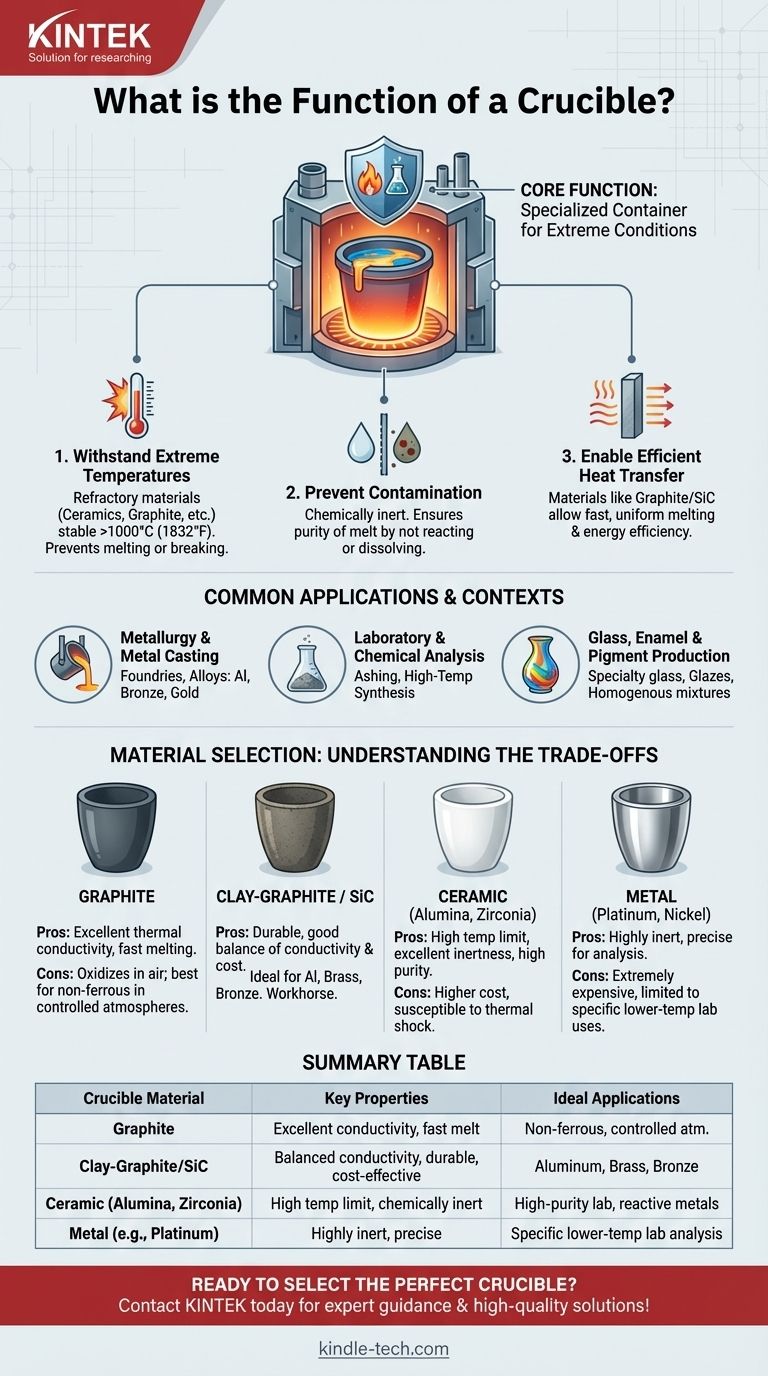
At its core, a crucible is a specialized container designed to withstand extremely high temperatures. Its primary function is to hold materials, such as metals or chemical compounds, while they are being melted, calcined, or subjected to other thermal or chemical transformations, without the container itself melting, breaking, or reacting with its contents.
A crucible is more than just a heat-proof bowl; it is a critical tool engineered from specific refractory materials to maintain its integrity and chemical inertness at extreme temperatures, ensuring the purity and success of the process it facilitates.

The Core Principle: Thermal and Chemical Stability
The function of a crucible is defined by its ability to perform under conditions that would destroy an ordinary container. This performance relies on two key properties.
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures
Crucibles are constructed from refractory materials, which are materials that have exceptionally high melting points and remain stable at high temperatures.
Common materials include ceramics (like alumina and zirconia), graphite, silicon carbide, and certain metals like platinum. This allows them to contain substances heated well over 1000°C (1832°F).
Preventing Contamination
A crucible must be chemically inert relative to the substance it holds. This means it should not react with, dissolve into, or otherwise contaminate the molten material.
Contamination can ruin the chemical composition of an alloy, introduce impurities into a laboratory sample, or alter the properties of the final product. The choice of crucible material is therefore critical for ensuring the purity of the melt.
Enabling Efficient Heat Transfer
While withstanding heat is primary, a good crucible also facilitates the efficient transfer of energy from the heat source (the furnace) to the material inside.
Materials like graphite and silicon carbide have excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for faster, more uniform melting and reduces the energy required for the process.
Common Applications and Contexts
Crucibles are indispensable tools across several industries and scientific fields, each leveraging their unique properties.
Metallurgy and Metal Casting
This is the most well-known application. Crucibles are used in foundries to melt metals and alloys—from aluminum and bronze to gold and steel—before they are poured into molds.
Laboratory and Chemical Analysis
In analytical chemistry, small crucibles are used for processes like ashing, where a sample is burned at a high temperature to determine its inorganic content. They are also used for carrying out high-temperature chemical synthesis.
Glass, Enamel, and Pigment Production
The manufacturing of specialty glasses, ceramic glazes, and high-temperature pigments often involves melting raw materials together in a crucible to achieve a homogenous, molten mixture before forming or cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection
No single crucible is perfect for every task. The choice of material involves critical trade-offs between temperature rating, chemical compatibility, and cost.
Graphite Crucibles
These offer excellent thermal conductivity, leading to fast melting. However, they can be consumed (oxidize) in the presence of air at high temperatures and are best suited for non-ferrous metals in controlled atmospheres.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide Crucibles
These are the workhorses of many foundries. They blend the thermal conductivity of graphite/silicon carbide with the durability of a ceramic binder, offering a great balance of performance, lifespan, and cost for melting metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze.
Ceramic Crucibles (Alumina, Zirconia)
Ceramic crucibles boast very high temperature limits and excellent chemical inertness, making them ideal for high-purity applications, research, or melting highly reactive metals. Their primary trade-offs are higher cost and greater susceptibility to thermal shock (cracking from rapid temperature changes).
Metal Crucibles (Platinum, Nickel)
For certain lower-temperature laboratory analyses, crucibles made of metals like platinum or nickel are used. Platinum is extremely inert but prohibitively expensive for most large-scale applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the ideal crucible. Consider your primary objective when making a selection.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of performance, durability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work or melting reactive metals: An alumina or zirconia ceramic crucible is necessary to prevent contamination, despite its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is the fastest possible melting in a controlled atmosphere: A pure graphite crucible provides superior thermal transfer.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible is a foundational step in ensuring the integrity and success of any high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Excellent thermal conductivity, fast melting | Non-ferrous metals in controlled atmospheres |
| Clay-Graphite / Silicon Carbide | Good balance of conductivity, durability, and cost | Melting aluminum, brass, bronze |
| Ceramic (Alumina, Zirconia) | High temperature limit, excellent chemical inertness | High-purity lab work, reactive metals |
| Metal (e.g., Platinum) | Highly inert, precise for analysis | Specific lower-temperature laboratory processes |
Ready to select the perfect crucible for your high-temperature process? The right crucible is critical for achieving purity, efficiency, and success in your lab or foundry. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles designed for specific applications and materials. Our experts can help you choose the ideal solution to ensure your process integrity and optimal results. Contact us today to discuss your needs and let KINTEK be your trusted partner in laboratory excellence!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data



















