to specific ISO or ASTM standards for aperture size and wire diameter to ensure your results are legally and scientifically defensible.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis gives you direct control over a material's most fundamental physical properties.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Component | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Separation | Precision Mesh Screen | Quality Control & R&D |
| Sieve Analysis (Particle Distribution) | Sieve Stack & Mechanical Shaker | Material Characterization |
| Standardized Data Generation | Certified Test Sieves (ISO/ASTM) | Compliance & Process Optimization |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis in your lab.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves, shakers, and consumables designed for accuracy and compliance with industry standards. Whether your focus is routine quality control, in-depth R&D, or meeting strict regulatory requirements, our equipment delivers the repeatable data you need to control material properties and ensure product quality.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific application and objectives.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















