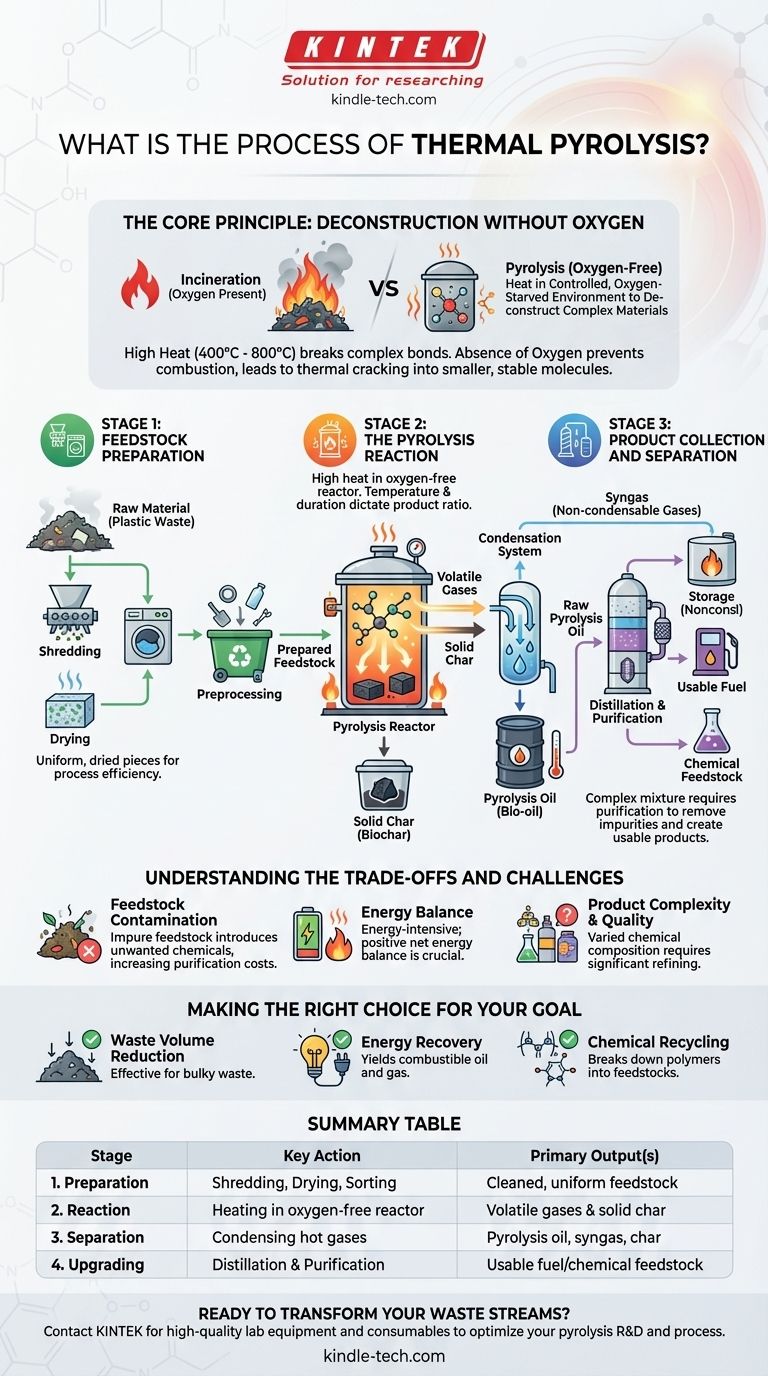
At its core, thermal pyrolysis is a multi-stage process of chemical decomposition. It begins with preparing raw material, such as plastic waste, by shredding and drying it. This prepared feedstock is then heated to high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment, breaking it down into oil, gas, and a solid char, which are then collected and purified for storage or further use.
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from incineration. Instead of burning material with oxygen, it uses heat in a controlled, oxygen-starved environment to deconstruct complex materials into their simpler, often more valuable, chemical components.

The Core Principle: Deconstruction Without Oxygen
The Critical Role of Heat
Pyrolysis relies on applying high heat, typically ranging from 400°C to over 800°C, to a feedstock. This thermal energy breaks the long, complex chemical bonds of materials like plastics or biomass.
The Oxygen-Free Environment
This process occurs in a sealed vessel called a pyrolysis reactor. The absence of oxygen is the most critical factor.
Without oxygen, the material cannot combust or burn. Instead of producing ash and smoke, it thermally "cracks" into smaller, more stable molecules.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Stage 1: Feedstock Preparation
Before entering the reactor, the raw material must be properly prepared. This is a crucial step for process efficiency and final product quality.
First, the material is shredded into smaller, uniform pieces to ensure even heat distribution. It is then dried to remove moisture, which can hinder the process and affect the quality of the pyrolysis oil.
Finally, a preprocessing stage often involves sorting to remove non-target materials, such as metals or glass, which do not break down and can damage equipment.
Stage 2: The Pyrolysis Reaction
The prepared feedstock is fed into the reactor, which is then sealed and purged of oxygen.
High heat is applied, causing the material to rapidly decompose into a mixture of volatile gases and solid char. The precise temperature and duration of this stage dictate the final ratio of oil, gas, and char produced.
Stage 3: Product Collection and Separation
The hot, volatile gases exit the reactor and enter a condensation system.
Here, the gases are cooled, causing the components with higher boiling points to condense into a liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
The remaining non-condensable gases, often called syngas, are collected separately. The solid residue left in the reactor is called char or biochar.
Stage 4: Post-Processing and Upgrading
The raw pyrolysis oil is rarely ready for immediate use. It is a complex mixture that often requires further processing.
Distillation and purification are common next steps to separate the oil into different fractions and remove impurities. This upgrading is necessary to convert it into a usable fuel or a chemical feedstock for creating new products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Feedstock Contamination
The purity of the initial feedstock is paramount. Contaminants within plastic waste streams, for example, can introduce unwanted chemicals into the final products, requiring more intensive and costly purification.
Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. A significant amount of thermal energy is required to operate the reactor. A successful operation depends on a positive net energy balance, where the energy value of the outputs exceeds the energy required to run the process.
Product Complexity and Quality
The outputs of pyrolysis—oil, gas, and char—are not uniform commodities. Their specific chemical composition varies dramatically based on the feedstock and process conditions, and the resulting oil is not a direct substitute for conventional crude oil without significant refining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the complete lifecycle of the pyrolysis process is essential for evaluating its role in any specific application.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is extremely effective at converting bulky waste streams like plastics into denser and more stable forms of oil and char.
- If your primary focus is energy recovery: The process yields combustible oil and gas, but you must carefully assess the energy required for the process and for upgrading the fuel to meet quality standards.
- If your primary focus is chemical recycling: Pyrolysis is a powerful tool for breaking down polymers into basic chemical feedstocks, though extensive purification is often needed before these can be used to manufacture new products.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis as a controlled chemical conversion process, rather than simple disposal, is the key to harnessing its potential.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Output(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Shredding, Drying, Sorting | Cleaned, uniform feedstock |
| 2. Reaction | Heating in oxygen-free reactor | Volatile gases & solid char |
| 3. Separation | Condensing hot gases | Pyrolysis oil, syngas, char |
| 4. Upgrading | Distillation & Purification | Usable fuel/chemical feedstock |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? The precise temperature control and reactor design are critical for a successful pyrolysis operation. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis R&D and process optimization. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve an efficient and profitable pyrolysis process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data



















