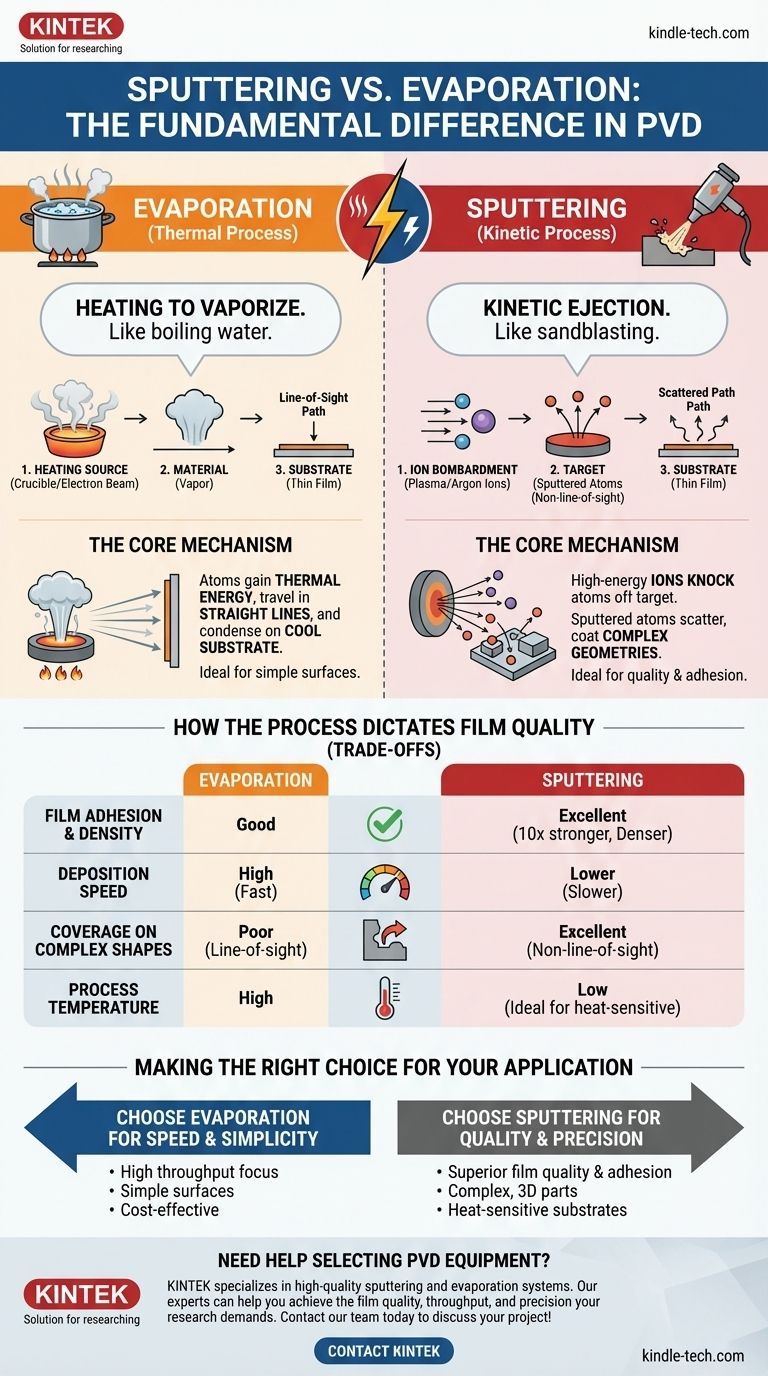
The fundamental difference between sputtering and evaporation is how atoms are liberated from the source material. Evaporation is a thermal process that uses heat to boil atoms off a source, much like boiling water creates steam. In contrast, sputtering is a kinetic process that uses high-energy ions to physically knock atoms off a target, similar to a sandblaster chipping away at a surface.
While both are primary methods of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the choice between them hinges on a critical trade-off: Evaporation offers speed and high deposition rates, while Sputtering provides superior film quality, adhesion, and coverage at the cost of speed.

The Core Mechanism: A Tale of Two Processes
To choose the right method, you must first understand how each one operates at an atomic level. The mechanism directly dictates the properties of the resulting thin film.
Evaporation: Thermal Vaporization
Evaporation works by heating a source material in a high vacuum chamber until its atoms gain enough thermal energy to vaporize.
This vapor then travels in a straight line—a "line-of-sight" path—until it condenses on the cooler substrate, forming a thin film. The most common industrial method is electron-beam evaporation, which uses a focused beam of electrons to intensely heat the source material.
Sputtering: Kinetic Ejection
Sputtering operates on an entirely different principle: momentum transfer. The process takes place in a low-pressure chamber filled with an inert gas, typically argon.
A strong electric field energizes the argon gas into a plasma. These positively charged argon ions are then accelerated into a negatively charged source material, called the "target."
Upon impact, the ions physically knock atoms off the target. These "sputtered" atoms travel through the chamber and deposit onto the substrate. Because they collide with gas atoms along the way, their path is less direct than in evaporation.
How the Process Dictates Film Quality
The differences in these two mechanisms have direct and predictable consequences for the final product. Understanding these is key to selecting the right tool for your application.
Film Adhesion and Density: Sputtering's Advantage
Sputtered atoms are ejected with significantly higher kinetic energy than thermally evaporated atoms.
This high energy means they impact the substrate with greater force, resulting in films that are denser, harder, and have far superior adhesion—often more than 10 times stronger than evaporated films.
Deposition Speed and Throughput: Evaporation's Strength
Evaporation is generally a much faster deposition process. Heating a material can generate a very high flux of vapor, leading to rapid film growth.
This makes evaporation the preferred method for applications where high throughput is a primary concern and the absolute highest film quality is not required.
Coverage on Complex Geometries
Because evaporated atoms travel in a straight line, the process struggles to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes, leading to "shadowing" effects.
Sputtered atoms, however, are scattered by the process gas. This allows them to coat non-line-of-sight surfaces, providing much better and more uniform coverage on complex parts.
Process Temperature and Control
Sputtering is fundamentally a lower-temperature process than evaporation. This makes it ideal for depositing films onto temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics, that could be damaged by the intense heat of an evaporation source.
Furthermore, sputtering offers finer control over deposition rates, which allows for greater precision in achieving a target film thickness and uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; they are optimized for different goals. Your choice will always involve balancing competing priorities.
Choose Evaporation for Speed and Simplicity
Evaporation systems are often simpler and can achieve higher deposition rates, making them cost-effective for high-volume production of films on simple, flat substrates where ultimate adhesion is not the top priority.
Choose Sputtering for Quality and Precision
When film performance is critical, sputtering is almost always the better choice. Its ability to produce dense, highly adherent, and uniform films on complex shapes is unmatched by evaporation. It is also the go-to process for depositing alloys and compounds with precise stoichiometry.
Material and Scalability Considerations
Sputtering is exceptionally scalable and well-suited for automated, in-line manufacturing processes. While it can deposit a vast range of materials, it can be slow for some dielectrics. Evaporation can also handle many materials but is more difficult to scale in the same integrated way as modern sputtering systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the most critical requirements of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is high throughput on simple surfaces: Choose evaporation for its speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is superior film quality, adhesion, and density: Choose sputtering, as the high energy of the deposited atoms ensures a more robust film.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, 3D parts: Sputtering's non-line-of-sight nature provides the uniform coverage you need.
- If your primary focus is depositing on heat-sensitive substrates: Sputtering's lower process temperature makes it the only viable option.
By understanding the physics behind each process, you can confidently select the method that delivers the performance and quality your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Evaporation | Sputtering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Thermal | Kinetic |
| Primary Mechanism | Heating to vaporize | Ion bombardment to eject atoms |
| Film Adhesion | Good | Excellent (10x stronger) |
| Deposition Speed | High (Fast) | Lower (Slower) |
| Coverage on Complex Shapes | Poor (Line-of-sight) | Excellent (Non-line-of-sight) |
| Process Temperature | High | Low |
| Ideal For | High throughput on simple surfaces | Superior quality, complex parts, heat-sensitive substrates |
Need help selecting the right PVD equipment for your lab's thin-film deposition needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both sputtering and evaporation systems. Our experts can help you choose the perfect solution to achieve the film quality, throughput, and precision your specific application demands.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















