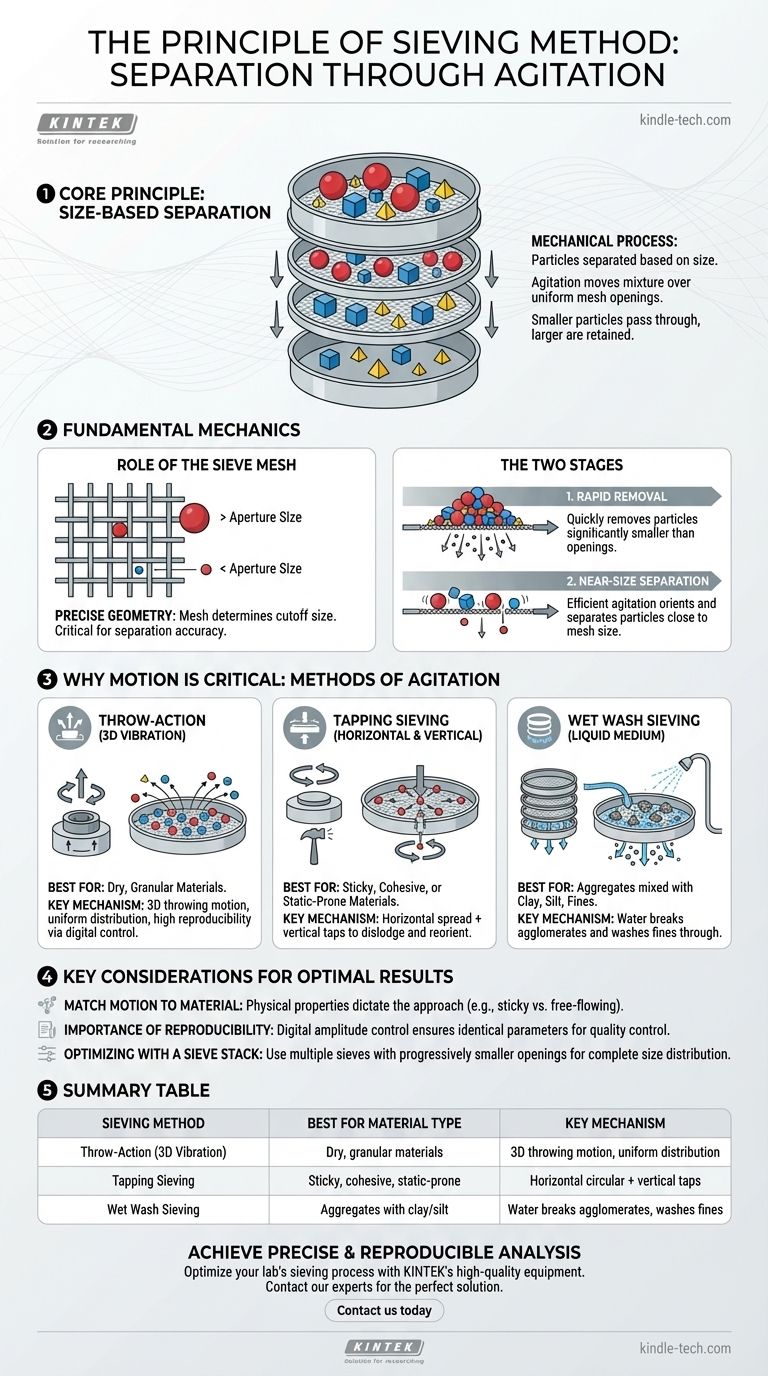
At its core, the principle of sieving is a mechanical process for separating particles based on size. A mixture of particles is placed on a screen, or mesh, with openings of a uniform size. Agitation is applied, causing smaller particles to pass through the mesh openings while larger particles are retained on the surface.
The fundamental concept of sieving is simple size-based separation. However, its practical effectiveness hinges entirely on the method of agitation used to ensure every particle is properly tested against the sieve's openings.

The Fundamental Mechanics of Separation
The sieving method, while straightforward in principle, involves a specific sequence to achieve accurate particle size distribution analysis. It relies on the precise geometry of the sieve itself and a clear, two-stage process.
The Role of the Sieve Mesh
The sieve mesh is the critical component. It is a surface, typically wire-mesh, containing a grid of apertures (holes) of a precise, uniform size. This size determines the cutoff point for the separation.
Any particle with dimensions smaller than the aperture size can pass through, while any particle larger in at least two dimensions will be retained.
The Two Stages of Sieving
Effective sieving happens in two distinct phases.
First, the agitation quickly removes all particles significantly smaller than the mesh openings. This is the easiest part of the separation.
Second, the process focuses on separating the remaining particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings. This requires more time and efficient agitation to orient these "near-size" particles correctly so they can pass through.
Why Particle Motion is Critical
Simply placing a sample on a sieve is not enough. The type of motion applied to the sieve stack is the most important factor in achieving an accurate and repeatable separation. Different methods create different motions tailored to specific material types.
Throw-Action Sieving (3D Vibration)
This common method uses an electromagnetic drive to create a three-dimensional throwing motion. The sample is lifted up and forward before falling back onto the sieve surface.
This 3D movement ensures the sample is distributed uniformly across the entire sieve area, maximizing the chances for each particle to encounter an opening. Modern instruments offer precise digital control of this motion, ensuring the results are highly reproducible.
Tapping Sieving (Horizontal and Vertical Motion)
Tapping sievers combine a horizontal circular motion with a vertical tapping impulse from below.
The circular motion spreads the material, while the sharp, vertical tap helps to dislodge stuck particles and reorient them on the mesh surface. This combination is effective for preventing particles from blinding the mesh apertures.
Wet Wash Sieving (Using a Liquid Medium)
For certain materials, especially those containing fine particles like clay or silt, dry sieving is ineffective.
In wet sieving, water is added to the sample. The liquid helps break down particle agglomerates and washes the fine material through the sieve, ensuring an accurate measurement of the coarser aggregate particles.
Understanding the Key Considerations
Choosing the right sieving method and parameters is not a one-size-fits-all decision. The nature of your material and the goal of your analysis dictate the best approach.
Matching Motion to Material Type
The physical properties of your sample are paramount. A free-flowing granular material works well with a standard throw-action sieve.
However, materials that are sticky, prone to static electricity, or tend to agglomerate may require the more aggressive action of a tapping sieve or the cleaning power of wet wash sieving.
The Importance of Reproducibility
For quality control and scientific analysis, getting the same result every time is crucial.
Throw-action sieves with digital amplitude control provide the highest level of reproducibility. By constantly measuring and adjusting the sieve's oscillation, they ensure that sieving parameters remain identical from one test to the next.
Optimizing with a Sieve Stack
Sieving is rarely done with a single sieve. Analysis is typically performed using a "sieve stack," which is a column of several sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes from top to bottom.
This allows you to separate the sample into multiple size fractions in a single run, providing a complete particle size distribution profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate sieving method, you must first define your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is reproducible analysis of dry, granular materials: A throw-action (vibratory) sieve with digital amplitude control is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is separating materials with high cohesion or static charge: A tapping sieve may provide the necessary force to break up clumps and ensure particle movement.
- If your primary focus is analyzing aggregates mixed with clay, silt, or other fines: Wet wash sieving is the only reliable method to clean the particles for accurate sizing.
Ultimately, understanding that sieving is a dynamic process driven by motion is the key to achieving accurate and meaningful results.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Method | Best For Material Type | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Throw-Action (3D Vibration) | Dry, granular materials | 3D throwing motion for uniform distribution and high reproducibility |
| Tapping Sieving | Sticky, cohesive, or static-prone materials | Horizontal circular motion with vertical taps to dislodge particles |
| Wet Wash Sieving | Aggregates mixed with clay, silt, or fines | Uses water to break agglomerates and wash fine particles through |
Need to achieve precise and reproducible particle size analysis in your lab? The right sieving method is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieving equipment and consumables, designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory particle separation. Whether you require throw-action, tapping, or wet wash sieving, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific material and application. Contact us today to optimize your sieving process and ensure the integrity of your data. Reach out to our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















